Introduction
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIP-R) is a G-protein coupled receptor stimulated by gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP). GIP is released from endocrine cells in the small intestine and binds to GIP-R, commonly expressed in pancreatic ß-cells, adipose tissue, osteoblasts, and the hypothalamus. GIP-R was biochemically discovered in 1969 and its structure was later determined using cryo-electron microscopy.
Function & Mechanism
When the , a GPCR pathway is activated, initiating a cascade of enzymes. After binding to GIP, GIP-R undergoes a conformational change that allows the G-alpha subunit to dissociate from the GPCR and travel down the phospholipid bilayer. A palmitic fatty acid keeps the G-alpha subunit tightly bound to the lipid bilayer as it travels to the target enzyme, adenylyl cyclase. The phosphorylation of adenylyl cyclase produces the second messenger, cyclic adenosine monophosphate, (cAMP). cAMP then activates the second enzyme, Protein Kinase A, (PKA), which inhibits potassium channels and activates calcium channels, causing an influx of Ca2+ ions into the cell. PKA also activates a transcription factor (CREB)[1] that promotes insulin release from the cell. The release of insulin into the bloodstream promotes the uptake of circulatory glucose into target tissues.
GIP-R plays a key role in mitigating Type II diabetes symptoms by promoting both weight loss and insulin secretion. Type II diabetes, or insulin resistance, is caused by two variables: a decrease in insulin-sensitive cell responses and insulin secretion from beta cells. Without adequate insulin secretion, cellular glucose uptake is diminished and blood glucose levels remain unhealthily high. Excess blood glucose is stored in the liver as glycogen, which is converted to fatty acids in adipose tissue. By reducing blood glucose levels, GIP-R acts to reduce excess storage of fat. GIP-R can be activated by either the natural ligand, GIP, or a synthetic agonist, such as Tirzepatide. Tirzepatide binds to both GIP-R and GLP-R (a GPCR with similar functionality). By binding to both receptors, Tirzepatide results in greater signal transduction, thus, a higher yield of insulin secretion.
Ligands
The natural ligand, , and synthetically made medication, , bind to GIP-R similarly to produce similar responses. The N-termini of each ligand, residues 1-15, binds to the transmembrane domain of GIP-R. Residues 15-30 of each ligand near the C-termini interact with the extracellular domain of GIP-R. Several modifications were made to Tirzepatide to improve its delivery and affinity to GIP-R[2]. At position 2, the alanine residue was modified to a 2-aminoisobutyric residue to prevent its inactivation by peptidase DPP-4, which cleaves the ligand between residues 2 and 3 (Fig. 1). This modification prolongs the cellular signaling induced by Tirzepatide bound to GIP-R. Residues 7 and 18 were modified in Tirzepatide to increase the affinity of the peptide for GIP-R (Fig. 1). Lastly, a glutamine residue was modified in Tirzepatide to a lipid-modified lysine at position 20 for transport in the blood serum via an albumin protein (Fig. 1).

Figure 1. Sequence alignment of GIP and Tirzepatide
GIP-R Domains
consists of three unique domains, each of which is sequestered in a different cellular environment. The extracellular domain consists of two helices and two loops that extend into the extracellular fluid and interact with the ligand. The transmembrane domain consists of seven alpha-helices bound in the cell membrane that interact with the N-terminus of the ligand. The cytoplasmic domain extends into the cytoplasm and interacts with the associated G-protein.
Along with a multitude of hydrophobic interactions at the cell membrane interface, two key hydrogen bonds within the sequester the G-protein to the receptor. The carbonyl oxygen of the L393 backbone and the sidechain of E392 of the G-protein form hydrogen bonds with the sidechain of R338 and amide nitrogen of N396 of GIP-R, respectively. The conformational change in the receptor induced by ligand-binding breaks these hydrogen bonds, allowing the G-protein to dissociate from GIP-R and continue its signaling pathway.
Transmembrane Domain
Y1 on the N-terminal end of the GIP ligand is crucial for ligand binding. Analogs[2] of GIP containing a mutation at residue 1 resulted in no ligand binding. forms a hydrogen bond to Q224 on GIP-R, pulling the GIP ligand deep into the transmembrane domain. In addition, Y1 parallel pi-stacks with W296 on GIP-R, further increasing the affinity of the ligand for the receptor. For these reasons, Y1 is conserved in Tirzepatide.
A key mutation in Tirzepatide is I7T. The mutated can form a hydrogen bond with R190 of GIP-R, an interaction that was not possible with the natural I7 residue. Due to this hydrogen bonding interaction, the alcohol group on Y1 of the ligand is tilted towards R190 and Q220, mediated by polar water molecules[2]. The additional interactions increase the affinity of Tirzepatide for GIP-R, which induces a greater cellular response than the natural ligand GIP.
Extracellular Domain
In the extracellular domain, extensive pi-stacking occurs between and . Aromatic residues F22 and W25 are conserved on Tirzepatide to maintain strong hydrophobic interactions with Y36 and W39 on GIP-R. However, Tirzepatide contains a key H18A mutation[2] that increases the affinity of the ligand compared to GIP. Although this mutation inactivates a hydrogen bond previously formed by H18, it increases Tirzepatide’s affinity for the GLP-R by reducing steric clashing and allowing the ligand to bind deeper into the receptor.
GIP-R Bound to GIP vs. Tirzepatide
The natural GIP ligand and the synthetic Tirzepatide ligand do not bind to the receptor analogously. The modifications applied to Tirzepatide caused a shift in the orientation of ligand binding (Fig. 2). Specifically, the H18A and I7T mutations shaped the synthetic ligand to bind differently than the natural ligand, in which the extracellular domain of GIP-R had to adjust to fit the new binding angle. Ultimately, the binding configuration induced by Tirzepatide tethers the ligand deeper into the receptor transmembrane domain, increasing its affinity for the receptor (Fig. 2).
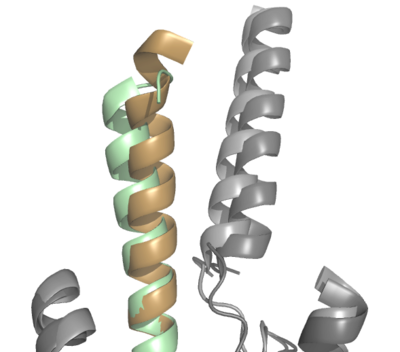
Figure 2. Overlay of GIP (tan with dark gray GIP-R) and Tirzepatide (green with light gray GIP-R) bound to GIP-R
Future Implications
Peptide 20
Peptide 20 is a tri-acting agonist of GIP, GLP (glucagon-like peptide), and GCG (glucagon). This tri-agonist drug maximizes the metabolic benefits of the GIP and GLP ligands while simultaneously increasing energy expenditure by binding to the GCG-receptor. In experimental studies[3], administration of peptide 20 to rats caused a reduction in body weight and blood glucose levels in addition to improving glucose tolerance. Administration of peptide 20 did not disrupt the architecture of pancreatic islets.
Peptide 20 adopts a helical structure with the first 15 residues buried in the transmembrane region and residues 16-30 recognized by the extracellular domain of each of the three receptors. The N-terminus was fairly conserved compared to each natural ligand, however, the I7T mutation found in Tirzepatide was utilized in peptide 20 to increase the affinity of the ligand to each receptor (Fig. 3). Peptide 20 also utilized the H18A substitution found in Tirzepatide, which reduced steric clashing in the extracellular domain (Fig. 3). These mutations found in peptide 20 increase affinity for the substrate, increasing cellular signaling pathways. The most impressive structural feature of peptide 20 binding is the lipidation at K10. After the substitution of a lysine residue at position 10, a 16-C palmitic chain was added and linked by a γ-carboxylate spacer. The hydrophobic chain inserts itself between TM1 and TM2, stabilizing peptide binding. The increased cAMP accumulation by almost 1300-fold[3].
K10 lipidation provides a fresh clue for peptide ligand design for G-protein coupled receptors. Multi-targeting agonists, such as peptide 20, improve energy metabolism without causing hypoglycemia, as proved with trials on mice. Profiling the receptors on the cell membrane of a given individual at any stage of their disease, when paired with multi-targeting drugs, allows for personalized therapeutic advantages. Further research into multi-targeting drugs opens the doors to manipulating metabolic pathways and provides solutions to diseases, such as type II diabetes.


