User:Camille Gaudet/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
=== Biological Role === | === Biological Role === | ||
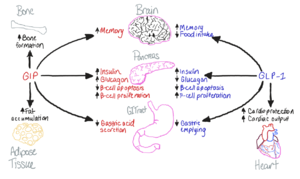
| - | [[Image:GIP-GLP1-Purpose.png|300 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. The biological roles of GIP and and GLP-1, incretin hormones.]] The GIP receptor (GIPR) helps facilitate the transport of glucose into/out of the cell through the stimulation of insulin secretion. <ref name='Sun'>PMID:35333651</ref>. GIPR is a type of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein-coupled_receptor G-Protein Coupled Receptor] (GPCR), and its natural ligand, GIP, serves as an initiator of a cellular signaling cascade, thereby activating adenylyl cyclase and increasing cAMP levels. Subsequently, insulin secretion is stimulated. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin Insulin], a peptide hormone, is secreted by the pancreas in response to glucose ingestion, allowing intake of glucose into the cell via the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GLUT2 Glut2] transporter. | + | [[Image:GIP-GLP1-Purpose.png|300 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. The biological roles of GIP and and GLP-1, incretin hormones.]] The GIP receptor (GIPR) helps facilitate the transport of glucose into/out of the cell through the stimulation of insulin secretion. <ref name='Sun'>PMID:35333651</ref>. GIPR is a type of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein-coupled_receptor G-Protein Coupled Receptor] (GPCR), and its natural ligand, GIP, serves as an initiator of a cellular signaling cascade, thereby activating adenylyl cyclase and increasing cAMP levels. Subsequently, insulin secretion is stimulated. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin Insulin], a peptide hormone, is secreted by the pancreas in response to glucose ingestion, allowing intake of glucose into the cell via the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GLUT2 Glut2] transporter. Notably, GIP, as well as GLP-1, serve a multitude of biological roles (Figure 1.) other than insulin signaling. |
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
== Medical Relevance == | == Medical Relevance == | ||
=== Tirzepatide === | === Tirzepatide === | ||
| - | Many anti-diabetes drugs exist for patients with both Type I and Type II diabetes, including a new dual GIP and GLP-1 agonist known as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tirzepatide Tirzepatide] (Brand Name: Mounjaro, Manufacturer: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eli_Lilly_and_Company Lilly]). Tirzepatide is capable of inducing the effects of GIP and GLP-1 cellular signalling by mimicking | + | Many anti-diabetes drugs exist for patients with both Type I and Type II diabetes, including a new dual GIP and GLP-1 agonist known as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tirzepatide Tirzepatide] (Brand Name: Mounjaro, Manufacturer: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eli_Lilly_and_Company Lilly]). Tirzepatide is capable of inducing the effects of both GIP and GLP-1 cellular signalling by mimicking each ligand and binding to their respective receptor. Increased presence of GIP and GLP-1 leads to enhanced stimulation of insulin secretion, thereby reducing blood glucose levels. |
| + | |||
| + | === Tirzepatide === | ||
| + | Structurally, as a dual agonist, <scene name='10/1037488/Tirz-bound/3'>Tirzepatide</scene> closely resembles GIP and GLP-1. The sequence alignment of all three polypeptides showcases the highly integrated nature of both GIP and GLP-1 into the amino acid sequence of Tirzepatide, with very few alterations (Figure 1). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:GIPGLPTirz.png|700 px|right|thumb|Figure 2. Sequence alignment of GLP-1, GIP, and Tirzepatide. Residues shown in black are found in all three amino acid sequences. Pink or red coloration denotes residues that are unique to GIP or GLP-1, respectively. The sequence of tirzepatide is colored accordingly, and residues differing from both GIP and GLP-1 are highlighted in blue. Residues that differ across all three structures are boxed.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<scene name='10/1037492/Gip_tirz/7'>sara tirz 1</scene> | <scene name='10/1037492/Gip_tirz/7'>sara tirz 1</scene> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 49: | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:GIPGLPTirz.png|700 px|right|thumb|Figure 2. Sequence alignment of GLP-1, GIP, and Tirzepatide. Residues shown in black are found in all three amino acid sequences. Pink or red coloration denotes residues that are unique to GIP or GLP-1, respectively. The sequence of tirzepatide is colored accordingly, and residues differing from both GIP and GLP-1 are highlighted in blue. Residues that differ across all three structures are boxed.]] | ||
Revision as of 21:23, 28 April 2024
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptor
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sun B, Willard FS, Feng D, Alsina-Fernandez J, Chen Q, Vieth M, Ho JD, Showalter AD, Stutsman C, Ding L, Suter TM, Dunbar JD, Carpenter JW, Mohammed FA, Aihara E, Brown RA, Bueno AB, Emmerson PJ, Moyers JS, Kobilka TS, Coghlan MP, Kobilka BK, Sloop KW. Structural determinants of dual incretin receptor agonism by tirzepatide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Mar 29;119(13):e2116506119. PMID:35333651 doi:10.1073/pnas.2116506119
Student Contributors
- Camille Gaudet
- Sara Kalkhoff