Introduction
When consuming food, the human body is tasked with secreting hormones and chemical messengers that will help regulate homeostasis. After a meal, the body has to maintain homeostasis by reducing blood glucose and signaling that enough nutrients have been consumed. During feeding, cells in the body will secrete the ligand, amylin. Amylin is a 37 amino acid glucoregulatory hormone that is produced within beta cells of the pancreas. When there is an influx of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract, the ligand will bind to the heterodimeric receptor, activating the receptor and triggering the corresponding signaling cascade. The overall effect of this cascade is increased satiety, delayed gastric emptying, and inhibition of glucagon secretion [1]. The amylin receptors are widely distributed throughout the central nervous system [2].
The amylin g-protein coupled receptor is a heterodimeric protein containing a calcitonin receptor domain, as well as one of three receptor activity modifying proteins (RAMP 1,2, or 3)[3].
RAMPs are accessory proteins required for the appropriate localization and function of GPCRs [4]. As of now, there are three notable roles of RAMPs. RAMPs can allow for the signaling and trafficking of GPCRs from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell membrane. Additionally, RAMPs are known to alter the interactions between the receptor and ligands, potentially inhibiting or activating the receptor. Lastly, RAMPs are also thought to play a role in the internalization and subsequent inactivation of GPCRs, by signaling receptor fate and recycling from the cell membrane [2]. In the case of the AMYR, the RAMP acts as a scaffold to hold the transmembrane domain in place. More importantly, the RAMP restricts the dynamic movement of the extracellular domain of the calcitonin receptor, anchoring the CTR into the membrane.
Structure
G-alpha Interactions with CTR TMD
To transduce the signal across the cell membrane, the binding of amylin will induce a conformational change that allows for the CTR to make favorable interactions with the G alpha subunit. Two interactions shown activate the G-protein and propel downstream signaling. As with a typical glucagon GPCR pathway, the G-alpha subunit becomes activated upon guanine exchange factor (GEF) echanging GDP for GTP. This G-alpha subunit transverses laterally in the membrane towards adenylyl cyclase, activating it and causing an increase in the second messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). This cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA), which can phosphorylate other proteins facilitating cellular response.
N-Terminus Disulfide
The amylin peptide contains a between residues C2 and C7. This disulfide provides stability and rigidity to the helical structure of the peptide, allowing for favorable binding to the extracellular domain (ECD). Notable interactions formed by this disulfide include hydrogen bonds between E294 of the transmembrane domain with K1 of amylin, and both R362 and W361 of the transmembrane domain forming a hydrogen bond with N3 of amylin.
Amidated C-Terminus
The of amylin contains an amide group, rather than a carboxylic acid group. This chemical modification allows for more extensive hydrogen bonding to nearby residues, due to the added hydrogen bond donor on the NH2 group. In turn, this allows for favorable hydrogen bonds between S129 of the transmembrane domain and the main chain of Y37 on amylin. This interaction causes a "kink" in the random coil of amylin, displacing Y37 into a hydrophobic pocket, allowing for favorable hydrophobic interactions with W79 of the transmembrane domain. This amidation is thought to be a post-translational modification. [5]
Transmembrane Domain
Within the transmembrane domain (TMD) of the CTR, hydrophobic R groups span the phospholipid bilayer, anchoring the protein into the cell membrane upon amylin binding to the receptor. The interior of the transmembrane domain contains the hydrophilic residues necessary for ligand binding and transduction of the signal across the cell membrane.
Bypass Motif
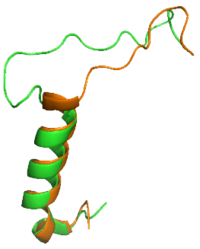
Figure 1: Overlay of sCT (orange) without the bypass motif and rAmy containing the bypass motif (green).
The is a series of residues in the midsection of the amylin peptide that are crucial for providing structural specificity for the AMYR. Without RAMP association, the CTR is in a relaxed, fluid state, allowing the binding of . When RAMP binds the receptor, it is forced into a new, rigid conformation, which interferes with calcitonin binding (Figure 1). Amylin's bypass motif contains a backbone configuration that does not interfere with AMYR, allowing the C-terminus of the peptide to interact with the extracellular domain. The Bypass Motif also binds and makes with the transmembrane region of AMYR, anchoring the peptide in place for the signaling process to occur. [3]
Amylin Receptor Binding
Two-Domain Model of Amylin Binding
It is hypothesized that amylin binds to the receptor via a two-domain model (Figure 2). The model suggests a series of steps for how amylin binds. First, the c-terminus of amylin binds to the n terminus of the extracellular domain of the receptor. This binding factors the alignment of amylin's n-terminus to the primary GPCR binding site. Once both the c-terminus and n-terminus of amylin are bound, the receptor becomes activated.
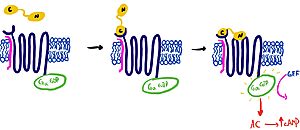
Figure 2: The Two Domain Model
RAMP-CTR Interface
The is a key interaction that stabilizes the protein complex and positions the receptor to favorably bind to amylin. The RAMP-CTR interface extends into the plasma membrane, providing additional non-covalent bonding between the protein complex and the cell membrane.
Extracellular Domain - RAMP interactions
The extracellular domain of the CTR primarily contains polar residues in the extracellular space. In order to orient these residues to facilitate amylin binding, to increase the rigidity of the receptor binding site.
Clinical Significance
Drug Development
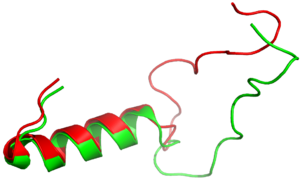
Figure 3:Amylin (green) aligned with Pramlintide (red)
is a synthetic analog of amylin (Figure 3) that is commonly used in accordance with mealtime
insulin to help treat type 1 and 2 diabetic patients
[2]. This drug binds to AMYR competitively, increasing the AMYR GPCR signaling. Increased action of the AMYR receptor has been shown to modestly lower HbA1c levels, which is often accompanied by weight loss
[6]. Pramlintide binds with more affinity than human amylin (hAmy) due to mutations from hydrophobic residues A29, S28 and S29 to proline (Figure 4). The proline residues increase the rigidity of the ligand by creating unfavorable phi and psi angles, which improves the ability of the ligand to bind AMYR. Pramlintide treatment has also been shown to consistently reduce
Amyloid β plaque aggregation in rodent models with
Alzheimer’s disease [7].
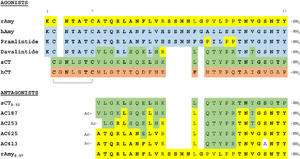
Figure 4:Pramlintide Sequence alignment with varying forms of amylin. Atoms C2—C7 and K1 of the N-terminal region are conserved. Y37 and T36 of the C-terminal region are also conserved.
It has been thought that missense mutations in residues C2 and C7 of the amylin peptide could lead to an increased risk of Alzheimer's Disease [8]. Because of the rigidity these cysteine resides provide, reductions of their disulfide interaction leads to an increased risk of amyloid plaques due to amylin misfolding and forming aggregates. During drug design, pharmaceutical companies have focused on maintaining amylin residues C2 and C7, as well as K1, which forms a hydrogen bond donor for the and main chain carbonyl. Additionally, pharmaceuticals companies have also opted to maintain residues , which are critical residues in stabilizing the C terminus of amylin to the receptor binding site. While there are hardly any differences in the helical portion of amylin and the synthetic analogue pramlintide, there is a difference in the extended random coil at the C terminus.
In order to restore basal amylin levels in mice, researchers have performed PEGylation, the addition of poly ethylene glycol, to amylin within residues 1-11 of the peptide, most likely at the two amine groups of K1[9]. Administration of the modified amylin in mice showed evidence of reduced glycemia and prolonged action compared to endogenous amylin [9].
References
- ↑ Bower RL, Hay DL. Amylin structure-function relationships and receptor pharmacology: implications for amylin mimetic drug development. Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;173(12):1883-98. PMID:27061187 doi:10.1111/bph.13496
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):564-600. PMID:26071095 doi:10.1124/pr.115.010629
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ Parameswaran N, Spielman WS. RAMPs: The past, present and future. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Nov;31(11):631-8. PMID:17010614 doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2006.09.006
- ↑ Vekic J, Silva-Nunes J, Rizzo M. Glucose Metabolism Disorders: Challenges and Opportunities for Diagnosis and Treatment. Metabolites. 2022 Jul 29;12(8):712. PMID:36005584 doi:10.3390/metabo12080712
- ↑ Hoogwerf BJ, Doshi KB, Diab D. Pramlintide, the synthetic analogue of amylin: physiology, pathophysiology, and effects on glycemic control, body weight, and selected biomarkers of vascular risk. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008;4(2):355-62. PMID:18561511 doi:10.2147/vhrm.s1978
- ↑ Gingell JJ, Burns ER, Hay DL. Activity of pramlintide, rat and human amylin but not Aβ1-42 at human amylin receptors. Endocrinology. 2014 Jan;155(1):21-6. PMID:24169554 doi:10.1210/en.2013-1658
- ↑ Grizzanti J, Corrigan R, Casadesus G. Neuroprotective Effects of Amylin Analogues on Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Cognition. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(1):11-23. PMID:30282360 doi:10.3233/JAD-180433
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Guerreiro LH, Guterres MF, Melo-Ferreira B, Erthal LC, Rosa Mda S, Lourenço D, Tinoco P, Lima LM. Preparation and characterization of PEGylated amylin. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2013 Sep;14(3):1083-97. PMID:23818080 doi:10.1208/s12249-013-9987-4




