We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox324
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
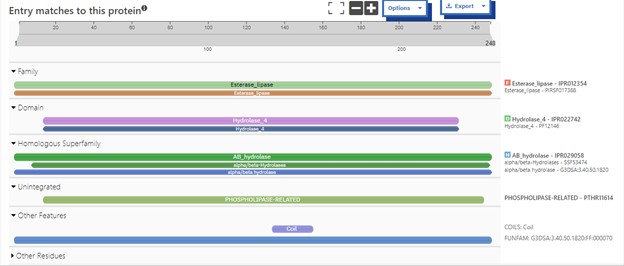
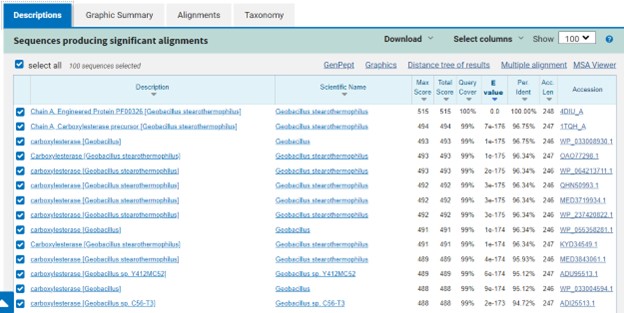
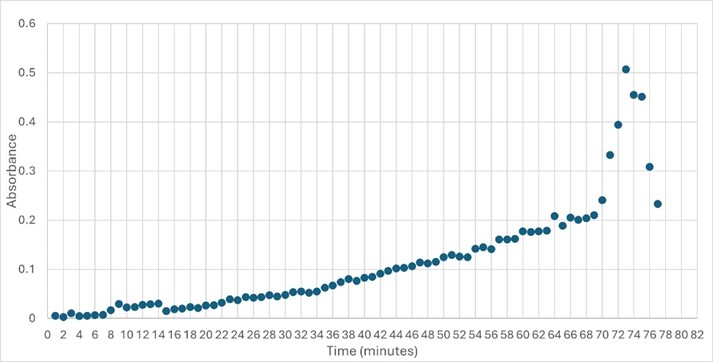
| - | SwissDock and Chimera allowed for protein-ligand docking studies. Many of the highlighted interactions were ester-containing ligands and others were susceptible to hydrolysis. The hydrolase activity of the protein needed to be tested with a substrate known to work with hydrolases. This substrate is p-nitrophenyl acetate | + | SwissDock and Chimera allowed for protein-ligand docking studies. Many of the highlighted interactions were ester-containing ligands and others were susceptible to hydrolysis. The hydrolase activity of the protein needed to be tested with a substrate known to work with hydrolases. This substrate is p-nitrophenyl acetate PNPA when hydrolyzed produces p-nitrophenol (PNP), a yellow colored product. The yellow product will lead to the solution absorbing more at 405nm. <ref>Zhang, S.; Sun, W.; Xu, L.; Zheng, X.; Chu, X.; Tian, J.; Wu, N.; Fan, Y. Identification of the Para-Nitrophenol Catabolic Pathway, and Characterization of Three Enzymes Involved in the Hydroquinone Pathway, in Pseudomonas Sp. 1-7. BMC Microbiology 2012, 12 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-27. |
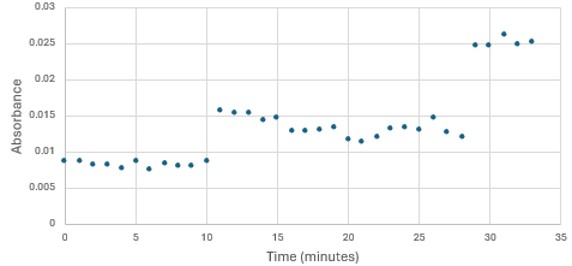
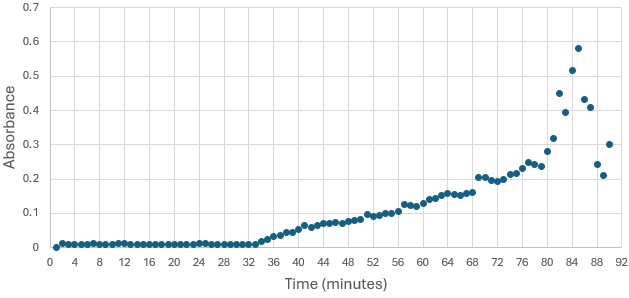
</ref>. This allows for the activity of the enzyme to be tracked by measuring the increase in absorbance over time. The isolated protein was introduced to p-nitrophenyl acetate in a buffer with a determined optimal pH of 6. Multiple trials can be seen in the figures below displaying the affect of pH on the enzyme activity. Enzyme activity was measured via a change in absorbance at 405nm over 30-80 minutes. The data collected was consistent with that of hydrolases in other studies.<ref>Vázquez-Mayorga, E.; Díaz-Sánchez, Á.; Dagda, R.; Domínguez-Solís, C.; Dagda, R.; Coronado-Ramírez, C.; Martínez-Martínez, A. Novel Redox-Dependent Esterase Activity (EC 3.1.1.2) for DJ-1: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2016, 17 (8), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081346. | </ref>. This allows for the activity of the enzyme to be tracked by measuring the increase in absorbance over time. The isolated protein was introduced to p-nitrophenyl acetate in a buffer with a determined optimal pH of 6. Multiple trials can be seen in the figures below displaying the affect of pH on the enzyme activity. Enzyme activity was measured via a change in absorbance at 405nm over 30-80 minutes. The data collected was consistent with that of hydrolases in other studies.<ref>Vázquez-Mayorga, E.; Díaz-Sánchez, Á.; Dagda, R.; Domínguez-Solís, C.; Dagda, R.; Coronado-Ramírez, C.; Martínez-Martínez, A. Novel Redox-Dependent Esterase Activity (EC 3.1.1.2) for DJ-1: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2016, 17 (8), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081346. | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
Revision as of 04:02, 29 April 2024
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Zhang, S.; Sun, W.; Xu, L.; Zheng, X.; Chu, X.; Tian, J.; Wu, N.; Fan, Y. Identification of the Para-Nitrophenol Catabolic Pathway, and Characterization of Three Enzymes Involved in the Hydroquinone Pathway, in Pseudomonas Sp. 1-7. BMC Microbiology 2012, 12 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-27.
- ↑ Vázquez-Mayorga, E.; Díaz-Sánchez, Á.; Dagda, R.; Domínguez-Solís, C.; Dagda, R.; Coronado-Ramírez, C.; Martínez-Martínez, A. Novel Redox-Dependent Esterase Activity (EC 3.1.1.2) for DJ-1: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2016, 17 (8), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081346.
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644