Protein 4DIU: Structure, Function, and Significance in Biological Systems
This study was designed to determine the function of unknown protein 4DIU and its optimal conditions. The protein 4DIU has been identified and characterized as a potential esterase enzyme based on in-depth analyses including bioinformatics, molecular docking studies, and laboratory experiments. Online tools such as BLAST, Dali, SPRITE, and InterPro often matched 4DIU with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. This data suggests that its function involves hydrolysis of esters. Results from Swiss Dock and Chimera predict protein 4DIU to have binding sites with an affinity to substrates such as acetate, butyrate, phosphate, proline, decanoate, and dodecanoate. The protein 4DIU was grown, harvested, and isolated in a laboratory. A Bradford assay was completed to determine the concentration of protein in each elution from a column. SDS-PAGE analysis was used to confirm the presence and identity of the protein via molecular weight. Once identified the enzyme's activity on the substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate was measured. This substrate was chosen because many hydrolases have an affinity for it and can hydrolyze the substrate. It was determined that the 4DIU protein functions best at a pH of 6. Using the change in absorbance and Beer's Law the amount of units of protein was calculated.
Materials
- Buffers: Sodium Phosphate buffer, Cell Lysis Buffer Tris-HCl, 10X SDS-PAGE Buffer, Re-Suspension Buffer, 1X Wash Buffer, 1X Elution Buffer
- Solutions for SDS-Page: Coomassie Blue Stain, and Destain
- Pre-cast SDS-Page Gel
- E. Coli
Overview of Esterase
This protein belongs to the esterase family and expresses alpha/beta-hydrolase activity. Esterases are broadly defined as hydrolases that split ester, amide, and/or thioester bonds in certain compounds that cause prodrug activation and/or detoxification. The ability of esterases to hydrolyze various drugs make them an important component in drug metabolism[1]. This protein's close association with carboxylesterases also indicates that this protein is potentially involved in the hydrolysis of carboxylic ester bonds. Esterases are most commonly located in the skin and liver of mammals, with carboxylesterases being frequently found in the cytosol and endoplasmic reticulum of the skin[2]. Drug metabolism (drug hydrolysis, drug absorption[3], etc.) would be inhibited if the function of an esterase is disrupted.
Proposed Function
This protein has alpha/beta-hydrolase activity and is of the esterase family. The SPRITE, BLAST, InterPro, and Dali Search along with other bioinformatics analyses consistently matched with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. SPRITE provided proteins that had similar residues in the active site of the enzyme. Multiple of the matching proteins were esterases and had an RMSD value of <0.5. The RMSD value gives insight into how similar the overlapping sections for the unknown and known proteins are. A value of less than 2 is desired when choosing proteins for reference as a value closer to zero means less deviation between sites.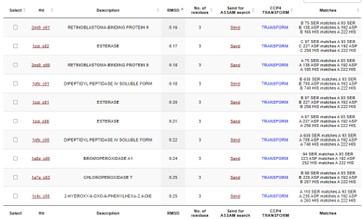
Figure 1: Results from SPRITE of top 10 matching proteins With 4DIU based on amino acid matches, RMSD, and ASSAM.
Additional evidence is provided by InteroPro which provided more information about the classification of the protein. As well, the BLAST search gave results of matching proteins and the specific functions of the proteins. All results again matched what was suggested by Sprite and Blast, further solidifying that 4DIU is an esterase with alpha/beta-hydrolase activity.
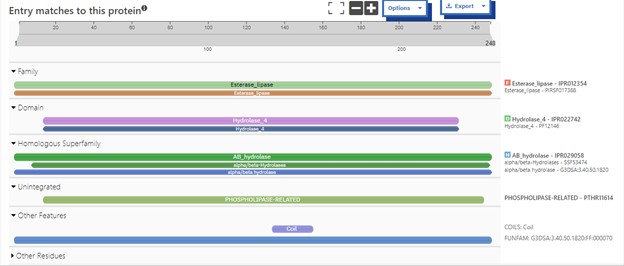
Figure 2: Interpro Scan results for 4DIU displaying proposed characterization
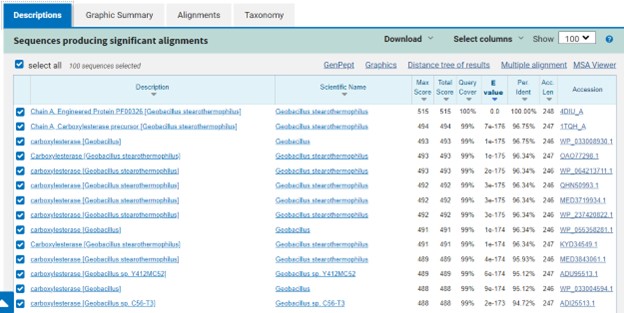
Figure 3: Blast search for protein sequences matching 4DIU
SwissDock and Chimera allowed for protein-ligand docking studies. Many of the highlighted interactions were ester-containing ligands and others were susceptible to hydrolysis. The hydrolase activity of the protein needed to be tested with a substrate known to work with hydrolases. This substrate is p-nitrophenyl acetate PNPA when hydrolyzed produces p-nitrophenol (PNP), a yellow colored product. The yellow product will lead to the solution absorbing more at 405nm. [4]. This allows for the activity of the enzyme to be tracked by measuring the increase in absorbance over time. The isolated protein was introduced to p-nitrophenyl acetate in a buffer with a determined optimal pH of 6. Multiple trials can be seen in the figures below displaying the affect of pH on the enzyme activity. Enzyme activity was measured via a change in absorbance at 405nm over 30-80 minutes. The data collected was consistent with that of hydrolases in other studies.[5]
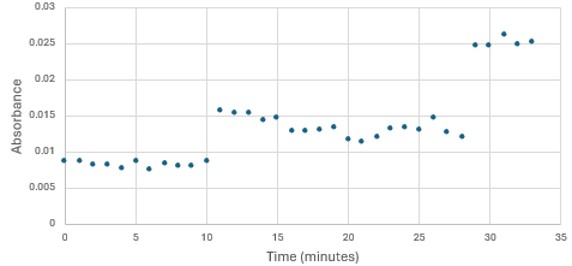
Figure 3: Trial 1 of 4DIU enzymatic activity measured over time via change in absorbance at 405nm in pH 8 buffer
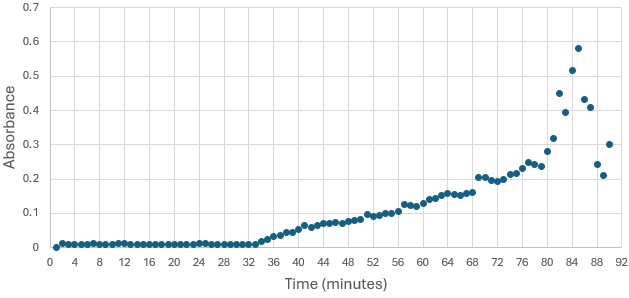
Figure 4: Trial 1 of 4DIU enzymatic activity measured over time via change in absorbance at 405nm in pH 6 buffer
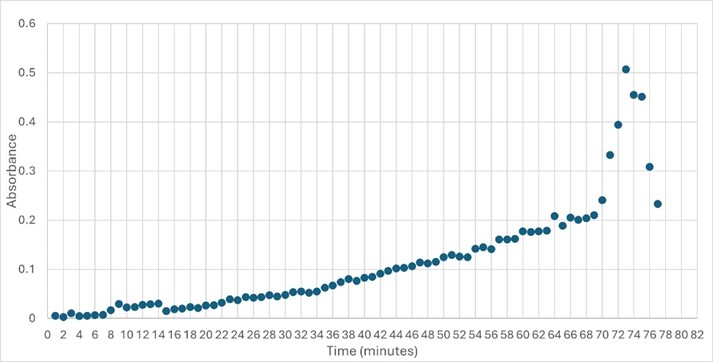
Figure 5: Trial 2 of 4DIU enzymatic activity measured over time via change in absorbance at 405nm in pH 6 buffer
Structural highlights of 4DIU
[6]
Highlight the data that helped you come to your conclusion here including any relevant figures. Make sure to include potential substrates and binding sites.
One of the distinctive structural characteristics of this protein is the alpha/beta-hydrolase (ABH) fold. Evidence for this fold consists of its structure (an open β-sheet surrounded by α-helices) and the presence of what is known as the "catalytic triad" (consisting of a nucleophile, an acid, and histidine)[7]. The presence of the active site residues His A 222, Asp A 192, and Ser A 93, as determined by SPRITE, Chimera, etc., confirms the presence of this catalytic triad.
[Write about potential substrates]
Conclusions
Overall, the research question was answered and the hypothesis was correct. Protein 4DIU has been identified as belonging to the esterase family and has hydrolytic activity. It appears that the optimal pH for this enzyme is 6 and it is active with p-nitrophenyl acetate. These results are fairly accurate and precise as two trials were run at a pH of 6 and the same trend was seen. Again, from this data, it is believed that protein 4DIU would be active in these parts of the body. In future experiments, it would be beneficial to test the activity at lower pHs such as 3, 4, and 5. Additionally, testing some of the substrates that were modeled to work to see if the bioinformatic data is trustworthy.





