This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
2pfu
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
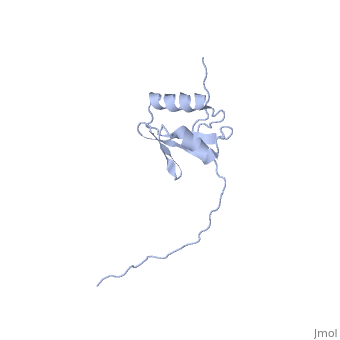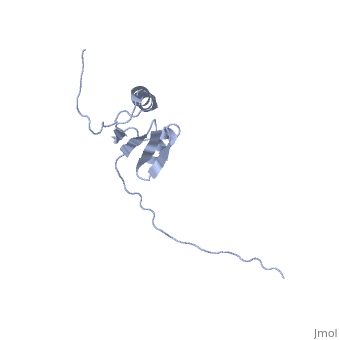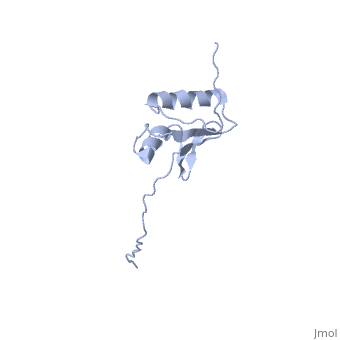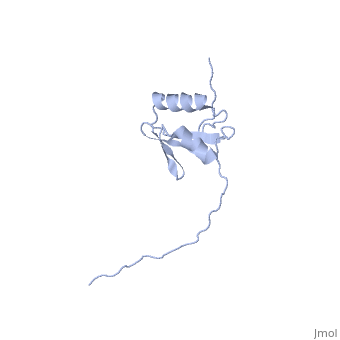
==NMR structure determination of the periplasmic domain of ExbD from E.coli== | ==NMR structure determination of the periplasmic domain of ExbD from E.coli== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='2pfu' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2pfu | + | <StructureSection load='2pfu' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2pfu]]' scene=''> |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2pfu]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2pfu]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli_K-12 Escherichia coli K-12]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2PFU OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2PFU FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">Solution NMR</td></tr> |
| + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2pfu FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2pfu OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2pfu PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2pfu RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2pfu PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2pfu ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | [ | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/EXBD_ECOLI EXBD_ECOLI] Involved in the TonB-dependent energy-dependent transport of various receptor-bound substrates. |
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=2pfu ConSurf]. | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=2pfu ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
| - | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| - | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| - | The transport of iron complexes through outer membrane transporters from Gram-negative bacteria is highly dependent on the TonB system. Together, the three components of the system, TonB, ExbB and ExbD, energize the transport of iron complexes through the outer membrane by utilizing the proton motive force across the cytoplasmic membrane. The three-dimensional (3D) structure of the periplasmic domain of TonB has previously been determined. However, no detailed structural information for the other two components of the TonB system is currently available and their role in the iron-uptake process is not yet clearly understood. ExbD from Escherichia coli contains 141 residues distributed in three domains: a small N-terminal cytoplasmic region, a single transmembrane helix and a C-terminal periplasmic domain. Here we describe the first well-defined solution structure of the periplasmic domain of ExbD (residues 44-141) solved by multidimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The monomeric structure presents three clearly distinct regions: an N-terminal flexible tail (residues 44-63), a well-defined folded region (residues 64-133) followed by a small C-terminal flexible region (residues 134-141). The folded region is formed by two alpha-helices that are located on one side of a single beta-sheet. The central beta-sheet is composed of five beta-strands, with a mixed parallel and antiparallel arrangement. Unexpectedly, this fold closely resembles that found in the C-terminal lobe of the siderophore-binding proteins FhuD and CeuE. The ExbD periplasmic domain has a strong tendency to aggregate in vitro and 3D-TROSY (transverse relaxation optimized spectroscopy) NMR experiments of the deuterated protein indicate that the multimeric protein has nearly identical secondary structure to that of the monomeric form. Chemical shift perturbation studies suggest that the Glu-Pro region (residues 70-83) of TonB can bind weakly to the surface and the flexible C-terminal region of ExbD. At the same time the Lys-Pro region (residues 84-102) and the folded C-terminal domain (residues 150-239) of TonB do not show significant binding to ExbD, suggesting that the main interactions forming the TonB complex occur in the cytoplasmic membrane. | ||
| - | |||
| - | The solution structure of the periplasmic domain of the TonB system ExbD protein reveals an unexpected structural homology with siderophore-binding proteins.,Garcia-Herrero A, Peacock RS, Howard SP, Vogel HJ Mol Microbiol. 2007 Nov;66(4):872-89. Epub 2007 Oct 10. PMID:17927700<ref>PMID:17927700</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
| - | </div> | ||
| - | <div class="pdbe-citations 2pfu" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[ExbD|ExbD]] | *[[ExbD|ExbD]] | ||
| - | == References == | ||
| - | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | [[Category: Escherichia coli]] | + | [[Category: Escherichia coli K-12]] |
[[Category: Large Structures]] | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Garcia-Herrero | + | [[Category: Garcia-Herrero A]] |
| - | [[Category: Howard | + | [[Category: Howard PS]] |
| - | [[Category: Peacock | + | [[Category: Peacock SR]] |
| - | [[Category: Vogel | + | [[Category: Vogel HJ]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
NMR structure determination of the periplasmic domain of ExbD from E.coli
| |||||||||||