This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
1rgw
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
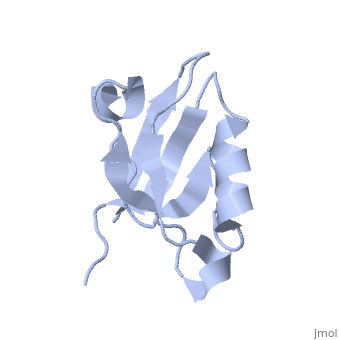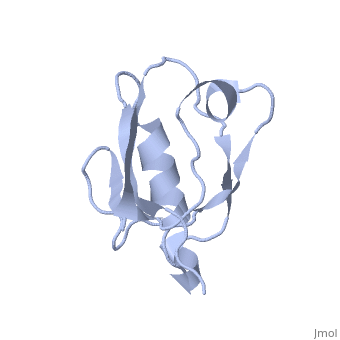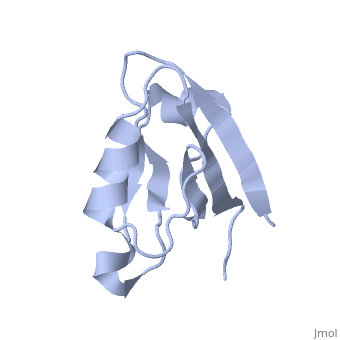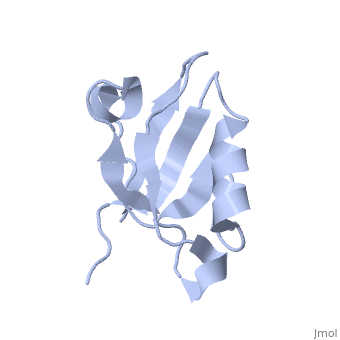
==Solution Structure of ZASP's PDZ domain== | ==Solution Structure of ZASP's PDZ domain== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1rgw' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1rgw | + | <StructureSection load='1rgw' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1rgw]]' scene=''> |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1rgw]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1rgw]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1RGW OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1RGW FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id=' | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">Solution NMR</td></tr> |
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1rgw FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1rgw OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1rgw PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1rgw RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1rgw PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1rgw ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1rgw FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1rgw OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1rgw PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1rgw RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1rgw PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1rgw ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/LDB3_HUMAN LDB3_HUMAN] Defects in LDB3 are the cause of cardiomyopathy dilated type 1C (CMD1C) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/601493 601493]. Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disorder characterized by ventricular dilation and impaired systolic function, resulting in congestive heart failure and arrhythmia. Patients are at risk of premature death.<ref>PMID:14662268</ref> <ref>PMID:14660611</ref> Defects in LDB3 are the cause of left ventricular non-compaction type 3 (LVNC3) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/601493 601493]. Left ventricular non-compaction is characterized by numerous prominent trabeculations and deep intertrabecular recesses in hypertrophied and hypokinetic segments of the left ventricle. Defects in LDB3 are the cause of myopathy myofibrillar type 4 (MFM4) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/609452 609452]. A neuromuscular disorder characterized by distal and proximal muscle weakness with signs of cardiomyopathy and neuropathy. | |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/LDB3_HUMAN LDB3_HUMAN] May function as an adapter in striated muscle to couple protein kinase C-mediated signaling via its LIM domains to the cytoskeleton.[:] | |
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1rgw ConSurf]. | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1rgw ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
| - | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| - | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| - | Z band alternately spliced PDZ-containing protein (ZASP) is a sarcomere Z disk protein expressed in human cardiac and skeletal muscle that is thought to be involved in a dominant familial dilated cardiomyopathy. The N-terminal PDZ domain of ZASP interacts with the C terminus of alpha-actinin-2, the major component of the Z disk, probably by forming a ternary complex with titin Z repeats. We have determined the structure of ZASP PDZ by NMR and showed that it is a classical class 1 PDZ domain that recognizes the carboxy-terminal sequence of an alpha-actinin-2 calmodulin-like domain with micromolar affinity. We also characterized the role of each component in the ternary complex ZASP/alpha-actinin-2/titin, showing that the alpha-actinin-2/ZASP PDZ interaction involves a binding surface distinct from that recognized by the titin Z repeats. ZASP PDZ structure was used to model other members of the enigma family by homology and to predict their abilities to bind alpha-actinin-2. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Solution structure of ZASP PDZ domain; implications for sarcomere ultrastructure and enigma family redundancy.,Au Y, Atkinson RA, Guerrini R, Kelly G, Joseph C, Martin SR, Muskett FW, Pallavicini A, Faulkner G, Pastore A Structure. 2004 Apr;12(4):611-22. PMID:15062084<ref>PMID:15062084</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
| - | </div> | ||
| - | <div class="pdbe-citations 1rgw" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 29: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
[[Category: Large Structures]] | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Atkinson | + | [[Category: Atkinson RA]] |
| - | [[Category: Au | + | [[Category: Au Y]] |
| - | [[Category: Faulkner | + | [[Category: Faulkner G]] |
| - | [[Category: Guerrini | + | [[Category: Guerrini R]] |
| - | [[Category: Joseph | + | [[Category: Joseph C]] |
| - | [[Category: Martin | + | [[Category: Martin SR]] |
| - | [[Category: Muskett | + | [[Category: Muskett FW]] |
| - | [[Category: Pallavicini | + | [[Category: Pallavicini A]] |
| - | [[Category: Pastore | + | [[Category: Pastore A]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 08:23, 1 May 2024
Solution Structure of ZASP's PDZ domain
| |||||||||||
Categories: Homo sapiens | Large Structures | Atkinson RA | Au Y | Faulkner G | Guerrini R | Joseph C | Martin SR | Muskett FW | Pallavicini A | Pastore A