We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
1ygp
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
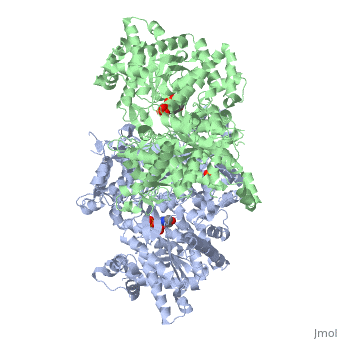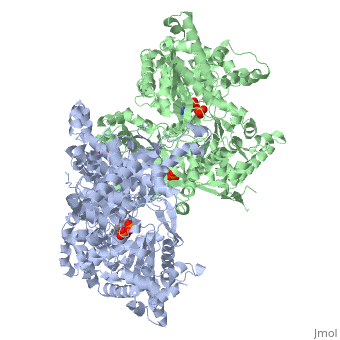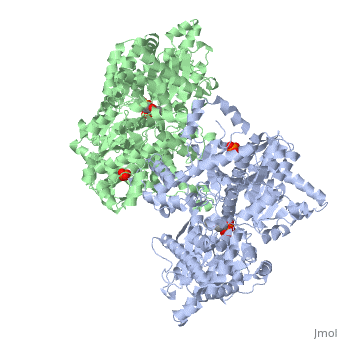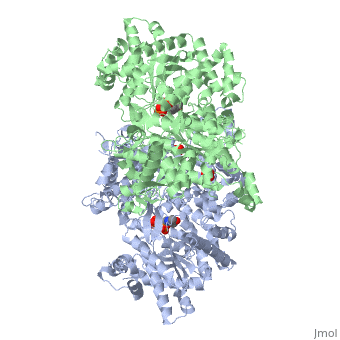
<StructureSection load='1ygp' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1ygp]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.80Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1ygp' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1ygp]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.80Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1ygp]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1ygp]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae Saccharomyces cerevisiae]. The December 2001 RCSB PDB [https://pdb.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/index.html Molecule of the Month] feature on ''Glycogen Phosphorylase'' by David S. Goodsell is [https://dx.doi.org/10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2001_12 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2001_12]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1YGP OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1YGP FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id=' | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.8Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id=' | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=PLP:PYRIDOXAL-5-PHOSPHATE'>PLP</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=PO4:PHOSPHATE+ION'>PO4</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1ygp FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1ygp OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1ygp PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1ygp RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1ygp PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1ygp ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | [ | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/PHSG_YEAST PHSG_YEAST] Phosphorylase is an important allosteric enzyme in carbohydrate metabolism. Enzymes from different sources differ in their regulatory mechanisms and in their natural substrates. However, all known phosphorylases share catalytic and structural properties. |
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | [[Category: Atcc 18824]] | ||
[[Category: Glycogen Phosphorylase]] | [[Category: Glycogen Phosphorylase]] | ||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month]] | [[Category: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month]] | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Saccharomyces cerevisiae]] |
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Dai SC]] |
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Fletterick RJ]] |
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Hwang PK]] |
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Lin K]] |
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Rath VL]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
PHOSPHORYLATED FORM OF YEAST GLYCOGEN PHOSPHORYLASE WITH PHOSPHATE BOUND IN THE ACTIVE SITE.
| |||||||||||