User:Melissa Siolin Martins/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Ohr protein== | ==Ohr protein== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='4XX2' size='300' side='right' caption='Ohr from Xylella fastidiosa in oxidized state. Model | + | <StructureSection load='4XX2' size='300' side='right' caption='Ohr from Xylella fastidiosa in oxidized state. Model from PDB=''> |
The '''Ohr protein (organic hydroperoxide resistance)''' is a thiol-dependent Cys-based peroxidase exclusive to bacteria, that participates in the antioxidant defense system of these organisms against damage induced by organic peroxides (OHPs), such as fatty acid peroxides and peroxynitrite <ref name="Alegria">PMID:20463026</ref><ref name="Meireles">PMID:35452809</ref>. This class of peroxides is toxic due to its ability to generate free radicals, highly reactive molecules containing an unpaired electron in an atomic orbital that can cause damage to important molecules such as DNA and proteins. Because of that, these substances are frequently used by the host defense against bacteria pathogens <ref>PMID:9573147</ref><ref>PMID:22228951</ref>. | The '''Ohr protein (organic hydroperoxide resistance)''' is a thiol-dependent Cys-based peroxidase exclusive to bacteria, that participates in the antioxidant defense system of these organisms against damage induced by organic peroxides (OHPs), such as fatty acid peroxides and peroxynitrite <ref name="Alegria">PMID:20463026</ref><ref name="Meireles">PMID:35452809</ref>. This class of peroxides is toxic due to its ability to generate free radicals, highly reactive molecules containing an unpaired electron in an atomic orbital that can cause damage to important molecules such as DNA and proteins. Because of that, these substances are frequently used by the host defense against bacteria pathogens <ref>PMID:9573147</ref><ref>PMID:22228951</ref>. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
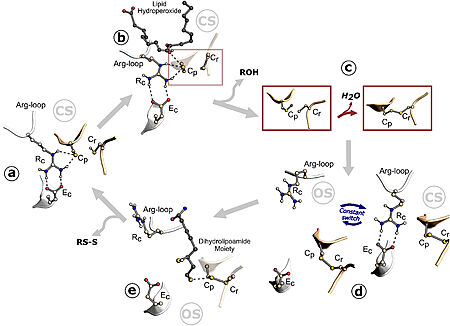
| - | [[Image:image 1.jpg|450px|left|thumb| Figure 1. Ohr catalytic cycle. Image | + | [[Image:image 1.jpg|450px|left|thumb| Figure 1. Ohr catalytic cycle. Image from Meireles et al. 2022]] |
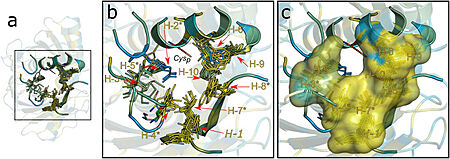
| - | [[Image:image 2.jpg|450px|left|thumb| Figure 2. Hydrophobic collar (HC) surrounding the active site of Ohrs. Image | + | [[Image:image 2.jpg|450px|left|thumb| Figure 2. Hydrophobic collar (HC) surrounding the active site of Ohrs. Image from Meireles et al. 2022]] |
The Ohr protein possesses an alpha/beta fold structure not found in peroxiredoxins or glutathione peroxidases (Cussiol, 2010). Ohr homologs and OsmC have motifs composed of well-conserved cysteine residues. One of these residues is part of a VCP motif, also found in peroxiredoxins, showing that Ohr can also participate in the peroxide decomposition process (Cussiol, 2003). | The Ohr protein possesses an alpha/beta fold structure not found in peroxiredoxins or glutathione peroxidases (Cussiol, 2010). Ohr homologs and OsmC have motifs composed of well-conserved cysteine residues. One of these residues is part of a VCP motif, also found in peroxiredoxins, showing that Ohr can also participate in the peroxide decomposition process (Cussiol, 2003). | ||
Revision as of 23:34, 28 May 2024
Ohr protein
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cussiol JR, Alegria TG, Szweda LI, Netto LE. Ohr (organic hydroperoxide resistance protein) possesses a previously undescribed activity, lipoyl-dependent peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 16;285(29):21943-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.117283. Epub, 2010 May 12. PMID:20463026 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.117283
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 Meireles DA, da Silva Neto JF, Domingos RM, Alegria TGP, Santos LCM, Netto LES. Ohr catalysis, phylogeny, regulation, and physiological roles. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 May 20;185:6-24. PMID:35452809 doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.04.001
- ↑ Mongkolsuk S, Praituan W, Loprasert S, Fuangthong M, Chamnongpol S. Identification and characterization of a new organic hydroperoxide resistance (ohr) gene with a novel pattern of oxidative stress regulation from Xanthomonas campestris pv. phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1998 May;180(10):2636-43. PMID:9573147
- ↑ Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn Rev. 2010 Jul;4(8):118-26. PMID:22228951 doi:10.4103/0973-7847.70902
- ↑ Chen SJ, Shu HY, Lin GH. Regulation of tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide Resistance by Chromosomal OhrR in A. baumannii ATCC 19606. Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 18;9(3):629. PMID:33803549 doi:10.3390/microorganisms9030629
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Meireles DA, Domingos RM, Gaiarsa JW, Ragnoni EG, Bannitz-Fernandes R, da Silva Neto JF, de Souza RF, Netto LES. Functional and evolutionary characterization of Ohr proteins in eukaryotes reveals many active homologs among pathogenic fungi. Redox Biol. 2017 Aug;12:600-609. PMID:28391181 doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.03.026