We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
1n88
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
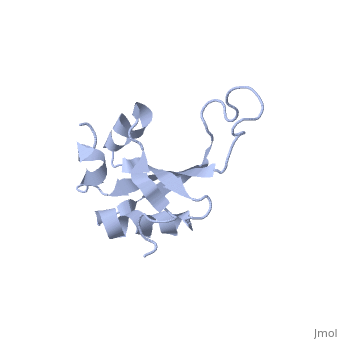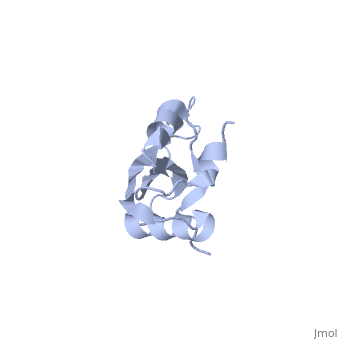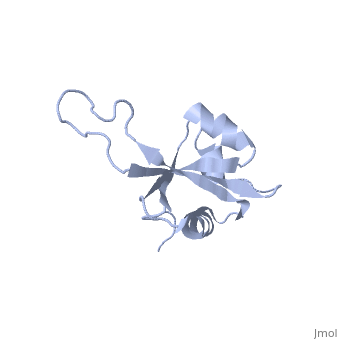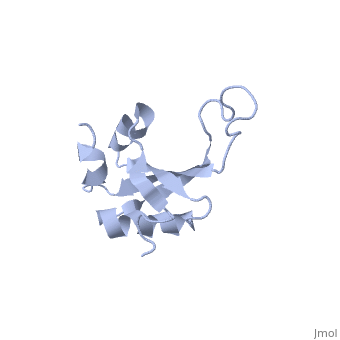
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1n88 ConSurf]. | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1n88 ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
| + | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| + | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| + | The ribosomal protein L23 is a component of the large ribosomal subunit in which it is located close to the peptide exit tunnel. In this position L23 plays a central role both for protein secretion and folding. We have determined the solution structure of L23 from Thermus thermophilus. Uncomplexed L23 consists of a well-ordered part, with four anti-parallel beta-strands and three alpha-helices connected as beta-alpha-beta-alpha-beta-beta-alpha, and a large and flexible loop inserted between the third and fourth beta-strand. The observed topology is distantly related to previously known structures, primarily within the area of RNA biochemistry. A comparison with RNA-complexed crystal structures of L23 from T. thermophilus, Deinococcus radiodurans and Haloarcula marismourtui, shows that the conformation of the well-ordered part is very similar in the uncomplexed and complexed states. However, the flexible loop found in the uncomplexed solution structure forms a rigid extended structure in the complexed crystal structures as it interacts with rRNA and becomes part of the exit tunnel wall. Structural characteristics of importance for the interaction with rRNA and with the ribosomal protein L29, as well as the functional role of L23, are discussed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NMR structure of the ribosomal protein L23 from Thermus thermophilus.,Ohman A, Rak A, Dontsova M, Garber MB, Hard T J Biomol NMR. 2003 Jun;26(2):131-7. PMID:12766408<ref>PMID:12766408</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="pdbe-citations 1n88" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Ribosomal protein L23|Ribosomal protein L23]] | *[[Ribosomal protein L23|Ribosomal protein L23]] | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Current revision
NMR structure of the ribosomal protein L23 from Thermus thermophilus.
| |||||||||||