User:Gustavo Sartorelli de Carvalho Rego/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Contrary to the flexible N-terminal domain, the <scene name='10/1050300/Phac_i_catalytic_c_domain/2'>C-terminal domain</scene> is relatively stable, making its crytalization process easier. Because of this, it was possible to obtain the <b><span class='text-gray'>C-terminal domain</span></b> structure from PhaC<sub>cn</sub>-CAT and PhaC<sub>cs</sub>-CAT through X-ray cristallography, with resolution of 1.8 Å and 1.48 Å, respectively. The C-terminal domain has the <scene name='10/1050300/Phac_i_catalytic_site/2'>catalytic site, with the aminoacid triad</scene> <b><span class='text-red'>(Cys-Asp-His)</span></b>, the substrate entrance and the product egress tunnel.<ref name='Neoh' /> | Contrary to the flexible N-terminal domain, the <scene name='10/1050300/Phac_i_catalytic_c_domain/2'>C-terminal domain</scene> is relatively stable, making its crytalization process easier. Because of this, it was possible to obtain the <b><span class='text-gray'>C-terminal domain</span></b> structure from PhaC<sub>cn</sub>-CAT and PhaC<sub>cs</sub>-CAT through X-ray cristallography, with resolution of 1.8 Å and 1.48 Å, respectively. The C-terminal domain has the <scene name='10/1050300/Phac_i_catalytic_site/2'>catalytic site, with the aminoacid triad</scene> <b><span class='text-red'>(Cys-Asp-His)</span></b>, the substrate entrance and the product egress tunnel.<ref name='Neoh' /> | ||
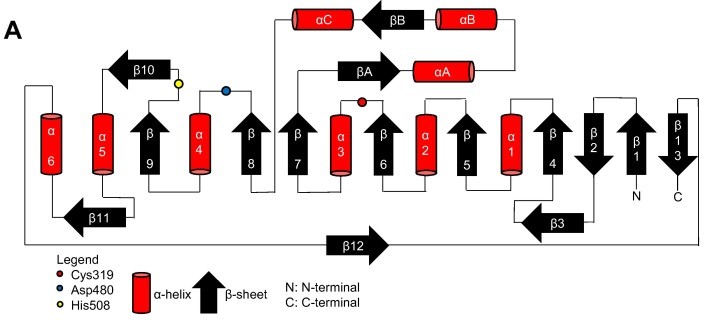
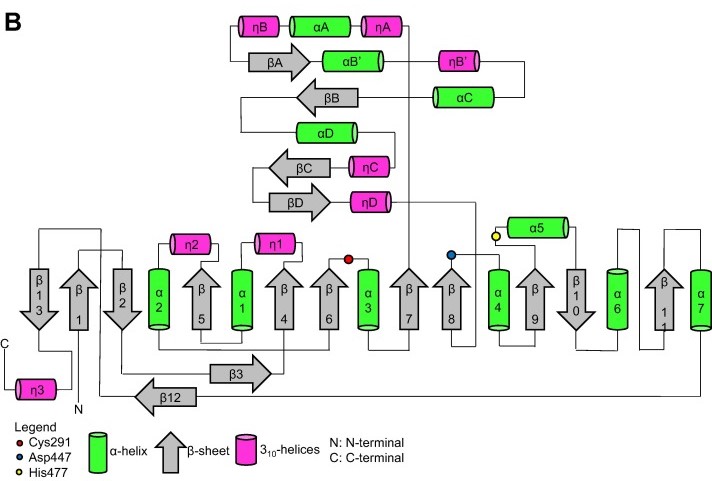
| - | The overall form of a phaC protein is that of a typical protein from the α/β-hydrolase-fold, with the C-terminal domain made of an <b><span class='text-cyan>α/β-hydrolase core</span></b> <scene name='10/1050300/Phac_i_catalytic_hydrolase_sub/1'>subdomain</scene> and a <b><span class='text-orange'>Cap</span></b> <scene name='10/1050300/Phac_i_catalytic_cap_sub/1'>subdomain</scene>, corresponding to the Thr347-Pro471 residues in PhaC<sub>cn</sub>, and Thr319-Pro438 residues in PhaC<sub>cs</sub>. It is in the α/β-hydrolase subdomain that the entrance tunnel, the catalytic site and the product egress tunnel are located. This region seems to be preserved in phaCs.<ref name='Neoh' /> | + | The overall form of a phaC protein is that of a typical protein from the α/β-hydrolase-fold, with the C-terminal domain made of an <b><span class='text-cyan'>α/β-hydrolase core</span></b> <scene name='10/1050300/Phac_i_catalytic_hydrolase_sub/1'>subdomain</scene> and a <b><span class='text-orange'>Cap</span></b> <scene name='10/1050300/Phac_i_catalytic_cap_sub/1'>subdomain</scene>, corresponding to the Thr347-Pro471 residues in PhaC<sub>cn</sub>, and Thr319-Pro438 residues in PhaC<sub>cs</sub>. It is in the α/β-hydrolase subdomain that the entrance tunnel, the catalytic site and the product egress tunnel are located. This region seems to be preserved in phaCs.<ref name='Neoh' /> |
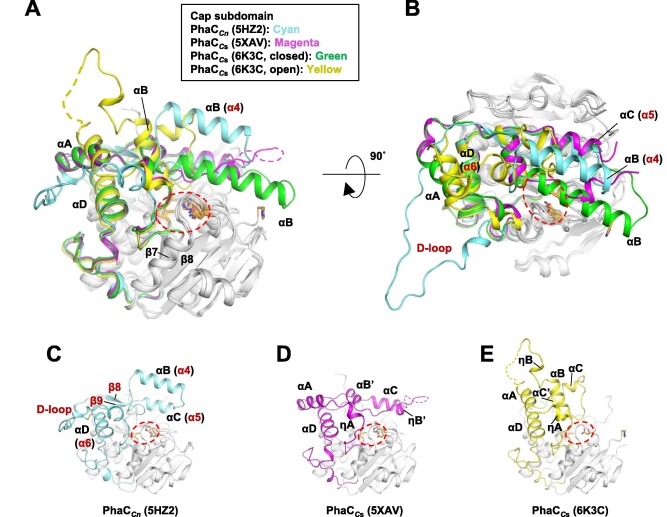
Regarding the <b><span class='text-orange'>Cap</span></b> <scene name='10/1050300/Phac_i_catalytic_cap_sub/1'>subdomain</scene>, the LID region is extremely dynamic and flexible, having an open or closed conformation based on structural changes. Because of this, the Cap subdomain, specially the LID region, is not as conserverd in the phaCs as the α/β-hydrolase subdomain. The Cap subdomain is located after the β7 sheet, and connects with the β8 sheet from the α/β-hydrolase core. In PhaC<sub>cn</sub>, the Cap subdomain is formed by three α-helixes (α4, α5 and α6) and two β-sheets (β8 and β9). Meanwhile, PhaC<sub>cs</sub> has six α-helixes (αA, αB, αC, αD, ηA and ηB').<ref name='Neoh' /> | Regarding the <b><span class='text-orange'>Cap</span></b> <scene name='10/1050300/Phac_i_catalytic_cap_sub/1'>subdomain</scene>, the LID region is extremely dynamic and flexible, having an open or closed conformation based on structural changes. Because of this, the Cap subdomain, specially the LID region, is not as conserverd in the phaCs as the α/β-hydrolase subdomain. The Cap subdomain is located after the β7 sheet, and connects with the β8 sheet from the α/β-hydrolase core. In PhaC<sub>cn</sub>, the Cap subdomain is formed by three α-helixes (α4, α5 and α6) and two β-sheets (β8 and β9). Meanwhile, PhaC<sub>cs</sub> has six α-helixes (αA, αB, αC, αD, ηA and ηB').<ref name='Neoh' /> | ||
Revision as of 18:43, 2 June 2024
Introduction
| |||||||||||