We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Histone
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
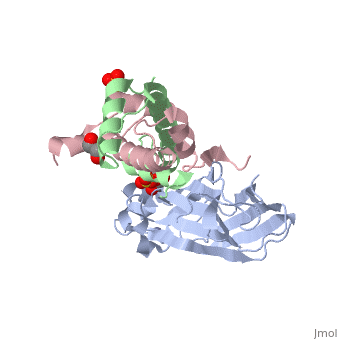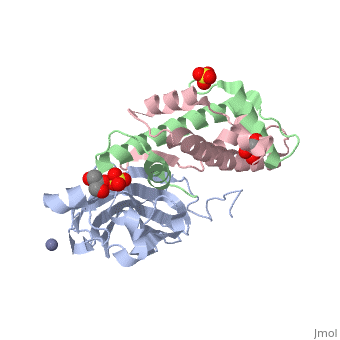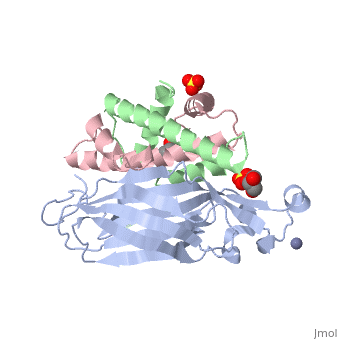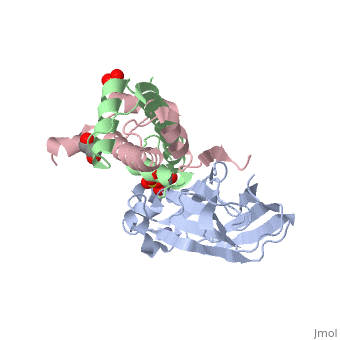
<StructureSection load='2hue' size='340' side='right' caption='Yeast H3 (green), H4 (pink) and anti-silencing protein (grey) complex with sulfate, glycerol and Zn+2 ion (grey), [[2hue]]' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2hue' size='340' side='right' caption='Yeast H3 (green), H4 (pink) and anti-silencing protein (grey) complex with sulfate, glycerol and Zn+2 ion (grey), [[2hue]]' scene=''> | ||
==Histone core protein structure== | ==Histone core protein structure== | ||
| - | Histones are highly <scene name='Taylor_histone_sandbox/Conservation/1'>conserved proteins</scene> (more purple = more conserved) with <scene name='Taylor_histone_sandbox/Charge_distribution/1'>positive charge</scene> (blue is positive charge, red is negative charge). Because of this positive charge, they interact electrostatically with the negatively charged phosphate groups in DNA. | + | '''Histones''' are highly <scene name='Taylor_histone_sandbox/Conservation/1'>conserved proteins</scene> (more purple = more conserved) with <scene name='Taylor_histone_sandbox/Charge_distribution/1'>positive charge</scene> (blue is positive charge, red is negative charge). Because of this positive charge, they interact electrostatically with the negatively charged phosphate groups in DNA. |
There are five major classes of histones: H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4.<ref>PMID: 16472024</ref><ref name="Voet, Voet, and Pratt">{{Cite book|surname1= Voet|given1= Donald |surname2= Voet|given2= Judith|surname3= Pratt|given3= Leon A.| year=1988|title=Basic Genetics|publication-place=Boston|publisher=Jones and Bartlett Publishers|isbn=0-86720-090-1}}</ref> Histones <scene name='46/468228/2a/3'>H2A</scene>, <scene name='46/468228/2b/4'>H2B</scene>, <scene name='46/468228/3/3'>H3</scene>, and <scene name='46/468228/H4/1'>H4</scene> are known as the core histones, while histones H1 and H5 are known as the linker histones. | There are five major classes of histones: H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4.<ref>PMID: 16472024</ref><ref name="Voet, Voet, and Pratt">{{Cite book|surname1= Voet|given1= Donald |surname2= Voet|given2= Judith|surname3= Pratt|given3= Leon A.| year=1988|title=Basic Genetics|publication-place=Boston|publisher=Jones and Bartlett Publishers|isbn=0-86720-090-1}}</ref> Histones <scene name='46/468228/2a/3'>H2A</scene>, <scene name='46/468228/2b/4'>H2B</scene>, <scene name='46/468228/3/3'>H3</scene>, and <scene name='46/468228/H4/1'>H4</scene> are known as the core histones, while histones H1 and H5 are known as the linker histones. | ||
Revision as of 07:36, 2 July 2024
| |||||||||||
- For nucleosome structure see
- User:Eric Martz/Nucleosomes
- Nucleosome structure
- Nucleosomes
- Nucleosome structure (Spanish)
3D Structures of histone
References
- ↑ Bhasin M, Reinherz EL, Reche PA. Recognition and classification of histones using support vector machine. J Comput Biol. 2006 Jan-Feb;13(1):102-12. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2006.13.102. PMID:16472024 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2006.13.102
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Redon C, Pilch D, Rogakou E, Sedelnikova O, Newrock K, Bonner W. Histone H2A variants H2AX and H2AZ. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002 Apr;12(2):162-9. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00282-4. PMID:11893489 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00282-4
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1997 Sep 18;389(6648):251-60. PMID:9305837 doi:10.1038/38444
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Strahl BD, Allis CD. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature. 2000 Jan 6;403(6765):41-5. doi: 10.1038/47412. PMID:10638745 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/47412
- ↑ Jenuwein T, Allis CD. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001 Aug 10;293(5532):1074-80. doi: 10.1126/science.1063127. PMID:11498575 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1063127
- ↑ Song N, Liu J, An S, Nishino T, Hishikawa Y, Koji T. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Histone H3 Modifications in Germ Cells during Mouse Spermatogenesis. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2011 Aug 27;44(4):183-90. doi: 10.1267/ahc.11027. Epub, 2011 Jul 20. PMID:21927517 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1267/ahc.11027
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Ann Taylor, Alexander Berchansky, Karsten Theis