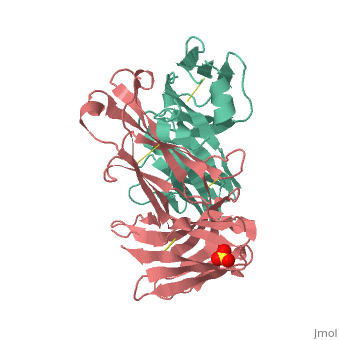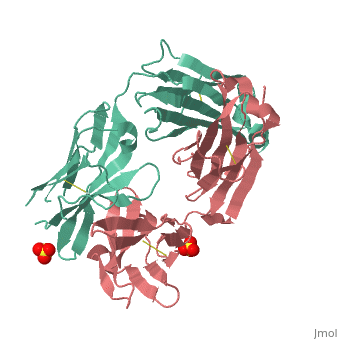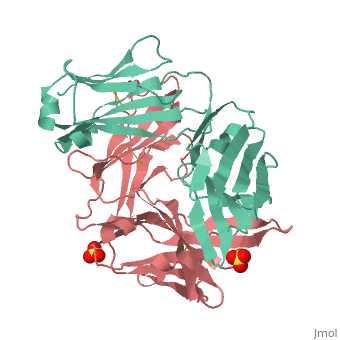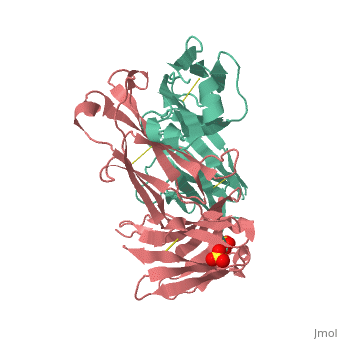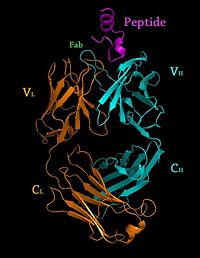
Crystal Structure of Rituximab Fab in complex with an epitope peptide
2oslMonoclonal antibodies are immunoglobulins produced by a single clone of cells and therefore a single pure homogeneous type of antibody. For structural information on immunoglobulins, see: Antibody The development of antibodies has revolutionized much of the science world both in the lab and in the medical world in treating cancer and autoimmune disorders. Humanized mouse antibody (hmFab) is a modified mFab which resembles more hFab. Catalytic antibody is a monoclonal antibody with catalytic activity.
- Catalytic antibody can catalyse certain reactions like an enzyme besides binding to an antigen[1]
, 3c08. Light (blue) and heavy (yellow) chains.
Brief History
Nobel Laureate Paul Ehrlich proposed the idea of a “magic bullet” at the beginning of the 20th century by postulating that if a compound could be made that selectively targets a disease causing organism, then toxins could be delivered to selectively kill any cell. He proposed that this could be a cure for nearly any disease. The monoclonal antibody is this “magic bullet,” and while they are extremely selective and effective, monoclonal antibodies have limitations. Georges Kholer, Cesar Milstein, and Niels kaj Jerne developed the monoclonal antibody and shared the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1984 for the discovery.
Original Monoclonal Antibody Technology
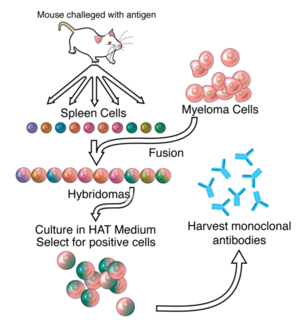
Monoclonal Antibody Production via Hybridomas
When an organism is exposed to an antigen, the immune system stages a complex immunological response. One such response is the activation of B-cells and subsequent release of antibodies. To any single antigen, thousands of different B-cells can be activated by their binding different epitopes on that antigen. When these B-cells subsequently mature into antibody releasing plasma cells, thousands of different antibodies are released into the blood binding and removing the invading antigen. The body creates these “polyclonal” antibodies to guarantee antigens are bound multiple times by antibodies to expedite their removal and serves as a redundant form of immunological security in case some of the antibodies produced are faulty.[2] In order to be a useful tool in research and medicine however, a single, monoclonal antibody must be isolated.
Monoclonal antibody production has changed drastically since Kholer and Milstein first did it in 1975. A brief description of their process however is insightful. First an antigen of choice is injected into a mouse and after 10 days, a sample of B-cells is extracted from the spleen of the mouse. These cells are added to a culture of myeloma cells, which are immortal cancer cells, to form hybridomas, cells formed by the fusion of a B-cell and myeloma cells.[2] Next, the hybridomas undergo selection hypozanthine-aminopterin-thimine (HAT) medium, in which only those cells that have successfully formed fusions will survive indefinitely. The hybridomas are then cultured and screened after doing SDS-PAGE and Western blots to identify those hybridomas creating the desired antibody. These hybridomas are immortal and can produce “murine” antibodies nearly indefinitely.[3]
Newer Monoclonal Technology
Early forms of monoclonal antibodies (murine antibodies) were problematic for therapeutic use because they were mouse antibodies, not human antibodies. When injected into humans, the antibodies would either be rapidly cleared from the body or worse, result in systemic inflammatory effects that were harmful. The human immune system recognized these mouse antibodies as foreign pathogens and rapidly produced human anti-mouse antibodies and unleashed the immune system on these invading pathogens.[4] To avoid this immune response, antibodies that the body recognized as native had to be created. Murine antibodies typically have a “mo” before the “mab” in their name, as is the case with Tositumomab (Marketed as Bexxar by GlaxoSmithKline), a drug used to treat lymphoma.
Chimeric Antibodies
(2osl).
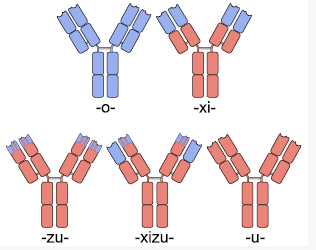
Different Types of Antibodies
One solution to this problem was the creation of chimeric antibodies. Chimeric anibodies are antibodies that have the , but have . These are created by fusing the Fab region coding DNA extracted from mice B-cells as above to human antibody DNA that only codes for the Fc region. Since it is the Fc region of an antibody that is glycosylated and used by the human immune system to determine self vs non-self, and the Fc region in chimeric antibodies is human, these chimeric antibodies typically cause a minimal immune response against them and thus have a longer half life.[5]. Chimeric antibodies typically have a “xi” before the “mab” at the end of their name to indicate their chain type, as is the case with “abciximab” (ReoPro), “cutximab” (Erbitux), or (Rituxan).
These chimeric antibodies can be further humanized through mutagenesis to the Fab sequence (excluding the ), identifying those parts which differ in humans and mutating them. This is a difficult process, but can create antibodies that are unrecognizable from human antibodies at the amino acid level.[6]. To avoid the added mutagenesis step, insertion of only the CDRs from mice into a full human antibody scaffold has been used to create humanized antibodies.[7] Humanized antibodies typically have a “zu” before the “mab” to indicate their chain type. The drug Alemtuzumab (marketed by Genzyme for the treatment of leukemia) is an example of a humanized antibody with foreign CDR regions.
Human Antibody Production & Phage Display
The major drawback with chimeric antibody production is it still involves using rodents as the original source of antigen binding, and requires significant effort to identify, purify and create the fusion antibody. Applying a technique called phage display to monoclonal antibody production expedites this entire process. In phage display, DNA coding the binding region of the antibody is ligated into the genes of a phage which code for proteins that are expressed on the protein coat of the virus. This phage gene hybrid is then transformed into bacterial cells. The virus hijacks the bacterial replication machinery, producing vast quantities of phage. By using many DNA fragments that are slightly different, a library of slightly different antibodies can be expressed on the outside of these phages, one type of antibody per phage. These antibody covered phages can then be selected for by running them through a column with the protein target immobilized on the column. Once the phages that bind the target protein well are identified, they can be used to reinfect bacterial cells and to isolate the DNA of antibodies that code for those antibodies with the greatest affinity for the target. Once the best antibodies are identified, they can be combined with human antibody scaffolds or human Fc regions as above to create humanized antibodies [8] [9]Antibodies created through phage display have a “u” before the “mab” in their name to indicate their chain origins as is the case for Adalimumab (HUMIRA)
Glycosylation of Monoclonal Antibodies
bound to a Protein Called Z34C,(1l6x).
Once an antibody gene is designed to contain the ideal sequence, the antibody then must be mass produced. An ideal system of production would be in bacterial cells because of the rapidity with which they replicate and ease of use. Unfortunately, bacterial cells do not glycosylate proteins the same way mammalian cells do. Since is critical for the immune system to recognize a protein as native, thus allowing the protein to stay in circulation in the human body without creating an immune response, antibody production had to be completed in cells that glycosylate the antibody appropriately. Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells are one type of cell that is able to glycosylate antibodies appropriately, but they are difficult to work with and relatively expensive at an industrial scale. Regardless, they are the most commonly used mammalian hosts for industrial production of recombinant protein therapeutics.[10] More recently, work by Dr. Tillman Gerngross, et al. have demonstrated that yeast can be genetically manipulated to produce human glycosylation on expressed antibodies. This is an important discovery because yeast replicate much faster than CHO cells, making them more ideal as hosts for industrial scale production of therapeutic proteins.[11] Gerngross’s startup company GlycoFi, which was based around this platform was purchased by Merck in 2006 and the technology is being employed in Merck’s pipeline. Gerngross’s new company, [www.adimab.com Adimab], also uses similar technology to produce human glycosylated proteins for the pharmaceutical industry.
Monoclonal Antibody Uses
Laboratory Research
Monoclonal antibodies have become a critical tool in most biochemistry labs. They are essential components in immunofluorescence experiments as well as in Western Blot and immuno dot blot tests to detect protein on a membrane.
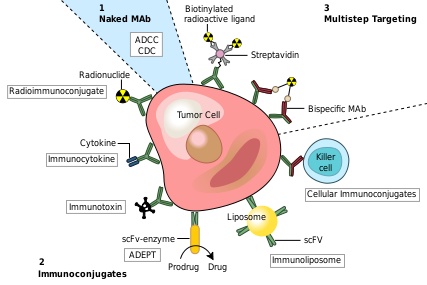
Monoclonal Antibody Therapeutic Uses
Medical Applications
Monoclonal antibodies have been utilized to create four major classes of drugs. The first activate the bodies own immune system. An example of this is Rituximab (Marketed as Rituxan by Roche and Genentech). to CD20 surface proteins on B-Cells and illicits natural immune responses to these cancerous cells via ADCC, activating cellular apoptosis, or by attracting compliment proteins which kill the cell via the compliment pathway. [12] Another example of this type of monoclonal antibody drug is Infliximab (Marketed as [www.remicade.com/ Remicade] by Merck and the best selling Monoclonal therapeutic in 2008 with over $6 billion in sales). See Remicade (Infliximab). This class of antibodies also includes those antibodies that simply bind a target, disrupting a key mechanism in the diseased cells.
The second class of monoclonal antibody drugs are those conjugated to a disruptive compound. One example of this is used in Radioimmunotherapy (RIT). By conjugating a radioactive isotope to a murine antibody, targeted immunotherapy is possible. The antibody binds to the targeted cancer cell and the cell is damaged or destroyed by emitted beta particles. Murine antibodies are used because they are cleared from the body rapidly so as to avoid extensive radiation damage from the drug. This is the mechanism used by Tositumomab (Bexxar) which uses radioactive Iodine-131. [13] Also within this class of antibodies are those antibodies conjugated to a chemotherapy drug. An example of this type would be Gemtuzumab (marketed as Mylotarg by Wyeth until June 2010, when it was removed from the market due to inefficacy and safety concerns)
The Third class of monoclonal antibody drugs are those conjugated to a drug activating enzyme also known as Antibody-Directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy (ADEPT). In this system, an enzyme that is able to activate a drug is attached to an antibody with specificity toward a target of choice. After injection of the antibody/enzyme compound and ample time for the antibodies to bind the target, a prodrug that is inert until activated by the enzyme is injected. This prodrug stays inert until it comes into contact with the antibody/enzyme compound bound to the target, whereupon the prodrug is activated and is able to attack cells in the local environment, which presumably would be populated by the infected target cells. No ADEPT system drugs have made it through the clinic yet, but the class holds promise. [14] [15]
The Final class of monoclonal antibody medical uses are those conjugated to liposomes or another form of nanotechnology drug delivery system. By attaching antibodies to the outside of a nanosized drug delivery device, large quantities of therapeutic drug can be delivered to a targeted environment. Many new nanotech devices including liposomes, nanotubes and other such containers have been developed and have demonstrated improved specificity for delivery existing drug compounds. [16]
Brand New Research
Here are some new tidbits of interesting information regarding monoclonal Antibodies
Lippow et al. have developed a computational method for improving antibody binding to targets. They were able to increase cetuximab (Erbitux) affinity 10 fold and comparable improvements in bevacizumab (Avastin), which disrupts Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor from binding VEGFR. [17]
Gribenko et al. developed a computation method for making any antibody more stable in the body by making specific changes to the amino acid sequence. [18]
A number of companies including MedImmune and Xencor have struck major deals in the past 2 years based on platforms of manipulating an antibodies Fc region to increase its half-life in the body or its immunological response.[19]
http://f1000scientist.com/article/display/57474/</ref>
3D structure of monoclonal antibody
3D structures of monoclonal antibody