Pho4
From Proteopedia
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Phosphate system positive regulatory protein '''Pho4''' is a transcriptional activator which regulates the expression of phosphatase under conditions of phosphate starvation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae <ref>PMID:2220078</ref>. For details see [[Pho4 bHLH Protein]]. | Phosphate system positive regulatory protein '''Pho4''' is a transcriptional activator which regulates the expression of phosphatase under conditions of phosphate starvation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae <ref>PMID:2220078</ref>. For details see [[Pho4 bHLH Protein]]. | ||
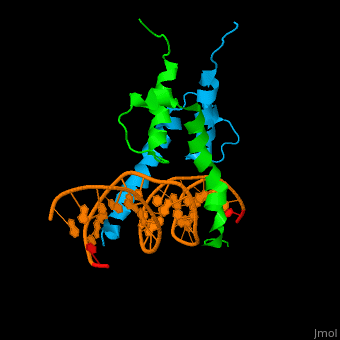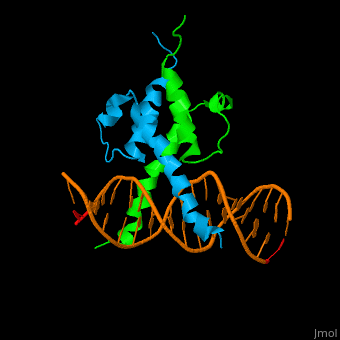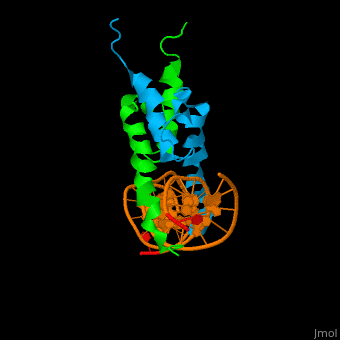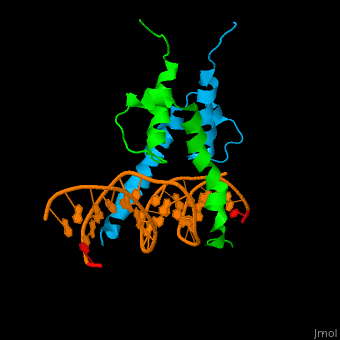
*<scene name='72/725407/Cv/3'>Yeast Pho4 DNA-binding domain interactions with DNA</scene>. | *<scene name='72/725407/Cv/3'>Yeast Pho4 DNA-binding domain interactions with DNA</scene>. | ||
| - | Its structure is a basic basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) | + | Its structure is a basic basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) |
The pho4 protein takes part in transcription of several yeast genes related to phosphate metabolism: | The pho4 protein takes part in transcription of several yeast genes related to phosphate metabolism: | ||
'''PH05 encoding repressible acid phosphatase,''' the expression of Pho5 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is derepressed by a specific level of inorganic phosphate (Pi), and depressed when the Pi concentrate in the medium is lowered, the regulatory system of the Pi signals coded by PHO4 PHO2 , PHO80, and PHO81 genes.<ref>PMID:2671650</ref> | '''PH05 encoding repressible acid phosphatase,''' the expression of Pho5 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is derepressed by a specific level of inorganic phosphate (Pi), and depressed when the Pi concentrate in the medium is lowered, the regulatory system of the Pi signals coded by PHO4 PHO2 , PHO80, and PHO81 genes.<ref>PMID:2671650</ref> | ||
| - | '''PH08 encoding alkaline phosphatase''' | + | '''PH08 encoding alkaline phosphatase''' |
| - | '''PH081 a regulatory gene''' regulated by PHO system wuth the use of Pi | + | '''PH081 a regulatory gene''' regulated by PHO system wuth the use of Pi |
'''PH084 phosphate permease gene'''<ref>PMID:3902805</ref> | '''PH084 phosphate permease gene'''<ref>PMID:3902805</ref> | ||
Revision as of 08:03, 21 July 2024
–
| |||||||||||
Structure
The structure of the Pho4 protein is a basic Helix-loop-helix(bHLH) motif, The linker sequence between Helix1(H1) and Helix2(H2) contains several residues: Asn, Glu, Pro and Ser[6]. The DNA binding site is a homodimer and two monomers in a left‐handed four‐helix bundle fold (identical to bHLH/Zip and bHLH proteins fold).
- loop structure
Pho4 loops (conserved structure?) are long but compact and forms a short alpha-helical structure [7]. The PHO4 loop contains a Trp residue that faces the aromatic rings of Tyr52 and His55 of helix H2, and Pro28 of H2 and H1. the Pho4 is lack of inner hydrogen network and the loop create one contact with phosphate group by Ser41[8]an aromatic cluster forms a cap structure is observed
- DNA binding
The Pho4 protein binds to DNA as a homodimer, and the binding region binds specifically to E-box sequence CACGTG and it's 3'-flanking bases by a specific subset of the basic region of the bHLH motif.[9] the residues who takes part in the E-box recognition are His5, Glu9, and Arg13.[10]
3D Structures of Pho
Updated on 21-July-2024
References
- ↑ Berben G, Legrain M, Gilliquet V, Hilger F. The yeast regulatory gene PHO4 encodes a helix-loop-helix motif. Yeast. 1990 Sep-Oct;6(5):451-4. PMID:2220078 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/yea.320060510
- ↑ Yoshida K, Ogawa N, Oshima Y. Function of the PHO regulatory genes for repressible acid phosphatase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):40-6. PMID:2671650
- ↑ Tamai Y, Toh-e A, Oshima Y. Regulation of inorganic phosphate transport systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):964-8. PMID:3902805
- ↑ . PMID:17850263
- ↑ Ogawa N, Oshima Y. Functional domains of a positive regulatory protein, PHO4, for transcriptional control of the phosphatase regulon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2224-36. PMID:2183025
- ↑ Leszczynski JF, Rose GD. Loops in globular proteins: a novel category of secondary structure. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):849-55. PMID:3775366
- ↑ Schmeckpeper BJ, Adams JM, Harris AW. Detection of a possible precursor of immunoglobulin light chain in MOPC 41 A plasmacytoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 15;53(1):95-8. PMID:1170095
- ↑ Shimizu T, Toumoto A, Ihara K, Shimizu M, Kyogoku Y, Ogawa N, Oshima Y, Hakoshima T. Crystal structure of PHO4 bHLH domain-DNA complex: flanking base recognition. EMBO J. 1997 Aug 1;16(15):4689-97. PMID:9303313 doi:10.1093/emboj/16.15.4689
- ↑ Fisher F, Jayaraman PS, Goding CR. C-myc and the yeast transcription factor PHO4 share a common CACGTG-binding motif. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1099-104. PMID:1861859
- ↑ Schmeckpeper BJ, Adams JM, Harris AW. Detection of a possible precursor of immunoglobulin light chain in MOPC 41 A plasmacytoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 15;53(1):95-8. PMID:1170095
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Inbar Yaffe, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman