We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Thrombin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
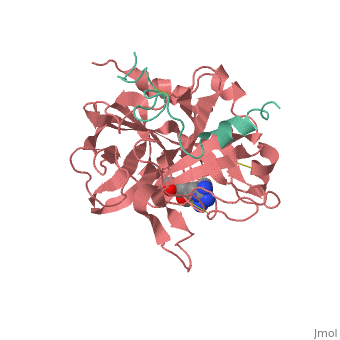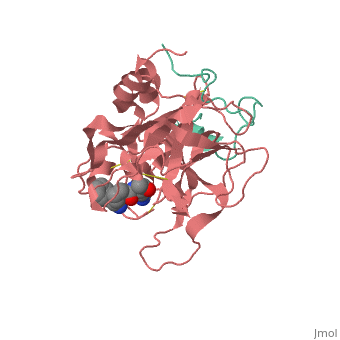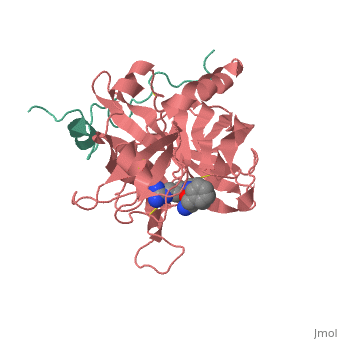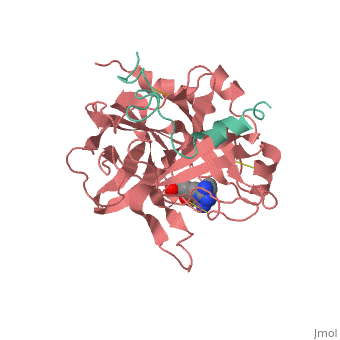
<StructureSection load='1ppb' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Human thrombin large (red) and small (green) subunits complex with prolinamide derivative (PDB code [[1ppb]])'> | <StructureSection load='1ppb' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Human thrombin large (red) and small (green) subunits complex with prolinamide derivative (PDB code [[1ppb]])'> | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
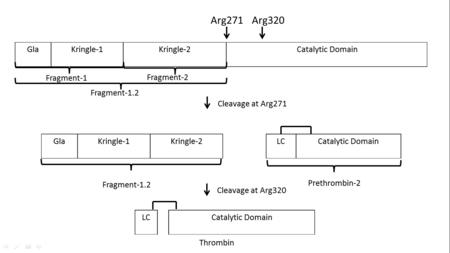
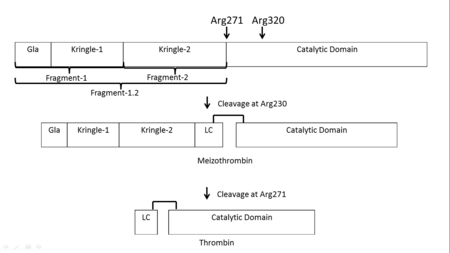
| - | '''Thrombin''' (Thr) is a serine protease. '''Prothrombin''' (PThr) is cleaved to form Thr in the coagulation cascade. The first step of the cleavage is at residue R320 and produces '''meizothrombin''' (MThr). Thr catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to the insoluble fibrin. Thr is composed of heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC). Prethrombin-1 lacks 155 N-terminal residues of PThr and is composed of a single polypeptide chain. '''Prethrombin-2''' is the product of proteolysis of '''prethrombin-1''' by trypsin or by active factor X. P-PACK Thr is a chemically modified Thr with inactivated catalytic site and active anion binding site. [[Hirudin]] is the most potent natural inhibitor of Thr ([[Sean Swale/Human Thrombin Inhibitor]]). For some more details see [[Serine Proteases]]. Prothrombin cleavage results in the creation of thrombin, a coagulative agent in plasma and is connected to fibrinolysis and platelet activation. During this process several peptides involved in the conversion are released into the plasma, and the remaining protein splits into two portions(http://www.uniprot.org/citations/3759958). It has been shown that prothrombin has a statistically significant connection to the occurrence of ischemic stroke with the presence of the G20210A mutation, though the cause was not isolated to prothrombin alone (http://www.uniprot.org/citations/15534175) (these links added by Connor Gramazio). Some additional details in<br /> | + | '''Thrombin''' (Thr) is a serine protease. '''Prothrombin''' (PThr) is cleaved by prothrombinase to form the 2 chains of Thr in the coagulation cascade<ref>PMID:23809130</ref>. The first step of the cleavage is at residue R320 and produces '''meizothrombin''' (MThr). Thr catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to the insoluble fibrin. Thr is composed of heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC). '''Prethrombin-1''' lacks 155 N-terminal residues of PThr and is composed of a single polypeptide chain. '''Prethrombin-2''' is the product of proteolysis of '''prethrombin-1''' by trypsin or by active factor X. P-PACK Thr is a chemically modified Thr with inactivated catalytic site and active anion binding site. [[Hirudin]] is the most potent natural inhibitor of Thr ([[Sean Swale/Human Thrombin Inhibitor]]). For some more details see [[Serine Proteases]]. Prothrombin cleavage results in the creation of thrombin, a coagulative agent in plasma and is connected to fibrinolysis and platelet activation. During this process several peptides involved in the conversion are released into the plasma, and the remaining protein splits into two portions(http://www.uniprot.org/citations/3759958). It has been shown that prothrombin has a statistically significant connection to the occurrence of ischemic stroke with the presence of the G20210A mutation, though the cause was not isolated to prothrombin alone (http://www.uniprot.org/citations/15534175) (these links added by Connor Gramazio). Some additional details in<br /> |
* [[Ann Taylor 115]]<br /> | * [[Ann Taylor 115]]<br /> | ||
* [[Sean Swale/Human Thrombin Inhibitor]]<br /> | * [[Sean Swale/Human Thrombin Inhibitor]]<br /> | ||
Revision as of 06:44, 19 August 2024
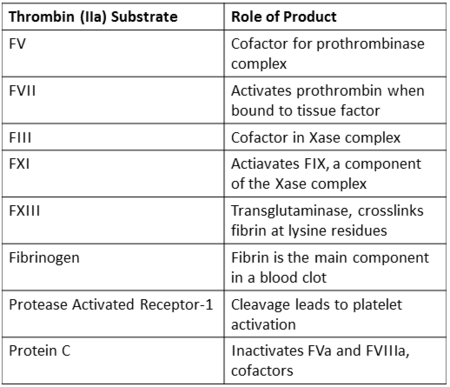
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Krishnaswamy S. The transition of prothrombin to thrombin. J Thromb Haemost. 2013 Jun;11 Suppl 1(0 1):265-76. PMID:23809130 doi:10.1111/jth.12217
- ↑ Fenton JW 2nd. Thrombin specificity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:468-95. PMID:7023326
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Coughlin SR. Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature. 2000 Sep 14;407(6801):258-64. PMID:11001069 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35025229
- ↑ Crawley JT, Lam JK, Rance JB, Mollica LR, O'Donnell JS, Lane DA. Proteolytic inactivation of ADAMTS13 by thrombin and plasmin. Blood. 2005 Feb 1;105(3):1085-93. Epub 2004 Sep 23. PMID:15388580 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-03-1101
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Lane DA, Philippou H, Huntington JA. Directing thrombin. Blood. 2005 Oct 15;106(8):2605-12. Epub 2005 Jun 30. PMID:15994286 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-04-1710
- ↑ Takagi T, Doolittle RF. Amino acid sequence studies on factor XIII and the peptide released during its activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):750-6. PMID:4811064
- ↑ Miljic P, Heylen E, Willemse J, Djordjevic V, Radojkovic D, Colovic M, Elezovic I, Hendriks D. Thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI): a molecular link between coagulation and fibrinolysis. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2010 Jan;138 Suppl 1:74-8. PMID:20229688
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Huntington JA. Natural inhibitors of thrombin. Thromb Haemost. 2014 Apr 1;111(4):583-9. doi: 10.1160/TH13-10-0811. Epub 2014 Jan, 30. PMID:24477356 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1160/TH13-10-0811
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Huntington JA. Thrombin inhibition by the serpins. J Thromb Haemost. 2013 Jun;11 Suppl 1:254-64. doi: 10.1111/jth.12252. PMID:23809129 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jth.12252
- ↑ Esmon CT. The regulation of natural anticoagulant pathways. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1348-52. PMID:3029867
- ↑ Kalafatis M, Rand MD, Mann KG. The mechanism of inactivation of human factor V and human factor Va by activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31869-80. PMID:7989361
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Lu D, Kalafatis M, Mann KG, Long GL. Comparison of activated protein C/protein S-mediated inactivation of human factor VIII and factor V. Blood. 1996 Jun 1;87(11):4708-17. PMID:8639840
- ↑ Duga S, Asselta R, Tenchini ML. Coagulation factor V. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Aug;36(8):1393-9. PMID:15147718 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2003.08.002
- ↑ Saenko EL, Shima M, Sarafanov AG. Role of activation of the coagulation factor VIII in interaction with vWf, phospholipid, and functioning within the factor Xase complex. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999 Oct;9(7):185-92. PMID:10881749
- ↑ Camire, R. M. (2010). Platelet factor V to the rescue. Blood, 115(4), 753-754. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-252619
- ↑ Berkner KL. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. Vitam Horm. 2008;78:131-56. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(07)00007-6. PMID:18374193 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0083-6729(07)00007-6
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 17.4 17.5 17.6 17.7 Lechtenberg BC, Freund SM, Huntington JA. An ensemble view of thrombin allostery. Biol Chem. 2012 Sep;393(9):889-98. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0178. PMID:22944689 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2012-0178
- ↑ Tijburg PN, van Heerde WL, Leenhouts HM, Hessing M, Bouma BN, de Groot PG. Formation of meizothrombin as intermediate in factor Xa-catalyzed prothrombin activation on endothelial cells. The influence of thrombin on the reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):4017-22. PMID:1995649
- ↑ Bobofchak KM, Pineda AO, Mathews FS, Di Cera E. Energetic and structural consequences of perturbing Gly-193 in the oxyanion hole of serine proteases. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 8;280(27):25644-50. Epub 2005 May 12. PMID:15890651 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M503499200
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 Bode W, Mayr I, Baumann U, Huber R, Stone SR, Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467-75. PMID:2583108
- ↑ Page MJ, Di Cera E. Evolution of peptidase diversity. J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 31;283(44):30010-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804650200. Epub 2008 , Sep 3. PMID:18768474 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M804650200
- ↑ Schechter I, Berger A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. 1967. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Aug 31;425(3):497-502. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.015. PMID:22925665 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.015
- ↑ Huntington JA. Molecular recognition mechanisms of thrombin. J Thromb Haemost. 2005 Aug;3(8):1861-72. PMID:16102053 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01363.x
- ↑ Zhang E, Tulinsky A. The molecular environment of the Na+ binding site of thrombin. Biophys Chem. 1997 Jan 31;63(2-3):185-200. PMID:9108691
- ↑ Li W, Johnson DJ, Esmon CT, Huntington JA. Structure of the antithrombin-thrombin-heparin ternary complex reveals the antithrombotic mechanism of heparin. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004 Sep;11(9):857-62. Epub 2004 Aug 15. PMID:15311269 doi:10.1038/nsmb811
- ↑ Spronk HM, Borissoff JI, ten Cate H. New insights into modulation of thrombin formation. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2013 Nov;15(11):363. doi: 10.1007/s11883-013-0363-3. PMID:24026641 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11883-013-0363-3
With participation by User:Cody Couperus
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Cody Couperus, Joel L. Sussman