We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
TNF receptor-associated factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
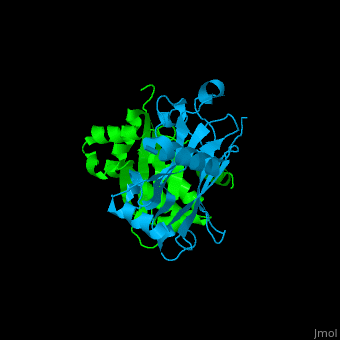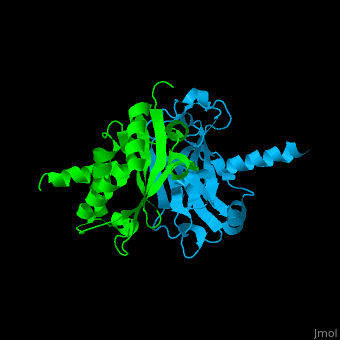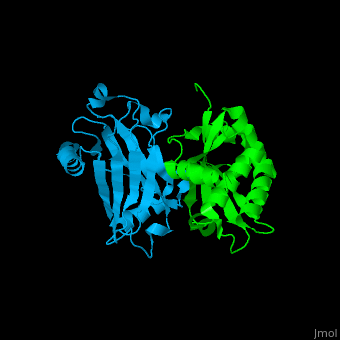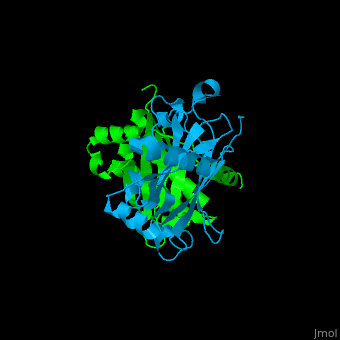
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human TRAF2 TRAF domain (green) complex with TNFR type 1 associated death domain protein TRADD (deepskyblue) (PDB code [[1f3v]])' scene='70/708054/Cv/1'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human TRAF2 TRAF domain (green) complex with TNFR type 1 associated death domain protein TRADD (deepskyblue) (PDB code [[1f3v]])' scene='70/708054/Cv/1'> | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''TNF receptor-associated factor''' (TRAF) are signal transducers and are involved in regulation of apoptosis, inflammation and antiviral response. There are 7 known TRAF proteins. All TRAF proteins share a C-terminal homology region named TRAF domain which can bind the cytoplasmic domain of receptors and other TRAF proteins<ref>PMID:11607847</ref>. '''TRAF1''' is the only TRAF which does not have N-terminal RING and zinc finger motifs. '''TRAF2, TRAF5 and TRAF6''' mediate activation of NF-κB and JNK. '''TRAF3''' mediates some innate immune receptor signals and regulates some post-translational modifications<ref>PMID:22017431</ref>. '''TRAF4''' is a binding partner of glycoproteins in platelets<ref>PMID:20946164</ref>. | '''TNF receptor-associated factor''' (TRAF) are signal transducers and are involved in regulation of apoptosis, inflammation and antiviral response. There are 7 known TRAF proteins. All TRAF proteins share a C-terminal homology region named TRAF domain which can bind the cytoplasmic domain of receptors and other TRAF proteins<ref>PMID:11607847</ref>. '''TRAF1''' is the only TRAF which does not have N-terminal RING and zinc finger motifs. '''TRAF2, TRAF5 and TRAF6''' mediate activation of NF-κB and JNK. '''TRAF3''' mediates some innate immune receptor signals and regulates some post-translational modifications<ref>PMID:22017431</ref>. '''TRAF4''' is a binding partner of glycoproteins in platelets<ref>PMID:20946164</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 08:59, 19 August 2024
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Bradley JR, Pober JS. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). Oncogene. 2001 Oct 1;20(44):6482-91. PMID:11607847 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204788
- ↑ Hildebrand JM, Yi Z, Buchta CM, Poovassery J, Stunz LL, Bishop GA. Roles of tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 3 (TRAF3) and TRAF5 in immune cell functions. Immunol Rev. 2011 Nov;244(1):55-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01055.x. PMID:22017431 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01055.x
- ↑ Arthur JF, Shen Y, Gardiner EE, Coleman L, Murphy D, Kenny D, Andrews RK, Berndt MC. TNF receptor-associated factor 4 (TRAF4) is a novel binding partner of glycoprotein Ib and glycoprotein VI in human platelets. J Thromb Haemost. 2011 Jan;9(1):163-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04091.x. PMID:20946164 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04091.x
- ↑ Park YC, Ye H, Hsia C, Segal D, Rich RL, Liou HC, Myszka DG, Wu H. A novel mechanism of TRAF signaling revealed by structural and functional analyses of the TRADD-TRAF2 interaction. Cell. 2000 Jun 23;101(7):777-87. PMID:10892748