Proteopedia:Featured EDU/7
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <table> <tr><td> <imagemap> Image:1bl8-epm-300pxsq.gif|center default Electrostatic_potential_maps </imagemap> </td></tr> <tr><td><div class="scrolling">'''Make Your Own Electrostatic ...) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<tr><td> | <tr><td> | ||
<imagemap> | <imagemap> | ||
| - | Image: | + | Image:7pmx-y-morph-solid.gif|center |
default [[Electrostatic_potential_maps]] | default [[Electrostatic_potential_maps]] | ||
</imagemap> | </imagemap> | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
| - | <tr><td><div class="scrolling">''' | + | <tr><td><div class="scrolling">'''Transport of Drugs & Nutrients'''<br> |
| - | + | Above is a protein that takes up, into your intestinal cells, orally consumed peptide nutrients and drugs. | |
| - | and | + | Its lumen-face opens and binds |
| - | <b><span class="text- | + | <b><span class="text-magenta">peptide or drug</span></b>, |
| - | + | then closes, while its cytoplasmic face opens to release its | |
| - | + | <b><span class="text-magenta">cargo</span></b> | |
| - | + | into the intestinal cell, and from there into circulating blood. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | >>> [[ | + | >>> [[Drug and peptide transport in humans|See more animations and explanation]] >>> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
Revision as of 01:00, 7 December 2024
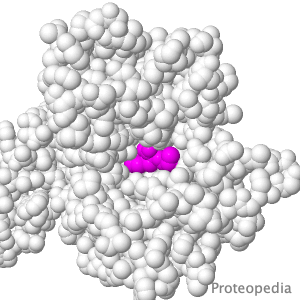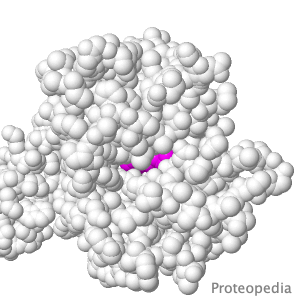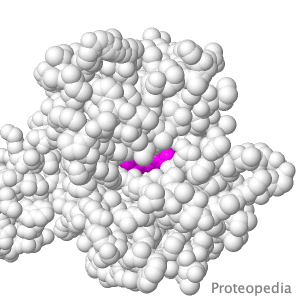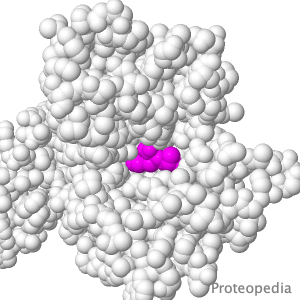
Transport of Drugs & Nutrients
Above is a protein that takes up, into your intestinal cells, orally consumed peptide nutrients and drugs. Its lumen-face opens and binds peptide or drug, then closes, while its cytoplasmic face opens to release its cargo into the intestinal cell, and from there into circulating blood. |