We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
DNA
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
[[Image:DNA grooves.png|200px]] | [[Image:DNA grooves.png|200px]] | ||
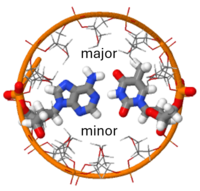
| - | This results in unequally spaced sugar-phosphate backbones and gives rise to <scene name='10/100853/Grooves/2'>two grooves</scene>: the | + | This results in unequally spaced sugar-phosphate backbones and gives rise to <scene name='10/100853/Grooves/2'>two grooves</scene>: the <scene name='DNA/Major_groove/2'>major groove</scene> and the <scene name='DNA/Major_groove/7'>minor groove</scene> of different width and depth. The <scene name='DNA/Major_groove/8'>oxygen atoms of the furanose rings</scene> are on the surface of the minor groove, and the major groove is on the opposite side. The floor or surface of major groove is filled with the <scene name='DNA/Major_floor/2'>atoms of the bases</scene>. The larger size of major groove allows for the binding of DNA specific proteins.<ref name="Saenger"> Saenger, Wolfram (1984). ''Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure '' (1st ed). Springer-Verlag. pp. 398. ISBN 0-12-645750-6.</ref><ref name='Watson'> Watson, James D, Nancy H. Hopkins, Jeffrey W. Roberts, Joan Argetsinger Steitz, Alan M.Weiner ''Molecular Biology of Gene'' (4th ed.). The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company Inc.pp. 239-249. ISBN 0-8053-9612-8</ref> |
| - | <scene name='DNA/Major_groove/2'>major groove</scene> and the <scene name='DNA/Major_groove/7'>minor groove</scene> of different width and depth. The <scene name='DNA/Major_groove/8'>oxygen atoms of the furanose rings</scene> are on the surface of the minor groove, and the major groove is on the opposite side. The floor or surface of major groove is filled with the <scene name='DNA/Major_floor/2'>atoms of the bases</scene>. The larger size of major groove allows for the binding of DNA specific proteins.<ref name="Saenger"> Saenger, Wolfram (1984). ''Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure '' (1st ed). Springer-Verlag. pp. 398. ISBN 0-12-645750-6.</ref><ref name='Watson'> Watson, James D, Nancy H. Hopkins, Jeffrey W. Roberts, Joan Argetsinger Steitz, Alan M.Weiner ''Molecular Biology of Gene'' (4th ed.). The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company Inc.pp. 239-249. ISBN 0-8053-9612-8</ref> | + | |
== Biological Functions == | == Biological Functions == | ||
Revision as of 20:10, 31 March 2025
This page, as it appeared on August 20, 2011, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.
| |||||||||||
See Also
Proteopedia Articles
- Forms of DNA
- Kinks vs. Bends in DNA are discussed in Lac repressor.
- DNA bulges occur when a nucleotide is inserted in one strand but not the other, causing an interruption in base pairing.
- 1ply
- DNA Replication, Repair, and Recombination - Articles in Proteopedia concerning DNA Replication, Repair, and/or Recombination
- DNA Replication,Transcription and Translation
- Z-DNA
- Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA)
- For additional information, see: Nucleic Acids
External Resources
- DNA.MolviZ.Org, an interactive DNA Structure tutorial that is available in nine languages.
- DNA / RNA Section of the Atlas of Macromolecules.
Interpretation of X-Ray Diffraction by DNA
- Anatomy of Photo 51, Rosalind Franklin's diffraction pattern used by Watson & Crick in developing their model of the DNA double helix (at PBS.Org, US Public Broadcasting System).
- Explanation of Franklin's X-Ray Diffraction Pattern at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, USA.
- More technical: How Rosalind Franklin Discovered the Helical Structure of DNA: Experiments in Diffraction.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://www.genome.gov/25520880
- ↑ Dahm R. Discovering DNA: Friedrich Miescher and the early years of nucleic acid research. Hum Genet. 2008 Jan;122(6):565-81. Epub 2007 Sep 28. PMID:17901982 doi:10.1007/s00439-007-0433-0
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Watson J.D. and Crick F.H.C. Nature 171, 737-738 (1953)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Watson, James D, Nancy H. Hopkins, Jeffrey W. Roberts, Joan Argetsinger Steitz, Alan M.Weiner Molecular Biology of Gene (4th ed.). The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company Inc.pp. 239-249. ISBN 0-8053-9612-8
- ↑ SantaLucia J Jr. A unified view of polymer, dumbbell, and oligonucleotide DNA nearest-neighbor thermodynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Feb 17;95(4):1460-5. PMID:9465037
- ↑ Saenger, Wolfram (1984). Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure (1st ed). Springer-Verlag. pp. 398. ISBN 0-12-645750-6.
- ↑ Rawn,David J. "Biochemistry"(1st ed.) Harper&Row,Publishers, Inc.pp. 1024-1050. ISBN-0-06045335-4
- ↑ Maddox, Brenda: Rosalind Franklin: Dark Lady of DNA, HarperCollins, 2002
- ↑ Berman HM, Gelbin A, Westbrook J. Nucleic acid crystallography: a view from the nucleic acid database. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1996;66(3):255-88. PMID:9284453
- ↑ Chandrasekaran R, Arnott S. The structure of B-DNA in oriented fibers. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1996 Jun;13(6):1015-27. PMID:8832384
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Adithya Sagar, Eran Hodis, Ala Jelani, Eric Martz, Wayne Decatur, Karsten Theis, Alexander Berchansky, Karl Oberholser, Joel L. Sussman, Ann Taylor, David Canner, Angel Herraez, Joseph M. Steinberger, Frédéric Dardel