We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox323
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
Research shows that 4Q7Q is a member of the SGNH Hydrolase protein super family. BLAST and InterPro research suggested 4Q7Q best fits this superfamily, and the known conserved residues seen from SPRITE analysis—Serine, Glycine, Asparagine, and Histidine—line up with those observed throughout this family.<ref name="SGNH" /><ref name = "Molgaard">Molgaard, A.; Kauppinen, S.; Larsen, S. Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase elucidates the structure and function of a new family of hydrolases. Struct., 2000, 8(4), 373-383. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969212600001180?via%3Dihub</ref>. Notably, this superfamily is also referred to as the GDSL Hydrolase superfamily.D,E<ref name="SGNH" /><ref name="Molgaard" />. | Research shows that 4Q7Q is a member of the SGNH Hydrolase protein super family. BLAST and InterPro research suggested 4Q7Q best fits this superfamily, and the known conserved residues seen from SPRITE analysis—Serine, Glycine, Asparagine, and Histidine—line up with those observed throughout this family.<ref name="SGNH" /><ref name = "Molgaard">Molgaard, A.; Kauppinen, S.; Larsen, S. Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase elucidates the structure and function of a new family of hydrolases. Struct., 2000, 8(4), 373-383. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969212600001180?via%3Dihub</ref>. Notably, this superfamily is also referred to as the GDSL Hydrolase superfamily.D,E<ref name="SGNH" /><ref name="Molgaard" />. | ||
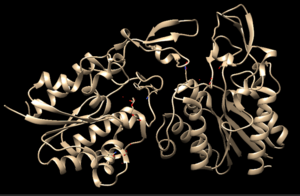
| - | [[Image:4Q7QAChain | + | [[Image:4Q7QAChain.png|300px|right|thumb|Chimera-generated representation of the A chain of 4Q7Q.<ref name="Chimera">UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE. J Comput Chem. 2004 Oct;25(13):1605-12.</ref>]] |
Regarding what protein family 4Q7Q belongs to, DALI results suggest it is a part of a sub-family of the greater GDSL/SGNH superfamily. A PDB90% DALI search labels 4Q7Q as a part of the “Lipolytic Protein G-D-S-L Family,” which refers to enzymes that hydrolyze lipid substrates.<ref name="Akoh">Akoh, C. C.; Lee, G.; Liaw, Y.; Huang, T.; Shaw, J. GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog. Lipid Res., 2004, 43(6), 534-552. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15522763/</ref>. | Regarding what protein family 4Q7Q belongs to, DALI results suggest it is a part of a sub-family of the greater GDSL/SGNH superfamily. A PDB90% DALI search labels 4Q7Q as a part of the “Lipolytic Protein G-D-S-L Family,” which refers to enzymes that hydrolyze lipid substrates.<ref name="Akoh">Akoh, C. C.; Lee, G.; Liaw, Y.; Huang, T.; Shaw, J. GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog. Lipid Res., 2004, 43(6), 534-552. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15522763/</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 20:37, 25 April 2025
4Q7Q Structure and Proposed Functionality
(NOTE TO ALL EDITORS: This page is part of a final project for a biochemistry lab at Elizabethtown College. Please do not edit this.)
4Q7Q is a homodimeric protein complex that originates from the bacterial species Chitinophaga Pinensis and has a mass of 58.5 kDa. It is a member of the SGNH Hydrolase Superfamily with structural and sequential similarities to esterases and lipases. Current evidence suggests it causes the hydrolysis of esters and/or acetyl groups on lipids/lipid-like molecules via a serine protease-like active site.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 4Q7Q. Protein Database, 2014. https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4Q7Q
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Nadzirin, N.; Gardiner, E.; Willett, P.; Artymiuk, P. J.; Firdaus-Raih, M. 2012. SPRITE and ASSAM: web servers for side chain 3D-motif searching in protein structures. Nucleic Acids Res., 40(Web Server Issue), W380-6.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Rio, T. G. D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Chitinophaga pinensis type strain (UQM 2034). Stand. Genomic. Sci., 2010, 2(1), 87-95. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3035255/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 SGNH hydrolase superfamily. InterPro, 2017. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/InterPro/IPR036514/
- ↑ Rio, T. G. D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Chitinophaga pinensis type strain (UQM 2034). Stand. Genomic. Sci., 2010, 2(1), 87-95. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3035255/
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Molgaard, A.; Kauppinen, S.; Larsen, S. Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase elucidates the structure and function of a new family of hydrolases. Struct., 2000, 8(4), 373-383. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969212600001180?via%3Dihub
- ↑ UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE. J Comput Chem. 2004 Oct;25(13):1605-12.
- ↑ Akoh, C. C.; Lee, G.; Liaw, Y.; Huang, T.; Shaw, J. GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog. Lipid Res., 2004, 43(6), 534-552. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15522763/
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Holm L, Laiho A, Toronen P, Salgado M (2023) DALI shines a light on remote homologs: one hundred discoveries. Protein Science 23, e4519