Methods
SPRITE:
The PBD ID for the protein of interest (3B7F) was entered and 2-residue hits excluded. Once the search was complete, "List of Hits" results were obtained. "Full details" result alignments also analyzed. Hits by each side of protein viewed by clicking "Arranged by sites" function. Alignments with an RMSD below 2.0 Angstroms were reviewed.
Chimera:
PBD ID of protein of interest entered and “fetch” was selected in order to show the structure of the protein. Based on the results from SPRITE, the protein of known function was loaded into Chimera using its PBD ID. Everything but the subunit of interest was hidden, and then the active site motif was aligned. The RMSD value was shown and used to determine the quality of alignment (anything below 2.0 Angstroms was considered high quality). To better visualize the alignment, "match" was deleted and replaced with "sel".
Dali:
PDB search tab was selected, and the four-letter PDB of the assigned protein (3B7F) was entered. The structure with the chain identifier was submitted. The job was viewed after completion.
BLAST:
The PDB ID was searched for in the RCSB webpage. "FASTA sequence” was selected and the protein sequence was copied into the NCBI BLAST search page. Proteins similar to the query protein were identified based on sequence.
InterPro:
An InterPro search was performed for the sequence of 3B7F. Protein superfamily identification and domains were reviewed. Related proteins in the domain organization were identified. The structures were also analyzed.
SwissDock:
The "Docking with AutoDock Vina" tab was selected on SwissDock. A ligand by submitted by using SMILES string (found through the PubChem database). "Prepare ligand" was clicked, and a target (can use PDB ID) was submitted. The search space was defined, and x, y, and z coordinates for the center of the space being searched were chosen. The parameters were checked and docking was started. Results were analyzed.
Buffers and Solutions:
General steps for Buffers and solutions included adding 80% of total DiH2O to a container, weighing and adding chemicals, adjusting pH as needed, and adding DiH2O to the total volume.
Hand Casting Polyacrylamide Gels:
Made a 4% stacking gel at a pH of 6.8, and a 10% resolving gel at a pH of 8.8.
Resolving and stacking gel solutions were prepared without APS or TEMED. A comb was placed into the assembled gel sandwich with a marker. A mark was placed on the glass plate 1 cm below the teeth of the comb, and the comb was removed. The APS and TEMED were added to the resolving gel, and the solution was poured to the mark. The gel was allowed to polymerize for 45-60 minutes. APS and TEMED were added to the stacking solution and poured above the resolving gel. The comb was placed in the cassette and tilted so that the teeth are at a 10º angle. This prevented air from becoming trapped under the comb. The gel was allowed to polymerize for 30-45 minutes. The gels were wrapped in a wet paper towel in the 4ºC fridge for storage.
Expression of Proteins from Lactose-Inducible Vectors:
The LB Broth was made by adding 10g of tryptone, 10g of NaCl, and 5g of yeast extract together. This was added to 1000 mL of Millipore water. Five mL of this mixture was poured into an overnight culture tube. The other broth was autoclaved for 1.5 hours.
Protein Purification:
500 mL of the protein was grown rather than 1L in an attempt to speed up induction. The overnights were grown at night on 03/16/2025 for 11 hours with 50 µg/mL of kanamycin. It was inoculated at 8 am on 03/17/2025. OD600 nm was taken in the morning until 0.4-0.8 OD (an OD of 0.4 was reached around 10 am). It was then induced with 1 nM IPTG and left to grow for three hours before centrifuging. In order to purify, the samples were centrifuged at 5000 x g for 20 minutes. Ten mL of lysis buffer was added, and the pellets were resuspended with a pipette (50 µL was added to a separate centrifuge tube). The cells were sonicated 5x for 30 seconds on ice in between each sonication (50 µL of a sample was added to a new centrifuge tube). The samples were centrifuged for 20 minutes at 15,000 x g (50 µL of a sample was added to a new centrifuge tube). The protein column was set up with 500 µL Ni-NTA beads and a lysis buffer was ran through it to equilibrate it (5x column volumes). The resin was pre-washed with a binding buffer. The cell extract was applied to the resin and allowed to enter. All of the supernatant was added (50 µL of a sample was added to a new centrifuge tube). The column was washed with 5 column volumes of buffer (50 µL of a sample was added to a new centrifuge tube). The column was eluted with 8 column volumes of buffer, the fractions were collected in 1 mL volumes and stored in 5 tubes. To store the column, 5 column volumes of water, and 1-2 mL of 20% EtOH were added, and the column was capped off and stored.
Protein Concentration:
Seven BSA standards were prepared using the buffer that the protein was stored in (elution buffer). One mL of Bradford Reagent was added to each cuvette. Twenty µL of water was added to the zero cuvette, while 20 µL of each BSA standard or elution was added to the rest of cuvettes. The cuvettes were covered with parafilm and mixed several times by inversion. They were maintained at room temperature for 5-45 minutes. Absorbance was recorded at 595 nm with a Vernier spectrophotometer. A standard curve was constructed and used to find the concentration of the unknown protein in each elution.
SDS-PAGE:
For sample prep, the protein samples were treated with SDS sample buffer and boiled before application. The final concentration of SDS sample buffer loaded onto the gel was 1x.
The set up was loaded with 1x running buffer. The ladder and samples were then loaded into the lanes (20 µL of samples loaded). The protective cover and cables were attached and connected to the power supply. The gel was run at a constant voltage of 120V. The gel was run until the sample line was about 1 cm from the bottom of the gel.
In order to stain the gel, it was removed from the gel sandwich and gently added to a shallow plastic container. InstantBlue stain was added to cover the gel, and it was agitated overnight. The stain was removed and the destaining solution added. The gel incubated for 30 minutes with a paper towel. It was then rinsed with water and captured on the gel imager.
Protein Activity Assay:
Three mL of buffer and 3 mg of substrate (PNPP or PNPA) were added to a cuvette. It was then placed in the spectrophotometer, and the instrument was zeroed at 405 nm. The desired amount of the protein of interest (25-75 uL) was added, and the solution was mixed quickly. The absorbance at 405 nm was read over time. Measurements were taken every minute until a change was observed, and then measurements were taken every 30 seconds.
Structural Alignment Through SPRITE, Chimera, Dali, and BLAST
Based on the findings through SPRITE and Chimera, 1XNY_C00 had the lowest RMSD value at 1.875 angstroms. Therefore, it is hypothesized that 3B7F was a carboxylase.
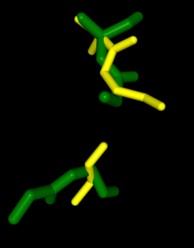
A 183 GLY matches A 207 GLY/
B 419 GLY matches A 154 GLY/
B 420 ALA matches A 153 ALA
Figure 1. SPRITE and Chimera binding of 3B7F (yellow) with 1XNY_C00 (green).
Dali provided mainly xyloglucanase matches and no matches were carboxylases. Therefore, the initial hypothesis that 3B7F was a carboxylase was no longer supported. Based on the Dali results, it is now hypothesized that 3B7F is a xyloglucanase. [2]
Table 1. Top Matches on Dali (Z: greater than 4.0 indicates structural significance; RMSD: root mean square deviation (distance in Angstroms between superimposed molecules); LALI: length of alignment; NRES: number of residues in hit structure; %ID: similarity between hit sequence and query sequence).
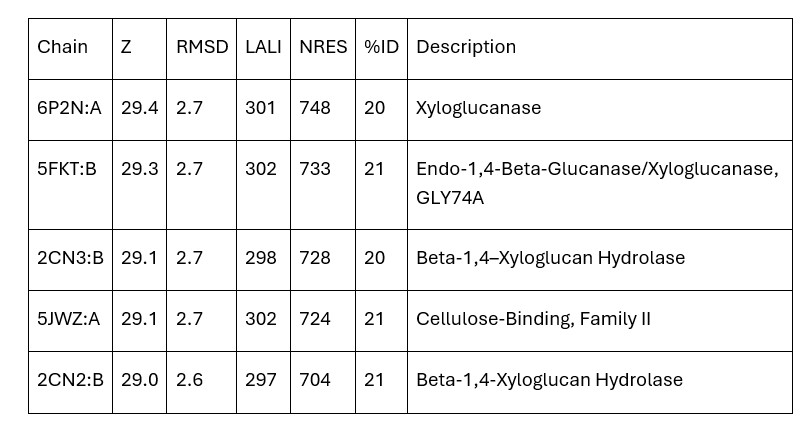

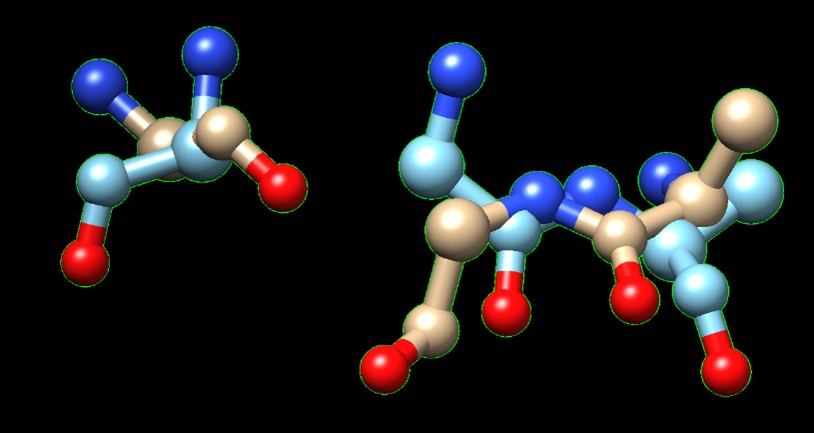
Figure 2. Superimposition of 6P2N:A (orange) and 3B7F (green).
Xyloglucanases break down xyloglucan, a hemicellulose in plant cell walls. The substrate is xyloglucan and water for the (endo-)beta-1,4-xyloglucanases, and a common cofactor is calcium. [3]
The BLAST search shows glycosyl hydrolases having similar sequences to 3B7F. The xyloglucanases/glycosyl hydrolases from the BLAST search come from Cupriavidus, a type of gram-negative bacteria. The E-values were 0.0 for most of the results, signifying high matches. The scores were high as well, with percent identification in the 90 percentage range. The query coverage was also 100% for most of the results. Based on the results, the protein family of 3B7F is likely sialidase, which breaks down sialic acid into carbohydrates. Sialidases are a family of proteins that include glycosyl hydrolases and xyloglucanases, which further supports the hypothesis that 3B7F is a xyloglucanase. [4]
Using InterPro to Predict Protein Function
The family with the closest similarities to 3B7F is xyloglucanase, which matches the BLAST and Dali findings. These enzymes act on xyloglucan, a plant wall polysaccharide, by breaking the glucosidic bonds of unbranched glucose residues. Most of the proteins in this family bind to cell wall structures or participate in photosystem II, which correlates with the expected activity of 3B7F, since it would be acting on plant cell walls. This family consists mainly of bacteria, as well as eukaryotes and archaea. This also matches the BLAST data because it suggested that the sequence was commonly found in bacteria. The proteomes are a lot of bacteria and marine life. The most closely matched structures are different xyloglucanases and oligoxyloglucan reducing end-specific cellobiohydralases, which is the superfamily that the protein belongs to. The main pathways are also structural degradation pathways, which also aligns with the results we have gained so far. [5]
Molecular Docking with SwissDock
Based on the hydrolase ligands that we analyzed, PNP phosphate seems to be the best ligand for 3B7F, with the highest binding affinity of -8.189 kcal/mol, and the lowest binding affinity of -6.146 kcal/mol. This is a very strong binding affinity, so this substrate was used for protein assays. Lysine p nitroanilide also has its highest binding affinity at -7.286 kcal/mol and the lowest binding affinity of -6.551 kcal/mol, indicating that it is another suitable substrate for 3B7F. [6]
Figure 3. 3B7F Binding with PNPP at -8.189 kcal/mol.
Protein Concentration
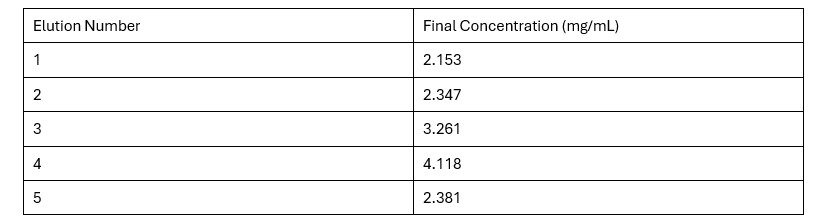
Based on the Bradford Assay, elution 4 had the most protein (4.118 mg/mL), while elution 3 had the second most amount of protein (3.261 mg/mL). The rest of the elutions had protein concentrations around 2 mg/mL. The R² value of the standard curve was 0.9857, indicating fairly accurate results.
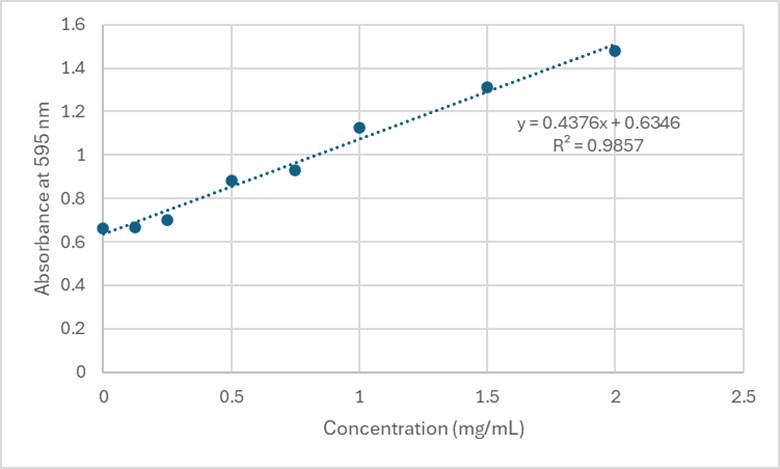
Figure 4. Standard Curve at 595 nm for 3B7F Elutions.
Table 2. Final Protein Concentration of Each Elution
Protein Analysis
Possibly due to errors during purification, no bands were seen on the SDS-PAGE gel for 3B7F.
Several conditions were analyzed through enzyme activity assays. Initially, 50 uL of 3B7F elution 4 with 1 mg/mL PNPP demonstrated some linearity between 0-600 seconds. However, this was not able to be replicated. Both 25 uL and 75 uL of 3B7F elution 4 were also used with PNPP, and no linearity was found. Due to the enzyme’s optimal conditions, it was also cooled down in -20°C for five minutes, however, no linearity was seen. The assay was also perfomed with elution 1 to identify if any protein was present after the wash. Again, no linearity was shown. PNPA was also used as a substrate with elution 4, and pHs of 1.5 and 5.0 were also used during separate trials in order to identify the optimal conditions of the enzyme. [7] However, these assays still showed no linearity. It was determined that there was an error during purification, leading to unidentifiable concentrations of 3B7F for enzymatic study.
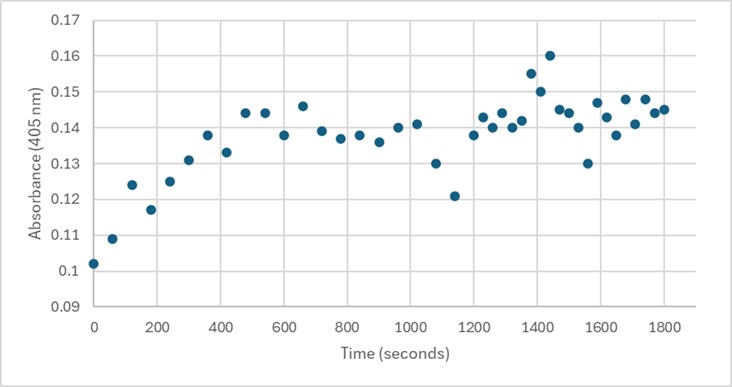
Figure 5. 50 uL of 3B7F Elution 4 with 1 mg/mL PNPP.
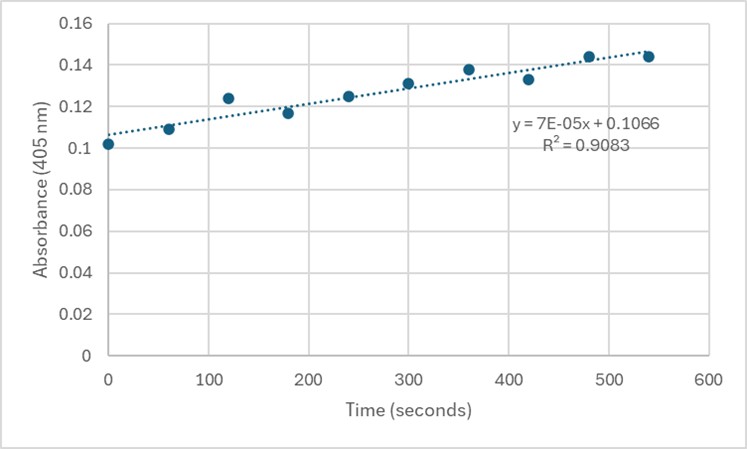
Slope = 7 x 10⁻⁵ Abs/sec
C = 7 x 10⁻⁵/18000*1
= 3.89 x 10⁻⁹ M/sec
Figure 6. Zoom in with linear trendline of Figure 5 and enzyme activity calculations.
Conclusion
Based on the results, no enzymatic function of 3B7F can be appropriately determined. However, based on the computational results, it is likely that 3B7F has xyloglucanase activity. In the future, the protein should be grown again in order to retest the protein’s enzymatic activity after a proper purification. The results that were successfully gathered did show accuracy and precision. However, likely due to incorrect solution making, the protein was not able to be properly purified, and therefore, was not present in the elutions. Interestingly enough, the Bradford Assay did show protein concentrations, but they likely were not for the desired protein (3B7F), which may be the reason for no protein present at the expected mass of approximately 43 kDa. If 3B7F is confirmed as a xyloglucanase, it can possibly be used for drug targeting in the colon through xyloglucan coatings. [8]








