| Function and Background
DNA glycosylases search the entire genome for DNA lesions. These highly selective enzymes recognize a damaged base and remove it. There are four super families: Udg, Nth, Nei, and AGG. DNA glycosylases are used to bind to and excise the base. hNTHL1 or human Endonuclease III (Nth) is a 34 kDa bifunctional DNA glycosylase involved in the base excision repair process. A bifunctional glycosylase refers to the ability of the protein to be able to recognize and excise damaged bases from DNA and cleave the DNA backbone at the abasic site. This enzyme has a preference for oxidized pyrimidines with, Tg (Thymine Glycol) being the preferred substrate. Upon encountering this damaged base, the protein cleaves the N-glycosidic bond, which leaves an apurinic site. From here, the backbone is cleaved via beta elimination, which leaves a 3’ aldehyde and creates a single-strand break. Next, the DNA is handed off to Apurinic endonuclease 1 or polynucleotide kinase, leaving a free 3′ hydroxyl for DNA polymerase β to insert the correct nucleotide. Finally, the nick is sealed by the DNA ligase IIIα. [1][2][3]
The gene encoding hNTHL1 is OCTS3, which is located on chromosome 16. It is widely expressed across tissues, with the highest levels observed in heart tissue. This elevated expression may reflect the heart’s high demand for ATP production, which generates significant oxidative stress and thus increases reliance on base excision repair (BER) proteins for genome maintenance. Additionally, hNTHL1 expression is regulated during the cell cycle, with transcription levels rising during the early and mid S phases. [4] [5] [6]
hNTHL1 has been observed in both the nucleus and mitochondria, meaning that the protein has dual transport signals to repair damaged bases within the nucleus and mitochondria. Green fluorescent protein tagging experiments have shown localization exclusively to the nucleus, whereas studies using antibody tagging have reported presence in both compartments. However, tagging methods have been criticized for potentially disrupting native protein folding, which could lead to incorrect localization. Importantly, nuclear localization signals (NLS) and mitochondrial localization signal (MLS) have been observed around the N-terminal region.[7] [8][9][10]
Mechanims and Repair
First, the DNA is “pinched” by the enzyme, which destabilizes the helix. From here, they use a wedge amino acid to “push” the lesion out of the helix. While the lesion is being flipped out, another amino acid “plugs” into the helix to fill the gap and maintain the structure of the helix. Finally, the lesion is “pulled” into the active site to allow for lesion removal. This has been termed the “pinch, push, plug, and pull” mechanism for base flipping.[11][12][13]
Recent studies have investigated how hNTH1 initiates BER of oxidative lesions in nucleosomes, where DNA is wrapped around a histone core. When lesions are away from the histone core, hNTHL1 processed them with nearly the same efficiency as in naked DNA (without histones). When lesions faced inward toward the histone core, repair was initially poor but improved significantly at higher hNTHL1 concentrations. Additionally, sesions near the edge of the nucleosome were repaired more efficiently than those near the nucleosome center. This suggests that both the partial unwrapping of DNA from the histone core and the positioning of the lesion outward fromthe nucleosome edge allow hNTHL1 to efficiently access and repair DNA lesions. [14]
Structural Highlights
This enzyme hNTHL1 belongs to the HhH (Helix-Hairpin-Helix) superfamily which consists of , which are connected by two linkers. The solved structure of hNTHl1, with the first 63 residues being removed due to disorder, reveals with the iron sulfur cluster, N- and C-termini, and a catalytic resiude (asp). has six helical barrels, hairpin-helix-hairpin, and the final catalytic residue (gly). The motif has a characteristic glycine and proline-rich loop. The HhH allows for hydrogen bond interactions with the DNA backbone. [15][16][17]
This structure is captured in an where the catalytic residues Lys220 and Asp239 are positioned approximately 25 Å apart, which is too far for catalysis. This implies that a conformational change is required to assemble the active site. To find the closed conformation, an engineered chimera was made by swapping the in human NTHL1 with a shorter, more rigid linker from a bacterial homolog. The structure adopts a closed conformation where Lys220 and Asp239 are approximately 5 Å apart, which mimics the configuration seen in catalytically active homologs. The linker is not fully modeled due to disorder in the electron density map. [18]
The role of the is highly debated. One of the views is that the cluster is involved in scanning for lesions. Researchers found that oxidizing the FeS cluster in hNTHL1 from [4Fe-4S]^2+ to [4Fe-4S]^3+ increases its binding to DNA. When a mismatch such as C:A is introduced, this can disrupt DNA charge transport not allowing electrons to travel along the helix. This could stop the reduction of [4Fe-4S]^3+ to [4Fe-4S]^2+ leaving Nth bound until all lesions are removed. Another view is that the FeS cluster plays a role as a structural scaffold to stabilize the interaction of the protein with the DNA. A Cys-Xaa6-Cys-Xaa2-Cys-Xaa5-Cys binds the iron/sulfur cluster. [19][20][21][22]
The function of the (AlphaFold Prediction) of hNHTL1 has been a subject of study [23][24]. It is theorized that the N-terminus, which is extended compared to homologs, functions as a means to remain bound to DNA, protecting the labile abasic site while waiting for its handoff with APE1. This was found through truncation of the N-terminal region (residues 1-96), which revealed that deletion of 55, 75, or 80 residues from the N-terminus resulted in a four to fivefold increase in catalytic activity. The rate-limiting step in hNTHL1's reaction is the release of the free 3’ aldehyde. [25]
Notability, the first 63 residues were not modeled within the structure of hNHTL1 which is due to disorder. This can be observed under a PONDR prediction.
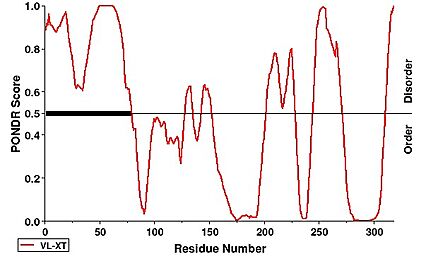 [26] [26]
Additionally, several motifs are present within the extended N-terminus of hNTHL1. A bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS) spans residues 28–52, while an overlaping region of basic and acidic residues range from residues 23–42. Two additional NLS motifs, characterized by clusters of basic residues, are located at residues 48–56 and 90–100. A mitochondrial localization signal (MLS) is also predicted at residues 1–16. These signals were identified using the PSORTII algorithm. [27][28][29]
Disease
When the base excision repair pathway is compromised, this leads to limitations in enzymes to repair damaged DNA. This turns into mutations throughout the genome, leading to the progression of cancer. NTHL1-Tumor Syndrome is a disease caused by variants affecting the gene, being diagnosed with the germline biallelic pathogenic variant, through molecular genetic testing renders the glycosylase inactive. When this is the case, one's cumulative lifetime risk of developing extracolonic cancer by age 60 is 45-78%. Oftentimes, this syndrome is characterized by an increased risk of colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and colorectal polyposis. Around 5% of colorectal cancers can be explained by germline mutations within a CRC predisposing gene. Exome sequencing has led to the identification of a homozygous nonsense mutation (c.268C>T encoding p.Q90*) in the base excision repair gene NTHL1 in three unrelated families.[30][31][32]
A functional non-mutated version of hNTHL1 can additionally play a role in cancer cell survival. In triple-negative breast cancer, BCL11A, a protein, is frequently overexpressed. BCL11A is a transcription factor shown to stimulate hNTHL1 activity, enhancing base excision repair (BER) and enabling cancer cells to proliferate in high levels of oxidative DNA damage. Separately, Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) is overexpressed in tumor cells, and hNTHL1 can be activated through direct interaction with YB-1. This boosts its ability to process oxidized bases. This YB–1–mediated stimulation of hNTHL1 causes resistance to cisplatin, a form of chemotherapy, allowing for cancer proliferation. [33][34]
References
- ↑ Carroll BL, Zahn KE, Hanley JP, Wallace SS, Dragon JA, Doublié S. Caught in motion: human NTHL1 undergoes interdomain rearrangement necessary for catalysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Dec 16;49(22):13165-13178. PMID:34871433 doi:10.1093/nar/gkab1162
- ↑ Odell ID, Newick K, Heintz NH, Wallace SS, Pederson DS. Non-specific DNA binding interferes with the efficient excision of oxidative lesions from chromatin by the human DNA glycosylase, NEIL1. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Feb 4;9(2):134-43. PMID:20005182 doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.11.005
- ↑ Cappelli E, Taylor R, Cevasco M, Abbondandolo A, Caldecott K, Frosina G. Involvement of XRCC1 and DNA ligase III gene products in DNA base excision repair. J Biol Chem. 1997 Sep 19;272(38):23970-5. PMID:9295348 doi:10.1074/jbc.272.38.23970
- ↑ https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P78549/entry
- ↑ Aspinwall R, Rothwell DG, Roldan-Arjona T, Anselmino C, Ward CJ, Cheadle JP, Sampson JR, Lindahl T, Harris PC, Hickson ID. Cloning and characterization of a functional human homolog of Escherichia coli endonuclease III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jan 7;94(1):109-14. PMID:8990169 doi:10.1073/pnas.94.1.109
- ↑ Luna L, Bjørås M, Hoff E, Rognes T, Seeberg E. Cell-cycle regulation, intracellular sorting and induced overexpression of the human NTH1 DNA glycosylase involved in removal of formamidopyrimidine residues from DNA. Mutat Res. 2000 Jul 25;460(2):95-104. PMID:10882850 doi:10.1016/s0921-8777(00)00015-x
- ↑ https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P78549/entry
- ↑ Luna L, Bjørås M, Hoff E, Rognes T, Seeberg E. Cell-cycle regulation, intracellular sorting and induced overexpression of the human NTH1 DNA glycosylase involved in removal of formamidopyrimidine residues from DNA. Mutat Res. 2000 Jul 25;460(2):95-104. PMID:10882850 doi:10.1016/s0921-8777(00)00015-x
- ↑ Ikeda S, Biswas T, Roy R, Izumi T, Boldogh I, Kurosky A, Sarker AH, Seki S, Mitra S. Purification and characterization of human NTH1, a homolog of Escherichia coli endonuclease III. Direct identification of Lys-212 as the active nucleophilic residue. J Biol Chem. 1998 Aug 21;273(34):21585-93. PMID:9705289 doi:10.1074/jbc.273.34.21585
- ↑ Nakai K, Kanehisa M. A knowledge base for predicting protein localization sites in eukaryotic cells. Genomics. 1992 Dec;14(4):897-911. PMID:1478671 doi:10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80111-9
- ↑ https://scholarworks.uvm.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2160&context=graddis
- ↑ Friedman JI, Stivers JT. Detection of damaged DNA bases by DNA glycosylase enzymes. Biochemistry. 2010 Jun 22;49(24):4957-67. PMID:20469926 doi:10.1021/bi100593a
- ↑ Jiang YL, Stivers JT. Mutational analysis of the base-flipping mechanism of uracil DNA glycosylase. Biochemistry. 2002 Sep 17;41(37):11236-47. PMID:12220189 doi:10.1021/bi026226r
- ↑ Prasad A, Wallace SS, Pederson DS. Initiation of base excision repair of oxidative lesions in nucleosomes by the human, bifunctional DNA glycosylase NTH1. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;27(24):8442-53. PMID:17923696 doi:10.1128/MCB.00791-07
- ↑ Fromme JC, Verdine GL. Structure of a trapped endonuclease III-DNA covalent intermediate. EMBO J. 2003 Jul 1;22(13):3461-71. PMID:12840008 doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg311
- ↑ https://scholarworks.uvm.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2160&context=graddis
- ↑ Fellbaum C, Sträter J, Hansmann ML, Fischer R. [Follicular dendritic cells in extranodal non-Hodgkin's lymphomas]. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1992;76:213-8 PMID:1283262
- ↑ Carroll BL, Zahn KE, Hanley JP, Wallace SS, Dragon JA, Doublié S. Caught in motion: human NTHL1 undergoes interdomain rearrangement necessary for catalysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Dec 16;49(22):13165-13178. PMID:34871433 doi:10.1093/nar/gkab1162
- ↑ Boal AK, Genereux JC, Sontz PA, Gralnick JA, Newman DK, Barton JK. Redox signaling between DNA repair proteins for efficient lesion detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 8;106(36):15237-42. PMID:19720997 doi:10.1073/pnas.0908059106
- ↑ Tse ECM, Zwang TJ, Barton JK. The Oxidation State of [4Fe4S] Clusters Modulates the DNA-Binding Affinity of DNA Repair Proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 2017 Sep 13;139(36):12784-12792. PMID:28817778 doi:10.1021/jacs.7b07230
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/https
- ↑ Aspinwall R, Rothwell DG, Roldan-Arjona T, Anselmino C, Ward CJ, Cheadle JP, Sampson JR, Lindahl T, Harris PC, Hickson ID. Cloning and characterization of a functional human homolog of Escherichia coli endonuclease III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jan 7;94(1):109-14. PMID:8990169 doi:10.1073/pnas.94.1.109
- ↑ https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-03819-2/
- ↑ Varadi M, Bertoni D, Magana P, Paramval U, Pidruchna I, Radhakrishnan M, Tsenkov M, Nair S, Mirdita M, Yeo J, Kovalevskiy O, Tunyasuvunakool K, Laydon A, Žídek A, Tomlinson H, Hariharan D, Abrahamson J, Green T, Jumper J, Birney E, Steinegger M, Hassabis D, Velankar S. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database in 2024: providing structure coverage for over 214 million protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 5;52(D1):D368-D375. PMID:37933859 doi:10.1093/nar/gkad1011
- ↑ Liu X, Roy R. Truncation of amino-terminal tail stimulates activity of human endonuclease III (hNTH1). J Mol Biol. 2002 Aug 9;321(2):265-76. PMID:12144783 doi:10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00623-x
- ↑ https://www.pondr.com/
- ↑ https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P78549/entry
- ↑ Luna L, Bjørås M, Hoff E, Rognes T, Seeberg E. Cell-cycle regulation, intracellular sorting and induced overexpression of the human NTH1 DNA glycosylase involved in removal of formamidopyrimidine residues from DNA. Mutat Res. 2000 Jul 25;460(2):95-104. PMID:10882850 doi:10.1016/s0921-8777(00)00015-x
- ↑ Nakai K, Kanehisa M. A knowledge base for predicting protein localization sites in eukaryotic cells. Genomics. 1992 Dec;14(4):897-911. PMID:1478671 doi:10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80111-9
- ↑ De Voer RM, Nielsen M, Gao W, Kuiper RP, Hoogerbrugge N. NTHL1 Tumor Syndrome. PMID:32239880
- ↑ Weren RD, Ligtenberg MJ, Kets CM, de Voer RM, Verwiel ET, Spruijt L, van Zelst-Stams WA, Jongmans MC, Gilissen C, Hehir-Kwa JY, Hoischen A, Shendure J, Boyle EA, Kamping EJ, Nagtegaal ID, Tops BB, Nagengast FM, Geurts van Kessel A, van Krieken JH, Kuiper RP, Hoogerbrugge N. A germline homozygous mutation in the base-excision repair gene NTHL1 causes adenomatous polyposis and colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 2015 Jun;47(6):668-71. PMID:25938944 doi:10.1038/ng.3287
- ↑ PMID:https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NTH_HUMAN NTH_HUMAN
- ↑ Vickridge E, Faraco CCF, Tehrani PS, Ramdzan ZM, Rahimian H, Leduy L, Gingras AC, Nepveu A. The DNA repair function of BCL11A suppresses senescence and promotes continued proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer cells. NAR Cancer. 2022 Sep 28;4(4):zcac028. PMID:36186110 doi:10.1093/narcan/zcac028
- ↑ Guay D, Garand C, Reddy S, Schmutte C, Lebel M. The human endonuclease III enzyme is a relevant target to potentiate cisplatin cytotoxicity in Y-box-binding protein-1 overexpressing tumor cells. Cancer Sci. 2008 Apr;99(4):762-9. PMID:18307537 doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00739.x
|

