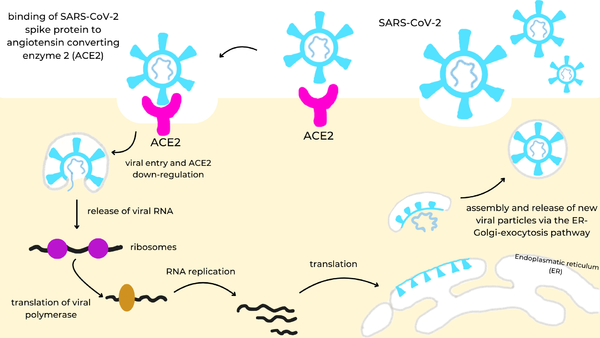
We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Carson Powers/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
===''Receptor Binding Domains''=== | ===''Receptor Binding Domains''=== | ||
| - | The spike protein | + | The spike protein contains three Receptor Binding Domains <scene name='10/1076042/Overallspikelabeledrbds/2'>(RBDs)</scene>, containing the binding site (one per chain). A <scene name='10/1076041/Spike_protein_only/3'>closer look</scene> at the RBDs reveal a mostly beta-sheet secondary structure with a handful of helices scattered about. There are also a couple variable loops where a number of interactions take place as well. These interactions are specific to the binding ligand and will be talked about in depth later. |
=ACE2 Receptor= | =ACE2 Receptor= | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
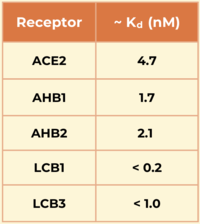
Another mini protein inhibitor, <scene name='10/1076041/Lcb3_only/3'>LCB3,</scene> was developed using the same computational method as LCB1 and binds to the same region of the RBD, except in the opposite direction. Its <scene name='10/1076041/Lcb3xspikecorlabel_intxn/1'>binding interactions</scene> also show a large number of hydrogen bonds. However, LCB1 has more surface area and fits more precisely with its computational model, giving it a slightly higher binding affinity. [[Image:Kd_table.png|200px|right|Table 1. Dissociation constants (Kd) in nM for SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD binding to ACE2 and engineered minibinders, measured by biolayer interferometry to compare affinities for the spike protein.]] | Another mini protein inhibitor, <scene name='10/1076041/Lcb3_only/3'>LCB3,</scene> was developed using the same computational method as LCB1 and binds to the same region of the RBD, except in the opposite direction. Its <scene name='10/1076041/Lcb3xspikecorlabel_intxn/1'>binding interactions</scene> also show a large number of hydrogen bonds. However, LCB1 has more surface area and fits more precisely with its computational model, giving it a slightly higher binding affinity. [[Image:Kd_table.png|200px|right|Table 1. Dissociation constants (Kd) in nM for SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD binding to ACE2 and engineered minibinders, measured by biolayer interferometry to compare affinities for the spike protein.]] | ||
| - | + | =Significance= | |
The designed mini protein inhibitors have a significantly higher affinity for the spike protein compared to the ACE2 receptor, especially the LCBs. The LCBs have a significantly higher affinity for the spike RBD and are smaller and more stable than traditional antibodies. Their reduced size allows these molecules to tightly pack more interactions in the active site as well as improve their ability to enter the respiratory system. | The designed mini protein inhibitors have a significantly higher affinity for the spike protein compared to the ACE2 receptor, especially the LCBs. The LCBs have a significantly higher affinity for the spike RBD and are smaller and more stable than traditional antibodies. Their reduced size allows these molecules to tightly pack more interactions in the active site as well as improve their ability to enter the respiratory system. | ||
| - | + | = Function = | |
<ref name="Ransey">PMID:28504306</ref> | <ref name="Ransey">PMID:28504306</ref> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
| - | + | =Therapeutic Relevance = | |
<ref name="Ransey"/> | <ref name="Ransey"/> | ||
Revision as of 21:31, 27 April 2025
De Novo Miniprotein COVID-19 Therapeutic
| |||||||||||