Sandbox323
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
=== General Structure and Origins === | === General Structure and Origins === | ||
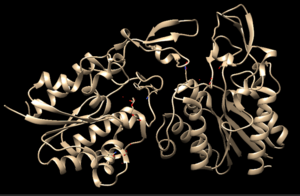
| - | 4Q7Q exists as a homodimer Quaternary structure.<ref name="Sequence">4Q7Q. Protein Database, 2014. https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4Q7Q</ref> Analyzing primary and Quaternary structures of 4Q7Q with SPRITE revealed two chains identical in both shape and sequence<ref name="SPRITE">Nadzirin, N.; Gardiner, E.; Willett, P.; Artymiuk, P. J.; Firdaus-Raih, M. 2012. SPRITE and ASSAM: web servers for side chain 3D-motif searching in protein structures. Nucleic Acids Res., 40(Web Server Issue), W380-6.</ref> Each chain is 266 residues long, and the entire complex has a molecular weight of approximately 58.5 kDa.<ref name="Sequence" /> | + | 4Q7Q exists as a homodimer Quaternary structure.<ref name="Sequence">4Q7Q. Protein Database, 2014. https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4Q7Q</ref> Analyzing primary and Quaternary structures of 4Q7Q with SPRITE revealed two chains identical in both shape and sequence<ref name="SPRITE">Nadzirin, N.; Gardiner, E.; Willett, P.; Artymiuk, P. J.; Firdaus-Raih, M. 2012. SPRITE and ASSAM: web servers for side chain 3D-motif searching in protein structures. Nucleic Acids Res., 40(Web Server Issue), W380-6.</ref> Each chain is 266 residues long, and the entire complex has a molecular weight of approximately 58.5 kDa.<ref name="Sequence" /> |
[[Image:4Q7QABSequence.png|400px|left|thumb| Primary Sequences of the A and B chains of 4Q7Q.<ref name="SPRITE" />.]] | [[Image:4Q7QABSequence.png|400px|left|thumb| Primary Sequences of the A and B chains of 4Q7Q.<ref name="SPRITE" />.]] | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
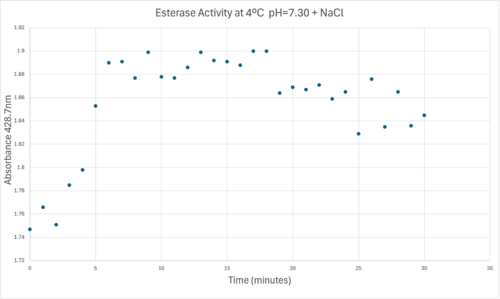
50uL of purified protein from the first elution was added to 3mL of cold 1mg/mL PNPA. Solid sodium chloride was added to achieve a final concentration of 5mM NaCl. The absorbance peak was measured every 60 seconds for 30 minutes. Peak maximum was located at 427.8nm. The sample incubated in an ice bath between measurements. No discernible relationship between time and absorbance was noted. pH of the solution was 10.60. The instrument to measure pH was Vernier Lab Quest 3 with Tris-compatible flat pH sensor calibrated with two points. Theorizing the enzyme would increase activity at the physiological pH of common prokaryotes, we lowered the pH with 2M HCl. 2M NaOH was used to raise the pH due to the weak buffering capacity of the PNPA solution near pH 7. Final pH of the 1mg/mL PNPA solution was 7.30 | 50uL of purified protein from the first elution was added to 3mL of cold 1mg/mL PNPA. Solid sodium chloride was added to achieve a final concentration of 5mM NaCl. The absorbance peak was measured every 60 seconds for 30 minutes. Peak maximum was located at 427.8nm. The sample incubated in an ice bath between measurements. No discernible relationship between time and absorbance was noted. pH of the solution was 10.60. The instrument to measure pH was Vernier Lab Quest 3 with Tris-compatible flat pH sensor calibrated with two points. Theorizing the enzyme would increase activity at the physiological pH of common prokaryotes, we lowered the pH with 2M HCl. 2M NaOH was used to raise the pH due to the weak buffering capacity of the PNPA solution near pH 7. Final pH of the 1mg/mL PNPA solution was 7.30 | ||
| - | [[Image:Absorbancelongph7cold.png| | + | [[Image:Absorbancelongph7cold.png|500px|left|]] |
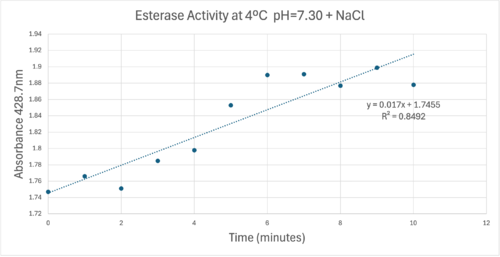
50uL of purified protein from the first elution was added to 3mL of cold 1mg/mL PNPA at pH=7.30. Chloride ion cofactor was provided by the 2M HCl. A change in absorbance at 428.7nm over time was noted. The time range of the run did not produce a linear response. The absorbance increased for the first ten minutes and plateaued. The time 0 to 10 minutes was used to create the third figure with a more refined linear range. | 50uL of purified protein from the first elution was added to 3mL of cold 1mg/mL PNPA at pH=7.30. Chloride ion cofactor was provided by the 2M HCl. A change in absorbance at 428.7nm over time was noted. The time range of the run did not produce a linear response. The absorbance increased for the first ten minutes and plateaued. The time 0 to 10 minutes was used to create the third figure with a more refined linear range. | ||
| - | [[Image:Absorbancecoldph7try.png| | + | [[Image:Absorbancecoldph7try.png|500px|left|]] |
A linear equation of y=9.275x10^-7x+1x10^-4 with a coefficient of determination of 0.8492 was calculated using linear regression. | A linear equation of y=9.275x10^-7x+1x10^-4 with a coefficient of determination of 0.8492 was calculated using linear regression. | ||
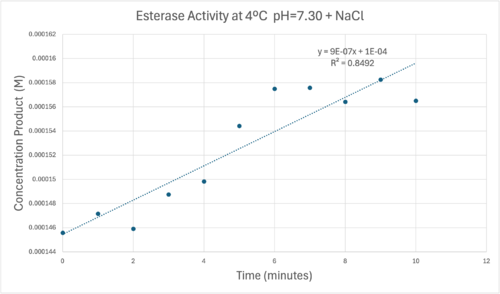
| - | [[Image:Concentrationcoldmolarabsorb12000ph7.png| | + | [[Image:Concentrationcoldmolarabsorb12000ph7.png|500px|left|]] |
Absorbance values can be transformed to units of concentration via the Beer-Lambert law. We must accept the approximation of the Molar Extinction Coefficient for PNPA hydrolysis at 428.7nm as 12000 M^-1 cm^-1. An example calculation is supplied in the table. | Absorbance values can be transformed to units of concentration via the Beer-Lambert law. We must accept the approximation of the Molar Extinction Coefficient for PNPA hydrolysis at 428.7nm as 12000 M^-1 cm^-1. An example calculation is supplied in the table. | ||
| - | [[Image:Tablebeerlaw.png| | + | [[Image:Tablebeerlaw.png|500px|left|]] |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 12:57, 28 April 2025
4Q7Q Structure and Proposed Functionality
(NOTE TO ALL EDITORS: This page is part of a final project for a biochemistry lab at Elizabethtown College. Please do not edit this. -Neil Divins)
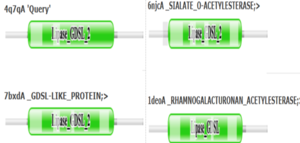
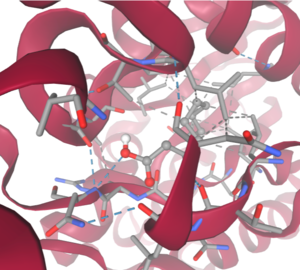
4Q7Q is a homodimeric protein complex that originates from the bacterial species Chitinophaga Pinensis and has a mass of 58.5 kDa. It is a member of the SGNH Hydrolase Superfamily with structural and sequential similarities to esterases and lipases. Current evidence suggests it causes the hydrolysis of esters and/or acetyl groups on lipids/lipid-like molecules via a catalytic triad-like active site.
| |||||||||||