Overview
General Structure and Origins
4Q7Q exists as a homodimer Quaternary structure.[1] Analyzing primary and Quaternary structures of 4Q7Q with SPRITE revealed two chains identical in both shape and sequence[2] Each chain is 266 residues long, and the entire complex has a molecular weight of approximately 58.5 kDa.[1]

Primary Sequences of the A and B chains of 4Q7Q.
[2].
4Q7Q proteins primarily appear in bacterial species.[3]. Research reveals how nearly every enzyme with similar sequencing to 4Q7Q is found in bacterium, with a slight exception to eukaryotes.[4] Additionally, the PDB entry for 4Q7Q notes how it potentially can be found in Chitinophaga pinensis, a gram-negative bacterial species which can degrade chitin.[3].[5].
Family and Superfamily
Research shows that 4Q7Q is a member of the SGNH Hydrolase protein super family. BLAST and InterPro research suggested 4Q7Q best fits this superfamily, and the known conserved residues seen from SPRITE analysis—Serine, Glycine, Asparagine, and Histidine—line up with those observed throughout this family.[4][6]. Notably, this superfamily is also referred to as the GDSL Hydrolase superfamily.[4][6].
Chimera-generated representation of the A chain of 4Q7Q.
[7]Regarding what protein family 4Q7Q belongs to, DALI results suggest it is a part of a sub-family of the greater GDSL/SGNH superfamily. A PDB90% DALI search labels 4Q7Q as a part of the “Lipolytic Protein G-D-S-L Family,” which refers to enzymes that hydrolyze lipid substrates.[8].
Structure/Sequence Analysis
Sequence Analysis
The primary sequence of 4Q7Q shows several conserved sequences between it and esterase-like proteins. A sequence of GDSI—similar to the GDSL sequence seen from its family and superfamily—can be seen between 4Q7Q and enzymes like Isoamyl Acetate-Hydrolyzing Esterase when using DALI.[9]. Other noteworthy conserved sequences between esterases and 4Q7Q include GxND and DGxH.[9].
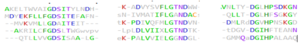
Conserved sequences of note between 4Q7Q and Esterases.
[9].
These enzymes also share similar secondary structures. Segments of alpha-helixes and beta-sheet strands appear and remain nearly entirely conserved throughout esterase analysis. A few conserved coils appear, but these sections do not appear as often as the other two secondary structures.

Conserved secondary structures of note between 4Q7Q and Esterases.
[9].
Similar conserved sequences could be found between 4Q7Q and lipases. The GDSI, GxND, and DGxH sequences can be seen from lipases like 7BXD.[9] The same secondary structure segments can also be located in the lipases analyzed.
Structural Analysis
Right-hand SPRITE analysis revealed 4Q7Q exhibited residues like those seen from enzymes operating with acetyl-like substrates.[2] Specifically, residues Ser. 30, Gly. 69, Asn. 97, Asp. 251, and His. 254 on the A and B chains of 4Q7Q line up with similarly positioned residues on esterases like Platelet-Activating Factor Acetylhyd (PAFA), which exhibited an RMSD of 0.25 angstroms when compared to 4Q7Q.[2]
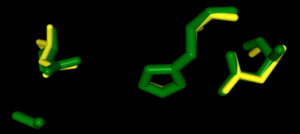
SPRITE-based alignment between motifs from 4Q7Q and PAFA.
[2].
Other proteins with similar motifs of note are Thioesterase I and Rhamnogalacturonan Acetylesterase, with RMSD values of 0.46 and 0.61, respectively.[2][6] These alignments focus on the same active site as PAFA did, suggesting the acetyl-like substrates 4Q7Q focuses on are similar to esters.
PFAM graphics from DALI revealed significant structural equivalence between 4Q7Q, a lipase-like protein, Rhamnogalacturonan Acetylesterase, and Sialate O-acetylesterase.[9]
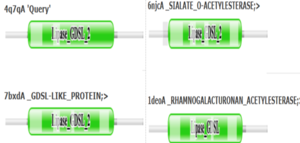
Pfam similarities between 4Q7Q and other enzymes.
[9].
4Q7Q’s superfamily also supports its SPRITE-derived hypothetical functionality. Rhamnogalacturonan Acetylesterase—the enzyme with one of the best SPRITE-based alignment relative to 4Q7Q—is a member of this family.[6][2] Proteins in this family are also known for containing a “unique hydrogen bond network that [stabilizes]” the active site.[2]
Proposed Functionality
Substrates and Docking Analysis
SwissDock analysis showed a preference for larger molecules, specifically fatty acids. Lactide, Ethyl Butyrate, and Triethylene Glycol exhibited noticeably weak binding affinities to the theorized active site of 4Q7Q. [10][11][12][13] These ligands may be ill-suited to act as substrates for 4Q7Q as they are remarkably polar, and lipids—one of the potential categories of substrates for 4Q7Q—are mostly non-polar.[10][11][12][13]
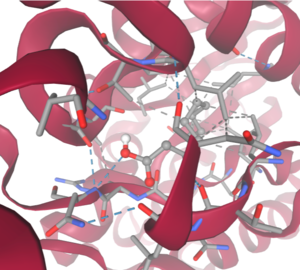
SwissDock-based analysis of the intermolecular interactions between Decanoate and 4Q7Q's proposed active site
[10][11][12][13]Despite this, these ligands show noticeable hydrophobic interactions with the active site. This implies 4Q7Q uses hydrophobic regions to help guide substrates into the right orientation for enzymatic processes. This also further supports the possibility that 4Q7Q primarily operates with hydrophobic lipid-based substrates. This also explains why Methyl Acetate exhibited a relatively weaker affinity for 4Q7Q, as its smaller structure prevented hydrophobic interactions.
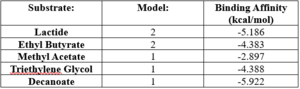
SwissDock-based analysis of the intermolecular interactions between Decanoate and 4Q7Q's proposed active site
[10][11][12][13] Hypothetical Function
Taking all of the above evidence into consideration, we currently believe 4Q7Q is an enzyme responsible for the hydrolysis of lipid esters and/or fatty acids via a catalytic triad active site. This may suggest 4Q7Q plays an important role in providing energy to the body in a method similar to the beta-oxidation of fatty acids [14] Other studies suggest that the hydrolysis of fatty acids could be involved in fermentation-related processes or even the degradation of aryl lipid esters.[15][5]
We also believe 4Q7Q undergoes several significant structural changes during enzymatic activities. Analysis into other members of its family reveal mechanisms wherein serine and histidine residues shift during substrate binding. [5] Specifically, the mechanism of note is similar to the ester hydrolysis or formation of lipases and esterases and is composed of four steps: First, the substrate is bound to the active serine, yielding a tetrahedral intermediate stabilized by the catalytic His and Asp residues. Next, the alcohol is released and an acyl–enzyme complex is formed. Attack of a nucleophile (water in hydrolysis) forms again a tetrahedral intermediate, which after resolution yields the product and free enzyme.[16] The residues involved with this catalytic mechanism are also similar to the residues located in the motif of note from SPRITE analysis.[2][16]
Experimental Data
Bacterium
Chitinophaga pinensis is an obligate aerobe, spore-forming, psychrophilic bacterium that was isolated from pine litter. Bacterium actively grows in pH 7 to 10 media with pH 7 being ideal.[17]
Substrate and Hydrolysis of Substrate
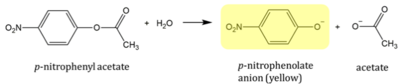
p-nitrophenyl acetate (PNPA) is an aromatic compound with an ester linkage. PNPA supplied by ThermoScientific 97% pure CAS: 830-03-5. In the presence of an esterase, the compound is susceptible to cleavage. The products are acetate and p-nitrophenolate anion (PNP). PNP is yellow in color so reaction progress can be monitored by measuring the absorption peak at 405nm using a spectrophotometer.[18]
Spectrophotometry
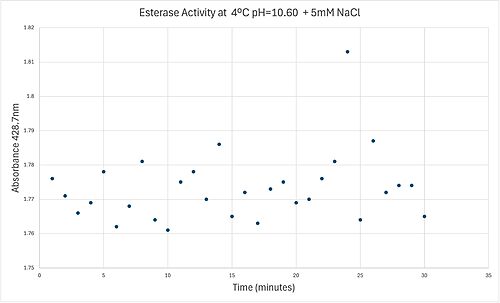
4 degrees C reaction under basic conditions
50uL of purified protein from the first elution was added to 3mL of cold 1mg/mL PNPA. Solid sodium chloride was added to achieve a final concentration of 5mM NaCl. The absorbance peak was measured every 60 seconds for 30 minutes via a Vernier Go Direct SpectroVis Plus Spectrophotometer. Peak maximum was located at 427.8nm. The sample incubated in an ice bath between measurements. No discernible relationship between time and absorbance was noted. pH of the solution was 10.60. The instrument to measure pH was Vernier Lab Quest 3 with Tris-compatible flat pH sensor calibrated with two points. Theorizing the enzyme would increase activity at the physiological pH of common prokaryotes, we lowered the pH with 2M HCl. 2M NaOH was used to raise the pH due to the weak buffering capacity of the PNPA solution near pH 7. Final pH of the 1mg/mL PNPA solution was 7.30
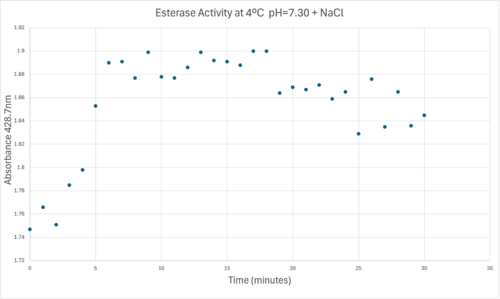
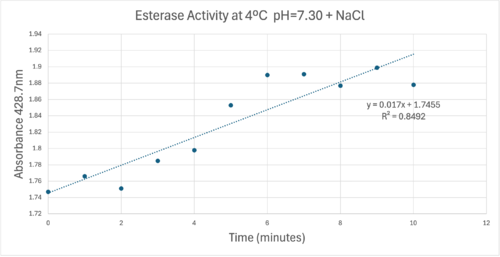
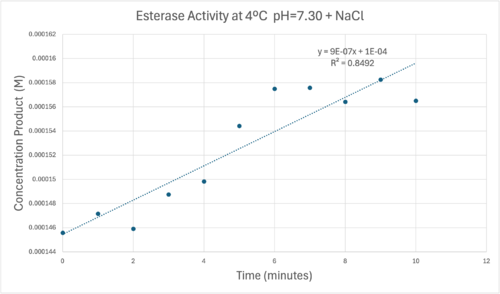
50uL of purified protein from the first elution was added to 3mL of cold 1mg/mL PNPA at pH=7.30. Chloride ion cofactor was provided by the 2M HCl. A change in absorbance at 428.7nm over time was noted. The time range of the run did not produce a linear response. The absorbance increased for the first ten minutes and plateaued. The time 0 to 10 minutes was used to create the third figure with a more refined linear range.
A linear equation of y=9.275x10^-7x+1x10^-4 with a coefficient of determination of 0.8492 was calculated using linear regression.

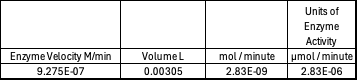
Beer-Lambert Law sample calculation
Absorbance values can be transformed to units of concentration via the Beer-Lambert law. We must accept the approximation of the Molar Extinction Coefficient for PNPA hydrolysis at 428.7nm as 12000 M^-1 cm^-1. An example calculation is supplied in the table. Graphing time versus concentration and determining the slope of the line yields the enzyme's velocity in M/min. 1mg/mL of PNPA is saturating conditions which implies the Vmax is also the slope. The reaction volume total times Vmax yields Units of Enzyme Activity. This value can be used as a relative comparison tool for enzyme performance in given conditions.
Enzyme Activity at neutral pH at cold temperature with Chloride cofactor
The cold 4 degrees C reaction was changed to room temperature 20 degrees C. All other conditions remained constant to evaluate the effect of temperature on enzyme. Temperature increase negatively affects enzyme performance. Considering the cold loving nature of Chitinophaga pinensis, the enzyme being more active at a lower temperature is a reasonable conclusion.
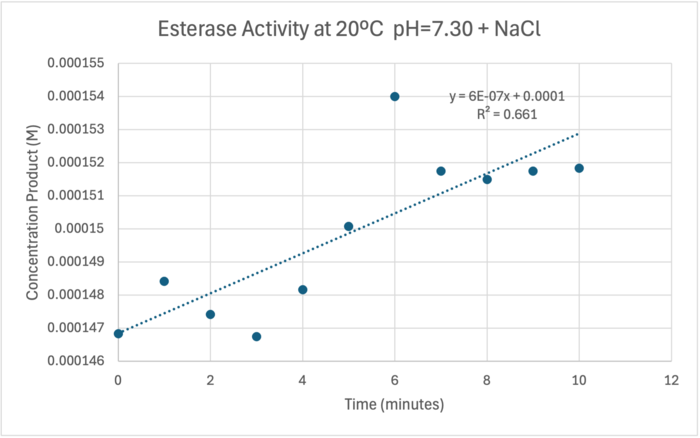
Enzyme Activity at neutral pH at room temperature with Chloride cofactor
Enzyme Activity at neutral pH at room temperature with Chloride cofactor
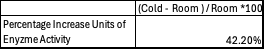
4 degrees C yields 42.2% increase in Units of Enzyme Activity цmol/minute
Discussion and Conclusion
42.2% increase in units of enzyme activity was a considerable gain. No replicates were done for this study. A future experiment would include replicates so t-test can be run to determine significance of the increase. Overall the temperature decrease had an effect on the conversion of PNPA to PNP.
A comparison model is the thermostable esterase from the moderate thermophile Bacillus circulans. Esterase activity was associated with a protein of molecular mass 95 kDa, composed of three identical subunits of 30 kDa. The esterase activity was thermostable with a maximum activity at 55 °C using PNPA assay. Literature reported units of enzyme activity in umol/minute at rate 790% greater than 4q7q. Taken as a comparison model, 4q7q rate is quite slow.[19]
The role of the chloride cofactor was not investigated thoroughly. Chloride ion was present in all reaction conditions, so it's independence was not tested. A future experiment would be testing the functionality of the enzyme without chloride in solution compared to with chloride ion.
</structure section>
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 4Q7Q. Protein Database, 2014. https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4Q7Q
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Nadzirin, N.; Gardiner, E.; Willett, P.; Artymiuk, P. J.; Firdaus-Raih, M. 2012. SPRITE and ASSAM: web servers for side chain 3D-motif searching in protein structures. Nucleic Acids Res., 40(Web Server Issue), W380-6.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Rio, T. G. D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Chitinophaga pinensis type strain (UQM 2034). Stand. Genomic. Sci., 2010, 2(1), 87-95. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3035255/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 SGNH hydrolase superfamily. InterPro, 2017. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/InterPro/IPR036514/
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Rio, T. G. D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Chitinophaga pinensis type strain (UQM 2034). Stand. Genomic. Sci., 2010, 2(1), 87-95. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3035255/
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Molgaard, A.; Kauppinen, S.; Larsen, S. Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase elucidates the structure and function of a new family of hydrolases. Struct., 2000, 8(4), 373-383. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969212600001180?via%3Dihub
- ↑ UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE. J Comput Chem. 2004 Oct;25(13):1605-12.
- ↑ Akoh, C. C.; Lee, G.; Liaw, Y.; Huang, T.; Shaw, J. GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog. Lipid Res., 2004, 43(6), 534-552. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15522763/
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 Holm L, Laiho A, Toronen P, Salgado M (2023) DALI shines a light on remote homologs: one hundred discoveries. Protein Science 23, e4519
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Bugnon M, Röhrig UF, Goullieux M, Perez MAS, Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V. SwissDock 2024: major enhancements for small-molecule docking with Attracting Cavities and AutoDock Vina. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52 (W1), W324-W332. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae300.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3
Grosdidier A, Zoete V, Michielin O. SwissDock, a protein-small molecule docking web service based on EADock DSS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39 (Web Server issue), W270-W277. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr366
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Eberhardt J, Santos-Martins D, Tillack AF, Forli S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2021, 61 (8), 3891–3898, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00203
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Trott O, Olson AJ. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem., 2010, 31 (2), 455–461, DOI: 10.1002/jcc.21334
- ↑ Miesfeld, R. L.; McEvoy, M. M. Biochemistry, 2nd ed.; W. W. Norton & Company, 2021
- ↑ Xia, L.; Qian, M.; Cheng, F.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Tian, J.; Jin, Y. The effect of lactic acid bacteria on lipid metabolism and flavor of fermented sausages. Food Biosci., 2023, 56, 103172.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Bornscheuer, U. T. Microbial carboxyl esterases: classification, properties and application in biocatalysis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2002, 26(1), 73-81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2002.tb00599.x
- ↑ Schober, I.; Koblitz, J.; Carbasse, J. S.; Ebeling, C.; Schmidt, M. L.; Podstawka, A.; Gupta, R.; Ilangovan, V.; Chamanara, J.; Overmann, J.; Reimer, L. C. BacDive in 2025: the core database for prokaryotic strain data. Nucleic Acids Res., 2024, 53(D1), D748-D756, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae959
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Protein Activity Assays Student Module. BASIL.
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1G-H0tskmSVRhC0qsDau-7-EzUcUYN8kBUHFZyBStYcs/edit?tab=t.0 (accessed 04/28/25).
- ↑ Kademi, A.; Ait-Abdelkader, N.; Fakhreddine, L.; Baratti, J. Purification and characterization of a thermostable esterase from the moderate thermophile Bacillus circulans. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2000, 54(1), 173-179, https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000353