We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Jacob A. Ray/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='4pz4' size='340' side='right' caption='Hyaluronan Binding Domain of Human CD44 (pdb: 4pz4)' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4pz4' size='340' side='right' caption='Hyaluronan Binding Domain of Human CD44 (pdb: 4pz4)' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
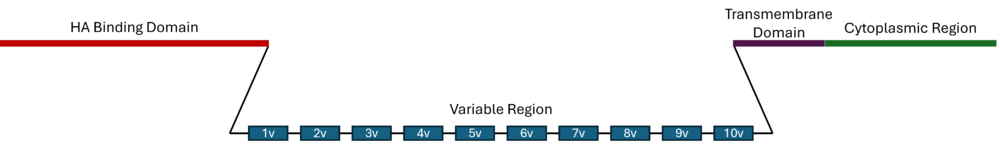
| - | <scene name='10/1079558/Link_domain/2'>CD44</scene> is a highly glycosylated multifunctional cell surface receptor that is involved in cell-cell interaction and maintenance of the extracellular matrix.<ref>DOI 10.3389/fcell.2017.00018</ref> The primary ligand for CD44 is hyaluronan (HA), but it has also been found to interact with other molecules including osteopontin | + | <scene name='10/1079558/Link_domain/2'>CD44</scene> is a highly glycosylated multifunctional cell surface receptor that is involved in cell-cell interaction and maintenance of the extracellular matrix.<ref>DOI 10.3389/fcell.2017.00018</ref> The primary ligand for CD44 is hyaluronan (HA), but it has also been found to interact with other molecules including osteopontin, collagens, and fibronectin. <ref>DOI 10.1136/mp.52.4.189</ref> CD44 is a single chain protein containing four distinct regions: the N-terminal HA binding Link domain<ref>DOI 10.1016/S1097-2765(04)00080-2</ref>, a flexible variable domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular signaling domain.<ref>DOI 10.3389/fcell.2017.00018</ref> The <scene name='10/1079558/Link_Highlight/2'>Link domain</scene> is an approximately 100 amino acid domain consisting of two antiparallel β-sheets, two α-helicies, and two disulfide bonds.<ref>DOI 10.1016/S1097-2765(04)00080-2</ref> This domain is found in most HA binding proteins, including aggrecan, versican, brevican, and tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 6.<ref>DOI 10.1006/prep.1998.0971</ref> |
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
Revision as of 04:26, 30 April 2025
CD44
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Senbanjo LT, Chellaiah MA. CD44: A Multifunctional Cell Surface Adhesion Receptor Is a Regulator of Progression and Metastasis of Cancer Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Mar 7;5:18. PMID:28326306 doi:10.3389/fcell.2017.00018
- ↑ Goodison S, Urquidi V, Tarin D. CD44 cell adhesion molecules. Mol Pathol. 1999 Aug;52(4):189-96. PMID:10694938 doi:10.1136/mp.52.4.189
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(04)00080-2
- ↑ Senbanjo LT, Chellaiah MA. CD44: A Multifunctional Cell Surface Adhesion Receptor Is a Regulator of Progression and Metastasis of Cancer Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Mar 7;5:18. PMID:28326306 doi:10.3389/fcell.2017.00018
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(04)00080-2
- ↑ Banerji S, Day AJ, Kahmann JD, Jackson DG. Characterization of a functional hyaluronan-binding domain from the human CD44 molecule expressed in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 1998 Dec;14(3):371-81. PMID:9882571 doi:10.1006/prep.1998.0971
- ↑ Senbanjo LT, Chellaiah MA. CD44: A Multifunctional Cell Surface Adhesion Receptor Is a Regulator of Progression and Metastasis of Cancer Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Mar 7;5:18. PMID:28326306 doi:10.3389/fcell.2017.00018
- ↑ Mackay CR, Terpe HJ, Stauder R, Marston WL, Stark H, Günthert U. Expression and modulation of CD44 variant isoforms in humans. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):71-82. PMID:7507492 doi:10.1083/jcb.124.1.71
- ↑ Chen C, Zhao S, Karnad A, Freeman JW. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: therapeutic implications. J Hematol Oncol. 2018 May 10;11(1):64. PMID:29747682 doi:10.1186/s13045-018-0605-5
- ↑ Banerji S, Wright AJ, Noble M, Mahoney DJ, Campbell ID, Day AJ, Jackson DG. Structures of the Cd44-hyaluronan complex provide insight into a fundamental carbohydrate-protein interaction. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Mar;14(3):234-9. Epub 2007 Feb 11. PMID:17293874 doi:10.1038/nsmb1201
- ↑ Mackay CR, Terpe HJ, Stauder R, Marston WL, Stark H, Günthert U. Expression and modulation of CD44 variant isoforms in humans. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):71-82. PMID:7507492 doi:10.1083/jcb.124.1.71
- ↑ Senbanjo LT, Chellaiah MA. CD44: A Multifunctional Cell Surface Adhesion Receptor Is a Regulator of Progression and Metastasis of Cancer Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Mar 7;5:18. PMID:28326306 doi:10.3389/fcell.2017.00018