Introduction
Ferritin is a non-enzymatic globular protein complex that primarily functions as the body’s iron storage system. [1]. It’s location is dependent on the organism and form of the ferritin molecule. Opposite to irons relatively poor insolubility, ferritin itself is a soluble protein. It plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular iron homeostasis by safely storing and releasing iron when needed. Its ability to contain up to 4,500 iron atoms within a spherical protein shell protects cell from the toxic effects of free iron and ensures availability for metabolic demands.
Structural highlights
Ferritin is a tetramer composed of 24 (24-mer) forming a hollow spherical shell, with a total molecular weight of approximately 478 kDa and a diameter of 8.66 nm. These subunits exist in two primary forms in humans: heavy (H, 21 kDa) and light (L, 19 kDa) chains. These two chains co-assemble in various proportions (H:L) to form the iron-storage complex. The ratio of H:L is greater in tissues in which the activity of iron oxidation is at a high level and iron needs to be detoxified, for example the heart or brain. The make-up of the subunits in the shell does not affect the iron/oxy mineral composition in the core. What’s interesting is that two identical ferritin proteins, meaning proteins with the same H:L ratio, will likely have different iron cores. Additionally, the H:L ratio will have some effect on the geometry of the crystalline structure as their properties are different.
Each individual subunit of the 24-mer consists of five alpha-helices and no beta-sheets, forming a couple of four-helix bundle (A-B and C-D) connected by loops, with a short C-terminal helix (A) providing protein stabilization. The H-chain posses ferroxidase activity, while the L-chain supports iron nucleation and mineralization. Subunits share about 55% sequence identity. Iron channels on the ferritin surface are lined with polar side chains primarily of glutamate, which makes a hydrophilic channel allowing iron ions into the core. Additionally, the negative charge on glutamate acts as a good binding site for iron ions.
Function
Ferritin stores iron in a safe, bioavailable form. By sequestering Fe³⁺ in a mineralized core, it prevents free iron from catalyzing harmful oxidative reactions. In addition to iron storage, ferritin contributes to intracellular iron delivery, especially during high-demand situations such as rapid growth repair. Its capacity to hold more iron than transferring makes it vital for systemic iron regulation.
Mechanism
Iron Storage
Ferritin acts as an iron delivery vehicle which brings in the Fe²⁺ form of iron to ferritin. Iron then enters ferritin through ion channels. The H-chain’s ferroxidase center oxidizes Fe²⁺ to Fe³⁺. This is then followed by nucleation and mineralization of Fe³⁺ into a ferrihydrite-like core, preventing participation in Fenton reactions that generate damaging hydroxyl radicals. Fenton reactions occur when Fe²⁺ interacts hydrogen peroxide and creates Fe³⁺, OH-, and a hydroxyl radical. This can ultimately lead to “rust”-like substances in cells which can cause DNA damage.
Figure 1. The Fenton reaction. This reaction involves iron(II) reacting with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), making a hydroxyl radical and hydroxide ion.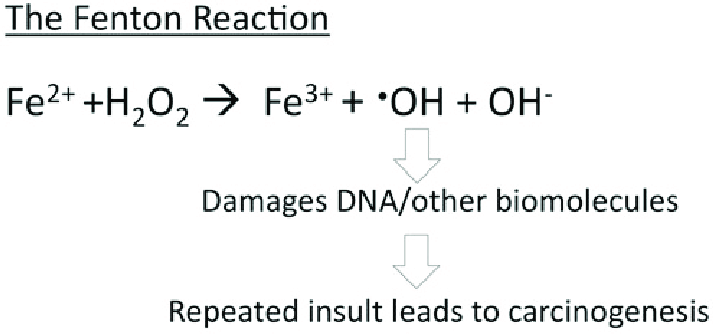
From a hard-soft acid-base (HSAB) perspective, this behavior is chemically intuitive. According to HSAB theory, hard acids prefer to bind with hard bases, and soft acids with soft bases. Fe³⁺ is a hard Lewis acid because it is small, highly charged, and not very polarizable. Ferritin’s iron-binding sites are rich in hard base residues such as glutamate and aspartate, which have oxygen donor atoms (hard bases). This makes the iron-glutamate/aspartate interactions highly favorable, stabilizing Fe³⁺ in the protein’s core. In contrast, Fe²⁺ is a borderline acid and is more reactive, converting it to Fe³⁺ reduces the risk of it catalyzing the harmful Fenton reactions.
Going into further detail, Fe²⁺ ions are brought into the core through the formed by the subunits of ferritin. As stated previously, the 3-fold channels are comprised primarily of aspartate and glutamate residues which makes the pore hydrophilic. This hydrophilicity allows for diffusion of water, metal cations, and hydrophilic molecules into the core. The 3-fold channel is hypothesized to be the main channel for iron entering the core. On the other hand, the are responsible for diffusion of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, not iron. It is lined with non-polar residues such as leucine and ultimately makes the channel hydrophobic. This hydrophobicity allows for diffusion of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide into and out of the ferritin core.
Ferritin has a unique way of stabilizing the iron ions as they are transported through its protein shell. Ferritin has known chelator regions on its shell which are used to support selectivity of iron. The chelate effect occurs when a ligand has multiple donor groups for a motel ion and has an entropic effect. This means that entropy is increased favorably when the chelator is bound because instead of multiple individual ligands interacting, there is one ligand bound to the metal ion through multiple donor groups. In the case of ferritin and the context of chelation, ferritin is considered a single, polydentate ligand. This means it is a molecule with multiple donor atoms that can simultaneously bind to iron, form multiple bonds, and create a ring-like structure around the metal.
Iron Delivery and Release
While the precise mechanism of iron release from ferritin remains unclear, there is an established pathway called ferritinophagy, a form of autophagy that targets ferritin for lysosomal degradation. In this process, the protein NCOA4 (Nuclear Receptor Coactivator 4) functions as a selective cargo receptor. It binds directly to ferritin and brings it to the autophagosome, where it is ultimately degraded in the lysosome. This breakdown releases iron stored in ferritin, making it available again its bioactive form.
NCOA4 plays a dual role as both a cargo receptor and an iron-level sensor. Under iron-rich conditions, NCOA4 is marked for degradation via ubiquitination by the E3 ubiquitin ligase HERC2. This reduction in NCOA4 prevents excessive ferritin degradation, thereby promoting iron sequestration. On the other hand, when iron levels are low, NCOA4 becomes more abundant, facilitating increased ferritinophagy. This releases stored Fe³⁺, which is then reduced to the more bioavailable Fe²⁺ for metabolic use.
Disruption of this pathway can have significant impacts. Experimental models lacking NCOA4 have showed impaired ferritin turnover, resulting in decreased levels of accessible iron. In mice models, NCOA4 deficiency leads to iron overload in organs like the liver and spleen, elevated transferrin saturation, higher serum ferritin levels, reduced expression of duodenal ferroportin, and symptoms consistent with mild microcytic hypochromic anemia.
Ultimately, ferritinophagy, mediated by NCOA4, is a tightly regulated process crucial for balancing iron storage and mobilization in response to the body’s needs.
Diffusion Control
is a ligand in ferratin and plays a role in controlling diffusion of water and influencing protein stability. Specifically, glycerol dictates diffusion rates, which can allow for a stronger understanding of how diffusion affects relaxation rates of protons near ferritin. On top of this, glycerol also has the ability to morph its diffusion pores to prevent water from entering the core and causing oxidation or release water from its core for further space for iron. Additionally, glycerol has the ability to stabilize ferritin and inhibit protein aggregation during refolding. However, glycerol does not have a direct impact of iron diffusion into the core.
Evolution
This structure tells us the conservation patterns on ferritin’s 3D structure. compares the sequence of ferritin proteins from different species. This reveals the location of highly conserved residues, which can indicate the functional importance. This information helps identify specific residues that are essential for iron storage and release, as well as the H-chain’s ferroxidase activity and the L-chain’s structural integrity. Most helices in this structure have a central magenta core, suggesting that the core residues of ferritin’s helices are highly conserved. This makes sense as the central glutamate residues are essential for proper iron diffusion. The ends of the helices and loops are more cyan, indicating greater variability. This would make sense as well since the ends, especially in 4-fold channels, are designed to be hydrophobic with any non-polar amino acid.
Disease Relevance
Ferritin serves as a key biomarker for diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions. Low ferritin levels indicate depleted iron stores, typically seen in iron-deficiency anemia. Conversely, high ferritin levels may reflect iron overload, chronic inflammation, or infection. Inflammatory conditions can cause iron sequestration in macrophages, contributing to anemia of chronic disease. Abnormal ferritin expression and metabolism have also been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, where iron misregulation contributes to neuronal damage.

