We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Jacob A. Ray/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='4pz4' size='340' side='right' caption='Hyaluronan Binding Domain of Human CD44 (pdb: 4pz4)' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4pz4' size='340' side='right' caption='Hyaluronan Binding Domain of Human CD44 (pdb: 4pz4)' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
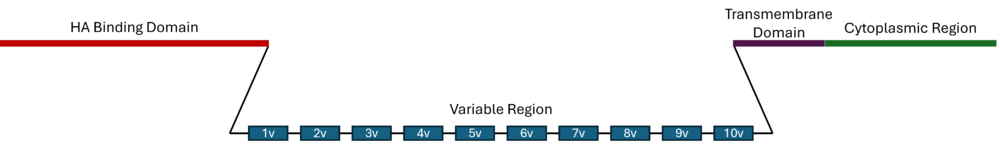
| - | <scene name='10/1079558/Link_domain/2'>CD44</scene> is a highly glycosylated multifunctional cell surface receptor that is involved in cell-cell interaction and maintenance of the extracellular matrix.<ref name="frontier">PMID: 28326306</ref> The primary ligand for CD44 is hyaluronan (HA), but it has also been found to interact with other molecules including osteopontin, collagens, and fibronectin. <ref name="adhesion">PMID: 10694938</ref> CD44 is a single chain protein containing four distinct regions: the N-terminal HA binding Link domain<ref name="struc">PMID: 14992719</ref>, a flexible variable domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular signaling domain.<ref name="frontier" /> The <scene name='10/1079558/Link_Highlight/2'>Link domain</scene> is an approximately 100 amino acid domain consisting of two antiparallel β-sheets, two α-helicies, and two disulfide bonds.<ref name="struc" /> This domain is found in most HA binding proteins, including aggrecan, versican, brevican, and tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 6.<ref> | + | <scene name='10/1079558/Link_domain/2'>CD44</scene> is a highly glycosylated multifunctional cell surface receptor that is involved in cell-cell interaction and maintenance of the extracellular matrix.<ref name="frontier">PMID: 28326306</ref> The primary ligand for CD44 is hyaluronan (HA), but it has also been found to interact with other molecules including osteopontin, collagens, and fibronectin. <ref name="adhesion">PMID: 10694938</ref> CD44 is a single chain protein containing four distinct regions: the N-terminal HA binding Link domain<ref name="struc">PMID: 14992719</ref>, a flexible variable domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular signaling domain.<ref name="frontier" /> The <scene name='10/1079558/Link_Highlight/2'>Link domain</scene> is an approximately 100 amino acid domain consisting of two antiparallel β-sheets, two α-helicies, and two disulfide bonds.<ref name="struc" /> This domain is found in most HA binding proteins, including aggrecan, versican, brevican, and tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 6.<ref>PMID: 9882571</ref> |
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
Revision as of 21:04, 4 May 2025
CD44
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Senbanjo LT, Chellaiah MA. CD44: A Multifunctional Cell Surface Adhesion Receptor Is a Regulator of Progression and Metastasis of Cancer Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Mar 7;5:18. PMID:28326306 doi:10.3389/fcell.2017.00018
- ↑ Goodison S, Urquidi V, Tarin D. CD44 cell adhesion molecules. Mol Pathol. 1999 Aug;52(4):189-96. PMID:10694938 doi:10.1136/mp.52.4.189
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Teriete P, Banerji S, Noble M, Blundell CD, Wright AJ, Pickford AR, Lowe E, Mahoney DJ, Tammi MI, Kahmann JD, Campbell ID, Day AJ, Jackson DG. Structure of the regulatory hyaluronan binding domain in the inflammatory leukocyte homing receptor CD44. Mol Cell. 2004 Feb 27;13(4):483-96. PMID:14992719
- ↑ Banerji S, Day AJ, Kahmann JD, Jackson DG. Characterization of a functional hyaluronan-binding domain from the human CD44 molecule expressed in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 1998 Dec;14(3):371-81. PMID:9882571 doi:10.1006/prep.1998.0971
- ↑ Chen C, Zhao S, Karnad A, Freeman JW. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: therapeutic implications. J Hematol Oncol. 2018 May 10;11(1):64. PMID:29747682 doi:10.1186/s13045-018-0605-5
- ↑ Banerji S, Wright AJ, Noble M, Mahoney DJ, Campbell ID, Day AJ, Jackson DG. Structures of the Cd44-hyaluronan complex provide insight into a fundamental carbohydrate-protein interaction. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Mar;14(3):234-9. Epub 2007 Feb 11. PMID:17293874 doi:10.1038/nsmb1201
- ↑ Mackay CR, Terpe HJ, Stauder R, Marston WL, Stark H, Günthert U. Expression and modulation of CD44 variant isoforms in humans. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):71-82. PMID:7507492 doi:10.1083/jcb.124.1.71