User:Burcu Baykal/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
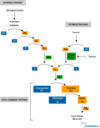
Secondary hemostasis is a complex system resulting fibrin formation as an output of the interaction between coagulation factors. Coagulation factors are serine proteases that forms coagulation cascade. It can be initiated via two different pathways: intrinsic and extrinsic. | Secondary hemostasis is a complex system resulting fibrin formation as an output of the interaction between coagulation factors. Coagulation factors are serine proteases that forms coagulation cascade. It can be initiated via two different pathways: intrinsic and extrinsic. | ||
[[Image:Cascade.jpg.png|left|100px]] | [[Image:Cascade.jpg.png|left|100px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Extrinsic cascade is activated upon a vascular damage by factor VII/VIIa and its membrane bound co-factor tissue factor(TF).The balance between hemostasis and thrombosis is very crucial that excessive cloth formation can be prevented by anticoagulants. Heparin-[[ATII]] is the most known anticoagulant that targets FXa and thrombi in the cascade. since the coagulation process starts with FVIIa-TF complex; it can be a very good therapeutic anticoagulant. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Factor VIIa''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is composed of 254-residue serine protease domain in the heavy chain and two EGF-like domains with a Gla domain in the light chain. Catalytic domain includes two six-stranded antiparallel β-barrels with the active-site cleft between them.N terminal Ile16 stabilizes active site forming salt bridge with Asp194.Catalytic Triad:Gly 193, Ser 195 and His 57.The amide nitrogen atoms of Gly 193 and Ser 195 form oxyanion hole. Oxyanion hole plays key role in stabilizing the negatively charged tetrahedral intermediate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:FVIIa uninhibited.png|left|250px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Revision as of 10:00, 9 December 2008
Hemostasis is a control mechanism in the circulatory system that responsible for the stoppage of bleeding by changing the fluid state of the blood into solid state. Hemostasis as two stages: primary homeostasis includes vascular contraction, platelet adhesion and formation of a soft aggregate plug. Primary Hemostasis starts very quickly after the injury. However it is temporary and local contraction that should be stabilized by the secondary hemostasis.
Secondary hemostasis is a complex system resulting fibrin formation as an output of the interaction between coagulation factors. Coagulation factors are serine proteases that forms coagulation cascade. It can be initiated via two different pathways: intrinsic and extrinsic.
Extrinsic cascade is activated upon a vascular damage by factor VII/VIIa and its membrane bound co-factor tissue factor(TF).The balance between hemostasis and thrombosis is very crucial that excessive cloth formation can be prevented by anticoagulants. Heparin-ATII is the most known anticoagulant that targets FXa and thrombi in the cascade. since the coagulation process starts with FVIIa-TF complex; it can be a very good therapeutic anticoagulant.
Factor VIIa
It is composed of 254-residue serine protease domain in the heavy chain and two EGF-like domains with a Gla domain in the light chain. Catalytic domain includes two six-stranded antiparallel β-barrels with the active-site cleft between them.N terminal Ile16 stabilizes active site forming salt bridge with Asp194.Catalytic Triad:Gly 193, Ser 195 and His 57.The amide nitrogen atoms of Gly 193 and Ser 195 form oxyanion hole. Oxyanion hole plays key role in stabilizing the negatively charged tetrahedral intermediate.
|