User:Grace Natalie
From Proteopedia
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
bacteria to introduce reduced nitrogen into cellular metabolism. GS is a dodecamer formed from | bacteria to introduce reduced nitrogen into cellular metabolism. GS is a dodecamer formed from | ||
two face-to-face hexameric rings of subunits, with 12 active sites formed between monomers. | two face-to-face hexameric rings of subunits, with 12 active sites formed between monomers. | ||
| - | Each active site is described as a bifunnel allowing ATP and glutamate to bind at opposite ends.<ref | + | Each active site is described as a bifunnel allowing ATP and glutamate to bind at opposite ends.<ref name="1"/> |
Divalent metal ions (Mg2+ or Mn2+) bind at the center of the bifunnel and are important for catalysis | Divalent metal ions (Mg2+ or Mn2+) bind at the center of the bifunnel and are important for catalysis | ||
and stutructural stability.</font> | and stutructural stability.</font> | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
<font size=4 face ="Arial">References</font> | <font size=4 face ="Arial">References</font> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <font size=2>1) Eisenberg, D., et.al., Structure-function relationships of glutamine synthetases, | + | <font size=2> .<ref name="1">1) Eisenberg, D., et.al., Structure-function relationships of glutamine synthetases, Biochim Biophys Acta 2000: 1477, 122-145.</ref><br> |
| - | Biochim Biophys Acta 2000: 1477, 122-145.< | + | 2) Gill, H & Eisenberg, D., Biochemistry 2001 40: 1903-1912<br> |
| - | + | 3) Liaw, S-H, et.al.,Discovery of the ammonium substrate site on glutamine synthetase, a third cation | |
| - | + | ||
binding site Protein Sci. 1995 4: 2358-2365 | binding site Protein Sci. 1995 4: 2358-2365 | ||
Revision as of 17:07, 18 December 2008
Background
Glutamine synthetase (GS) catalyzes the ATP-dependent condensation of ammonia and
glutamate to yield glutamine, ADP, and inorganic phosphate in the presence of divalent cations.
The reaction occurs in two steps with γ-glutamyl phosphate as an intermediate and is used by
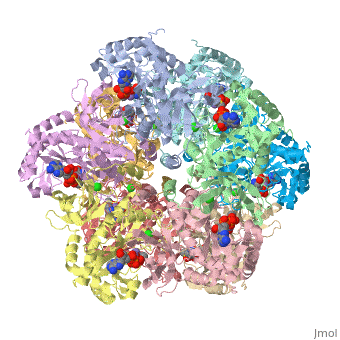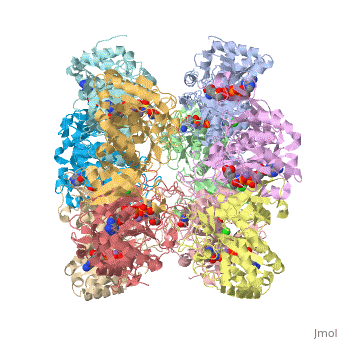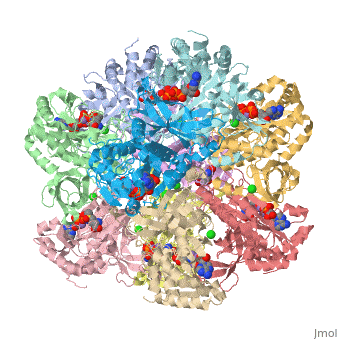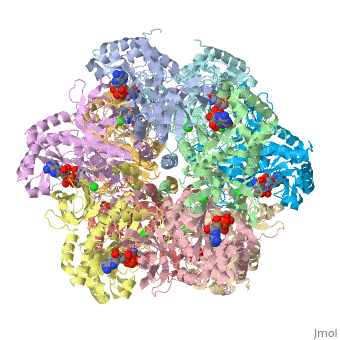
bacteria to introduce reduced nitrogen into cellular metabolism. GS is a dodecamer formed from
two face-to-face hexameric rings of subunits, with 12 active sites formed between monomers.
Each active site is described as a bifunnel allowing ATP and glutamate to bind at opposite ends.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag;
name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Divalent metal ions (Mg2+ or Mn2+) bind at the center of the bifunnel and are important for catalysis
and stutructural stability.
Overall Mechanism
The first step is the formation of the activated intermediate γ-glutamyl phosphate.
The n2 ion coordinates the phosphate oxygens of ATP to allow phosphoryl transfer to the
γ-carboxylate group of glutatmate, yeilding the intermediate. The second step is the attack on the
intermediate by ammonia therefore releasing free phosphate to yield glutamine.
ATP binding site
ATP binds at the top of the active site cavity and the glutamate binds at the bottom,
adjacent to the n1 ion (Liaw 1994). The movement of Arg 359 toward the
glutamate site, induced by ATP binding, increases the binding affinity of glutamate. The active site
of GS is located at the subunit interface (which contains n1 & n2) and is constituted mainly by the C domain
of one subunit (Liaw 1995).
(insert wiki below that maps the ATP binding)
Involving Residues
Most residues involved in enzymatic catalysis are located at the C domain but Asp50 is
contributed from the N domain of the other subunit. The binding of ADP induces Asp50 in order to
enhance the ammonium binding, and then to deprotonate the ammonium ion to form the active ammonia
to attack the gamma-glutamyl phosphate.
| Residue | Role in enzymatic mechanism |
| Arg-321 | Coordinates the carboxylate of glutamate |
| Glu-327 | Closes active site and shields intermediate from hydrolysis |
| His-269 | Coordinates the n2 ion |
| Glu-220 | Coordinates the n1 ion |
| Asp-50 | Increases the affinity for ammonium binding |
References
.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag;
name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
2) Gill, H & Eisenberg, D., Biochemistry 2001 40: 1903-1912
3) Liaw, S-H, et.al.,Discovery of the ammonium substrate site on glutamine synthetase, a third cation
binding site Protein Sci. 1995 4: 2358-2365
|