User:Tilman Schirmer/Sandbox 201
From Proteopedia
(→Intro) |
(→Intro) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Substrate binding=== | ||
<applet load='2v0n' scene='User:Tilman_Schirmer/Sandbox_201/Substrate_binding_site/4' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Diguanylate cyclase PleD (2v0n)' /> | <applet load='2v0n' scene='User:Tilman_Schirmer/Sandbox_201/Substrate_binding_site/4' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Diguanylate cyclase PleD (2v0n)' /> | ||
Revision as of 21:02, 20 June 2009
PleD
Contents |
Intro
|
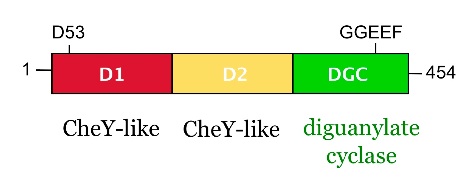
from Caulobacter crescentus is a response regulator with an unorthodox catalytic, diguanylate cyclase, output domain. It is composed of a canonical CheY-like response regulator receiver () domain,
a Rec-like () adaptor domain,
and a C-terminal domain that confers the catalytic acitvity.
The GGDEF domain is named after the highly conserved (in PleD it is GGEEF) that locates to a β-hairpin.
Substrate binding
|
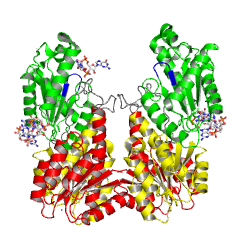
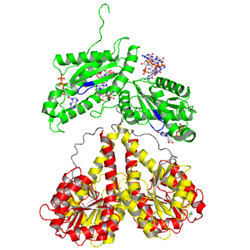
The motif is part of the as identified in the structure of PleD in complex with . The GGDEFY domain binds only one GTP subsrate molecule. For the reaction to proceed, two GTP loaded GGDEF domains have to align antiparallely. MODEL.
Allosteric product binding site
|
C-di-GMP
Primary inhibition site (Ip)
Secondary inhibition site (Is)
Primary and secondary inhibition sites
Two conformations
|
|