Phosphoglucoisomerase
From Proteopedia
|
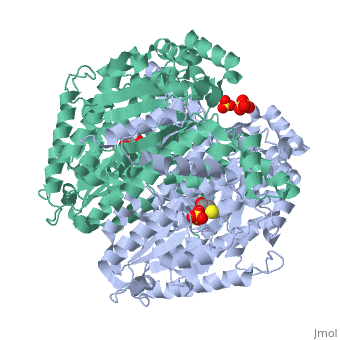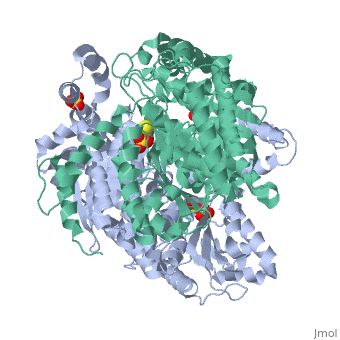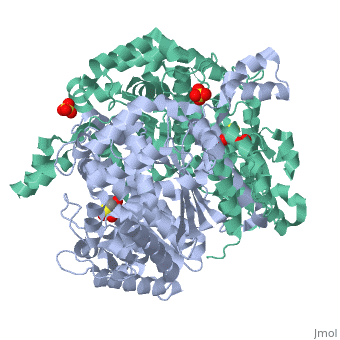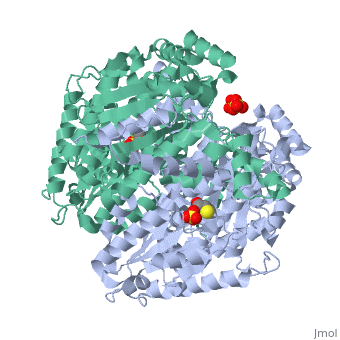
Phosphoglucoisomerase (alternatively known as phosphoglucose isomerase or Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase) are a group of enzymes of the isomerase family (EC 5.3.1.9), so named for their main function in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. In both these pathways phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI) is used to inter-convert glucose-6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate, reaction driven by the relative concentrations of these sugars in the cytoplasmic matrix of the cell.
Phosphoglucoisomerase is also know for a list of activities outside the cells:
- Neuroleukin (NLK)- nerve growth factor secreted by T cells, also used to stimulate the production of immunoglobulin.
- Autocrine motility factor (AMF)- product of tumor cells, it promotes cell migration and viewed as a possible cause in cancer metastasis.
- Maturation factor(MF)
- Myofibril-bound serine protese inhibitor (MBSPI)
Contents |
Structure
Mechanism
Links
References
- ↑ Read J, Pearce J, Li X, Muirhead H, Chirgwin J, Davies C. The crystal structure of human phosphoglucose isomerase at 1.6 A resolution: implications for catalytic mechanism, cytokine activity and haemolytic anaemia. J Mol Biol. 2001 Jun 1;309(2):447-63. PMID:11371164 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4680
- ↑ Lee JH, Chang KZ, Patel V, Jeffery CJ. Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with its substrate D-fructose 6-phosphate. Biochemistry. 2001 Jul 3;40(26):7799-805. PMID:11425306
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Bogdan Stancu, Michal Harel, Andrew Gilman, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner