This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
1vz4
From Proteopedia
|
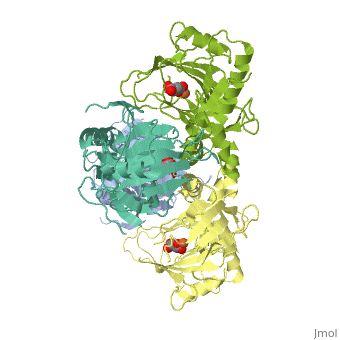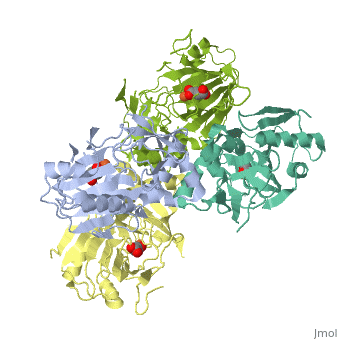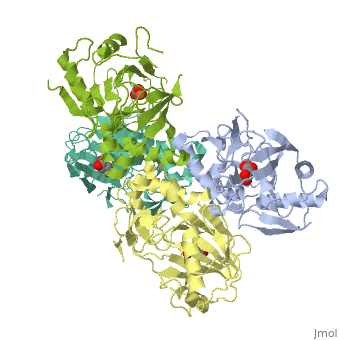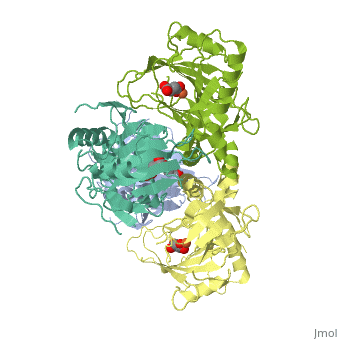
FE-SUCCINATE COMPLEX OF ATSK
Overview
The alkylsulfatase AtsK from Pseudomonas putida S-313 is a member of the, non-heme iron(II)-alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase superfamily., In the initial step of their catalytic cycle, enzymes belonging to this, widespread and versatile family coordinate molecular oxygen to the iron, center in the active site. The subsequent decarboxylation of the, cosubstrate alpha-ketoglutarate yields carbon dioxide, succinate, and a, highly reactive ferryl (IV) species, which is required for substrate, oxidation via a complex mechanism involving the transfer of radical, species. Non-productive activation of oxygen may lead to harmful side, reactions; therefore, such enzymes need an effective built-in protection, mechanism. One of the ways of controlling undesired side reactions is the, ... [(full description)]
About this Structure
1VZ4 is a [Single protein] structure of sequence from [Pseudomonas putida] with FE2 and SIN as [ligands]. Structure known Active Site: AC1. Full crystallographic information is available from [OCA].
Reference
Succinate complex crystal structures of the alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase AtsK: steric aspects of enzyme self-hydroxylation., Muller I, Stuckl C, Wakeley J, Kertesz M, Uson I, J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 18;280(7):5716-23. Epub 2004 Nov 12. PMID:15542595
Page seeded by OCA on Tue Oct 30 16:19:58 2007