This is a default text for your page Kelly Degnon/Sandbox 1. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Structure
Location
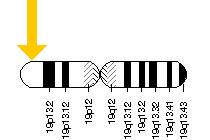
The STK11 gene is located on chromosome 19 on the p arm of the chromosome, also known as the short arm. The exact location is between base pair 1,205,799 and 1,228,435. Location is found in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. In humans, when STK11 is over express it is mostly located in the nucleus, having limited portions in the cytoplasm. When a cell is undergoing apoptosis, STK11 is found to translocate to the mitochondria. STK11 is mostly expressed in the seminiferous tubules of the testes, showing higher expression in the fetal tissues than in adult tissues.
Function
Disease
The function of the STK11 is to suppress tumors. A mutation in this protein increases the risk of cancer and carcinomas, cancer arising from the epithelial tissue of internal organs primarily in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The risk of cancer and carcinomas not only increases with mutation, but is influenced by old age as well. In addition to cancer, a germline mutation of STK11 also increases the chances of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, an autosomal genetic dominant mutation characterized by the growth of hamartomatous polyps in the GI tract, neoplasm, and discoloration of the skin and mouth. Polyps are masses of tissues that arise in the bowl and penetrates the lumen, which can be removed though endoscopic technology. Neoplasm is abnormal growth of tissues that can be categorized into four categories- benign, institu, malignant, and unknown.
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.