Function
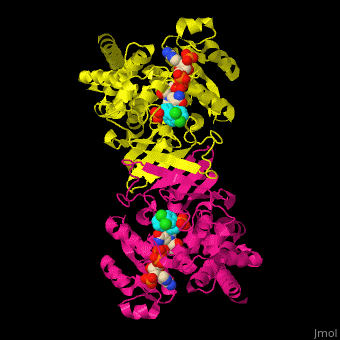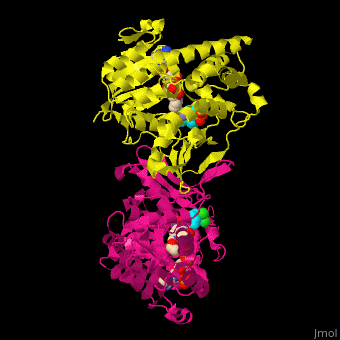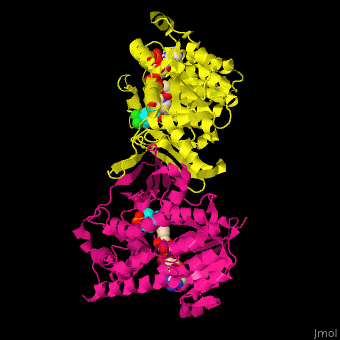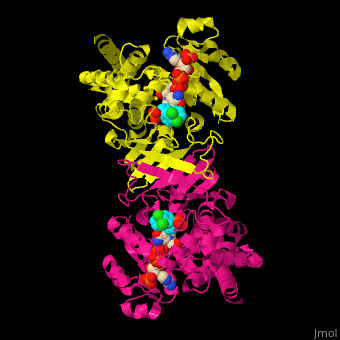
DXP reductoisomerase (DXR) or 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase or IspC catalyzes the conversion of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) to 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate. DXR is part of the nonmevalonate pathway which synthesizes isoprenoids which are essential components of bacterial cell wall. NADPH is a cofactor of the reaction. Divalent metal cations (Mg+2, Mn+2) are involved in binding of the DXP substrate to DXR.[1]
Disease
The antibiotic fosmidomycin is a structural analog of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate is a powerful inhibitor of DXR and is used as an anti-malaria drug.
Structural highlights
DXR contains Mn+2 cation and the product analog fosmidomycin. (water molecules shown as red spheres).[2]