This is a default text for your page '. Click above on edit this page' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Function(s) and Biological Relevance
Lignostilbene-α,ß-dioxygenase A (LsdA) from the bacterium Sphingomonas paucimobilis TMY1009 is a nonheme iron oxygenase that catalyzes the cleavage via oxygenolytic fission of lignostilbene, a compound arising in lignin transformation, to two vanillin molecules (see images below). Lignin is a common component of biomass from industry that scientists are interested in finding ways to break down to simpler and useful materials such as biofuels and commodity chemicals. Though natural occurring lignostilbenoids are rare, they are a very comm on byproduct of industry due to condensation reactions. Other lignin-based stilbenes are thought to be produces from bacterial catabolic processing of diaryl propane and phenylcoumarane [3]
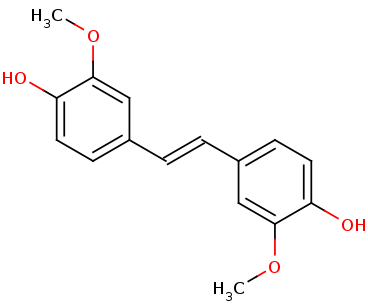 Vanillin
Vanillin