| 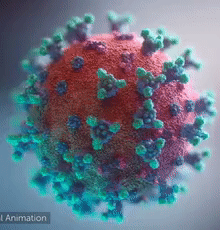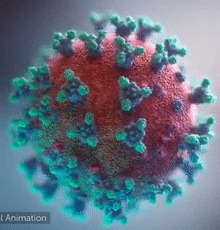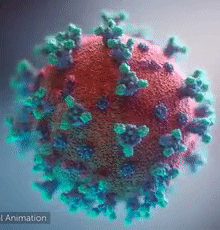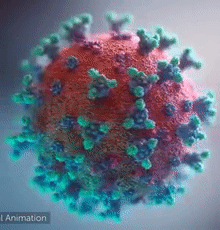 Overall view of the COVID-19 virus. Note the spikes, aqua, that adorn the outer surface, red, which imparts a corona like appearance (Fusion Animation).
LEFT: Overall view of the virus, showing the spikes in aqua.
RIGHT: Close up view of the spikes, from the McLellan Lab[1].
An animation shows how the virus interacts with its host, via these spikes, thus permitting its genome to enter the human (host) cell and begin infection (by Elara Systems).
Potential treatments and ways to minimize exposure to COVID-19
- A USA, French UK study identified 69 drugs to test against the coronavirus[2]. As reported in the New York Times (23-Mar-2020) "The researchers sought drugs that also latch onto the human proteins that the coronavirus seems to need to enter and replicate in human cells."
- A French study[3] showed, despite its small sample size (20 patients treated), that hydroxychloroquine treatment is significantly associated with viral load reduction/disappearance in COVID-19 patients and its effect is reinforced by azithromycin.
Movies helping to explain COVID-19
How COVID-19 Impacts your Body (Mar 20 2020)
by High Impact
Fighting Coronavirus with Soap
by PDB-101.
COVID-19 details of its 3D structure
by biolution GmBH.
Outbreak of COVID-19 (Feb 11, 2020)
by Sci Animations.
Bill Gates Ted Talk (Apr 3, 2015) We're not ready for the next epidemic.
by Ted Talks.
Useful sites on COVID-19
- A summary of key findings about COVID-19 can be found at CDC.
- A computer game, developed at the Inst for Protein Design (U Washington), uses crowdsourcing to try to find new lead compound that might become drugs to treat COVID-19.
- Crowdfight COVID-19 - A scientific crowdsourcing initiative to put all available resources at the service of the fight against COVID-19
Recent published papers
- Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved α-ketoamide inhibitors, from the Hilgenfeld lab[4], Apo Struture: PDB-ID 6Y2E, and complexes with inhibitors: PDB-ID 6Y2F and 6Y2G.
- 3D Structure of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19, a major antiviral drug target from the Rao lab in Beijing[5].
- Crystal structure of the Mpro from COVID-19 and discovery of inhibitors in a study by scientists from Shanghai & Beijing [6], PDB-ID 2h2z.
- Crystal structure of Nsp15 endoribonuclease NendoU from SARS-CoV-2 in a study by scientists from USA[7], PDB-ID 6w01.
- Coronavirus Evolved Naturally, and ‘Is Not a Laboratory Construct,’ in a study in Nature Med by Anderson and colleagues [8].
- A study by Zhou & colleagues in Science on the structural basis for the recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) by full-length human ACE2 gives insights to the molecular basis for coronavirus recognition and infection[9].
- The CoV spike (S) glycoprotein is a key target for vaccines, therapeutic antibodies, and diagnostics. A study by McLellan and colleagues in "Science" on the Cryo-EM structure of the COVID-19 spike protein. This structure should greatly aid in the rapid development and evaluation of medical countermeasures to address the ongoing public health crisis[1], PDB-ID 6vsb.
- Scientists are endeavoring to find antivirals specific to the virus. Several drugs such as chloroquine, arbidol, remdesivir, and favipiravir are currently undergoing clinical studies to test their efficacy and safety in the treatment of COVID-19 in China, with some promising results summarized.[10].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Wrapp D, Wang N, Corbett KS, Goldsmith JA, Hsieh CL, Abiona O, Graham BS, McLellan JS. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science. 2020 Feb 19. pii: science.abb2507. doi: 10.1126/science.abb2507. PMID:32075877 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abb2507
- ↑ Gordon, et al. A SARS-CoV-2-Human Protein-Protein Interaction Map Reveals Drug Targets and Potential Drug-Repurposing: bioRxiv (online) 2020 http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.22.002386
- ↑ Gautret, et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open- label non-randomized clinical trial: Intl J Antimcrob Agents (in press) 2020 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949
- ↑ Zhang L, Lin D, Sun X, Curth U, Drosten C, Sauerhering L, Becker S, Rox K, Hilgenfeld R. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved alpha-ketoamide inhibitors. Science. 2020 Mar 20. pii: science.abb3405. doi: 10.1126/science.abb3405. PMID:32198291 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abb3405
- ↑ Gao, et al. Structure of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from 2019-nCoV, a major antiviral drug target: bioRxiv (online) 2020 https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.16.993386
- ↑ Jin, et al. Structure of Mpro from COVID-19 virus and discovery of its inhibitors: bioRxiv (online) 2020 http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.26.964882
- ↑ Kim, et al. Crystal structure of Nsp15 endoribonuclease NendoU from SARS-CoV-2: bioRxiv (online) 2020 http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.02.968388
- ↑ Andersen, et al. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2: Nature Med (in press) 2020 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9]
- ↑ Yan R, Zhang Y, Li Y, Xia L, Guo Y, Zhou Q. Structural basis for the recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science. 2020 Mar 4. pii: science.abb2762. doi: 10.1126/science.abb2762. PMID:32132184 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abb2762
- ↑ Dong L, Hu S, Gao J. Discovering drugs to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Drug Discov Ther. 2020;14(1):58-60. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2020.01012. PMID:32147628 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5582/ddt.2020.01012
|

