Introduction
(LPL) is an important enzyme for the breakdown of triglycerides in the body (Figure 1).
[1] 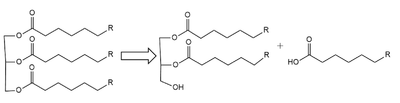
Figure 1: breakdown of a triglyceride into a diglyceride and creation of one free fatty acid by LPL
A
lipase is an enzyme that is capable of catalyzing the
hydrolysis of fats/lipids which are consumed through oils. It is encoded by the
p22 region in chromosome 8. Once synthesized, it is secreted into the interstitial space in several tissues. The main site of action for is in the
capillary lumen within muscle and adipose tissues.
[2] The function of this lipase is to hydrolyze
triglycerides of very-low-density lipoproteins (
VLDL) and to aid in the delivery of lipid nutrients to vital tissues.
[3]
References
- ↑ Arora R, Nimonkar AV, Baird D, Wang C, Chiu CH, Horton PA, Hanrahan S, Cubbon R, Weldon S, Tschantz WR, Mueller S, Brunner R, Lehr P, Meier P, Ottl J, Voznesensky A, Pandey P, Smith TM, Stojanovic A, Flyer A, Benson TE, Romanowski MJ, Trauger JW. Structure of lipoprotein lipase in complex with GPIHBP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 21;116(21):10360-10365. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1820171116. Epub 2019 May 9. PMID:31072929 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820171116
- ↑ Birrane G, Beigneux AP, Dwyer B, Strack-Logue B, Kristensen KK, Francone OL, Fong LG, Mertens HDT, Pan CQ, Ploug M, Young SG, Meiyappan M. Structure of the lipoprotein lipase-GPIHBP1 complex that mediates plasma triglyceride hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 17. pii: 1817984116. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1817984116. PMID:30559189 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1817984116
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref> tag;
no text was provided for refs named Birrane