This is a default text for your page Max Hideki Oliveira Homma/Sandbox 1. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Function
Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) is an enzyme responsible for converting deoxyribonucleotides (dNTPs) from ribonucleotides (NTPs). It catalyzes this chemical reaction by removing the 2'-hydroxyl group of ribose ring of ribonucleotides. Therefore, this enzyme is also known as ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase (rNDP). In this way, this enzyme promotes the synthesis of precursors for regeneration and construction of DNA.
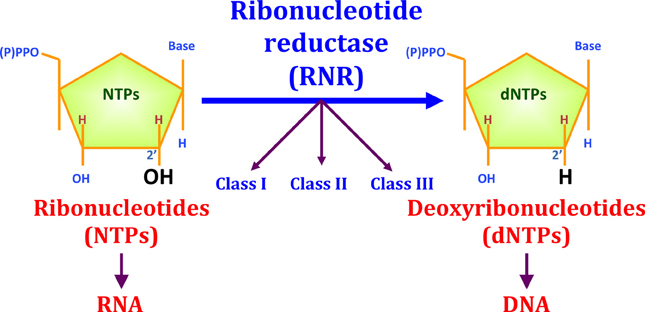
Because of its essential function for the structure of DNA, knowing that all cellular organisms have DNA as a hereditary structure, it is likely that RNR is present in all growing cells of all living beings. In addition, it is also speculated that the RNR played a key role in the transition from the "RNA world" to the "DNA world". In this question, RNR are subdivided into three classes, and the third class can function without oxygen and uses simple structures, thus, it is believed that this class is the oldest.
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.

