Introduction
Impact of Scaffold Rigidity
General Structure
Active Site
Residues are the important residues in the binding site.
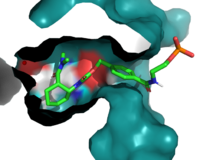
Figure 1. The coolest image of this protein EVAH!!
Helix Cap
Mechanism
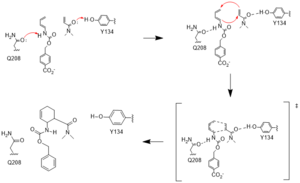
Figure #. Active site mechanism
HUMO and LUMO
Hydrogen Binding
Development and Evolution
DA_20_10
Q162R
Residue 162 resides near the top of the binding entrance to the enzyme, and is within 3A in most models on the enzyme. It can act as a hydrogen bond donor to the terminal phosphate on the ligand when in proximity. To increase this interaction, the group chose a Q to , which decreased the length of the potential hydrogen bond to within 2.5A, increasing the strength of the interaction.
CE20
In this generation, it was found that the most catalytically efficient models had mutated T34, P48, and R56 to . These mutations further tightened the binding pocket and create a more hydrophobic environment.
Application
Relevance
[1]
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.


