STRUCTURE 1BM0
From Proteopedia
Contents |
Abstract
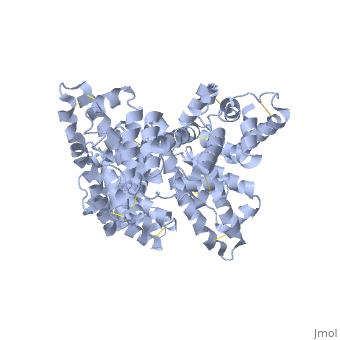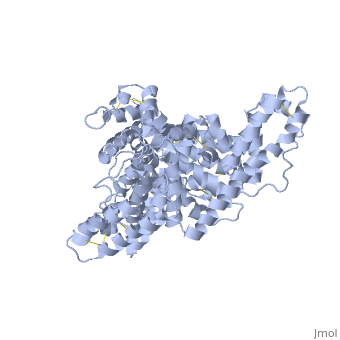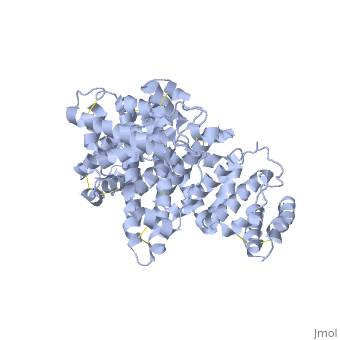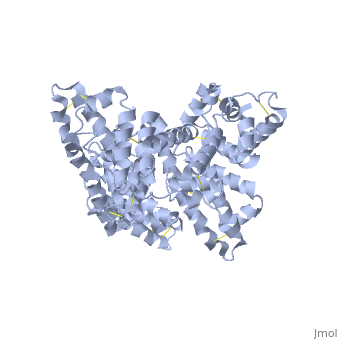
The three dimensional structures of pHSA and rHSA triclinic crystals were determined at 2.5A°resolution through multiple isomorphous replacement with a known tetragonal crystal. The pHSA and rHSA structures are similar with an r.m.s deviation of 0.24 A° for all the cα atoms. Cys 34 does not have a disulfide link with any ligand. A pocket of hydrophobic and positively charged residues is formed at domains 2 and 3 where a wide range of compounds can be accommodated. The surface of the domain has three binding sites for long chain fatty acids.
Introduction
HSA has a blood concentration of 5g/100ml and is the most abundant protein in the blood plasma. HSA has a high affinity for cu+2, zn+2, fatty acids , amino acids , metabolites and many other drug compounds. The protein brings solutes in the blood to the target organs and also maintains the PH and osmotic pressure of the plasma hence it is used as a carrier of drugs to their targets. HSA has 585 residues with 17 disulfide bridges and one free cysteine. Many reports contained crystal forms of HSA but none provided structural information. This article discusses the crystal form of defatted HSA and the molecular aspects of the protein are determined at the highest resolution.
Crystallization of the tetragonal crystal
crystallization of the triclinic crystal
structural determination of the triclinic crystal
Results
Structural determination and quality
Local symmetry in the triclinic lattice
Overall structure
Subdomains
Free sulfhydryl group at cys34
Binding sites for drugs and other compounds
Conclusion
References
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Bhagiradhi Somalanka, Irene Becerra, Neeharika Pothuri, Michal Harel, Valerie Orovwigho