ToxT
From Proteopedia
|
Introduction
ToxT is a molecule at the end of a transcriptional cascade that autoregulates the transcription of the primary virulence factors of Vibrio cholerae[1] and itself. These two factors, cholera toxin (CT)[2] and the toxin co-regulated pilus (TCP), are instrumental in causing the disease cholera[3]. This is an intestinal infection resulting in massive water loss in the affected individual, causing extreme dehydration.[4]
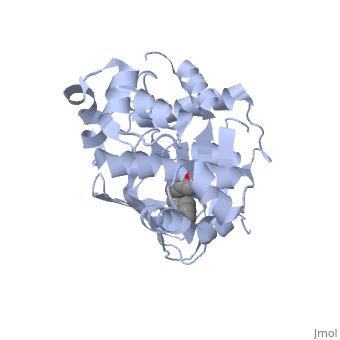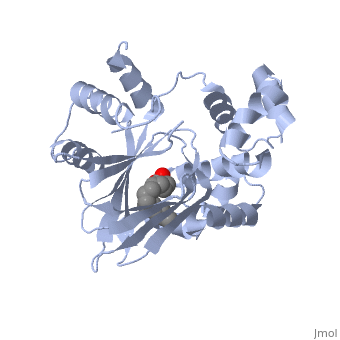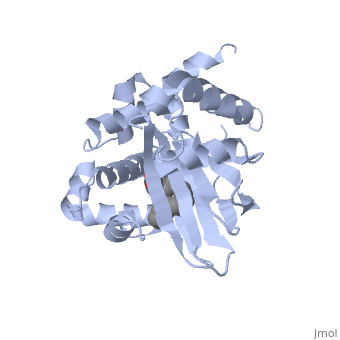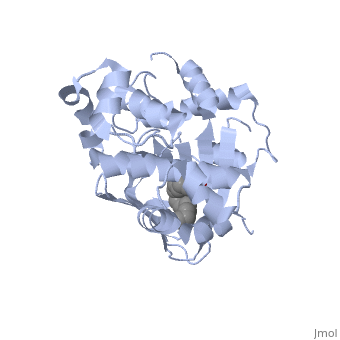
Structural Features
ToxT belongs to a family of transcriptional regulators known as AraC.[1] The AraC family is defined by a 100 amino acid region of sequence similarity that forms a DNA-binding domain with two helix-turn-helix motifs. [2]
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Ingrid Youngworth, Yang Yang, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky