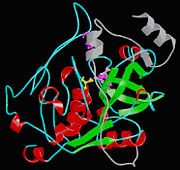
Isolated from human liver, the protein Cathepsin B has a very unique structure. Human Cathepsin B contains 14 cysteine residues, with Cys29 representing the active site cysteine, and 12 other cysteine residues found to be involved in disulfide bridges. Cathepsin B contains six dilsulfide bridges which are enclosed to the amino-terminal half of the molecule. Two of the cysteine residues (Cys 29 and Cys 240) are unpaired. The crystal structure of Cathepsin B consist of a double-chain form, with one light chain and one heavy chain composed of residues Leu1-Asn47 and Val50-Asp254. Some other features of Cathepsin B is that it has a diameter of 50 angstroms and a thickness of 30 angstroms. Also, you can see that there is a marked incision on the structure which represents the active site cleft. The polypeptide chain is described as being folded into two distinct domains which are known to interact with one another through an extended polar interface which opens to the V-shaped active site cleft. The left-hand” L” domain is formed by the amino-terminal half of the polypeptide chain up to about Tyr 148 and by the last carboxy-terminal residues. The right hand “R” domain is composed of the first ten residues and the carboxy-terminal half of the polypeptide chain. The amino and the carboxy-terminal ends act as ‘straps’ which help in clamping both domains together. The occluding loop of the structure has a 20-residue insertion that blocks primed terminus of the active site cleft. A critical feature of the structure is that it contains two histidine residues (His110 and His111) in the occluding loop of the structure and this allows positively charged anchors for the C-terminal carboxylate group of polypeptide substrates. These structural features give reasons for the dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase activity of cathepsin B. The structure of human Cathepsin B proteins have been solved using X-ray crystallography.
Function
The protein Cathepsin B has many molecular functions. Some of these functions include endopeptidase activity, cysteine-type endopeptidase activity, protein binding, peptidase activity, cysteine-type peptidase activity, hydrolase activity, kininogen binding, and peptide binding.
Mechanism of Action
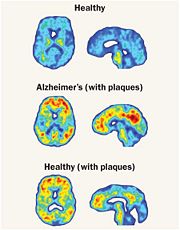
One very crucial function of Cathepsin B that is emphasized on is its ability to break down the proteins that cause amyloid plaque, the root cause of Alzheimer’s disease systems. Cathepsin B has a built in protective mechanism against Alzheimer’s disease. Cathepsin B functions by “snipping” apart proteins which are closely associated with the amyloid protein that forms the amyloid plaques. Once, Cathepsin B breaks down these amyloid plaques, it signals other enzymes to further degrade the protein. An experiment with mice was conducted by Dr. Li Gan's lab at the University of California San Francisco in which Dr. Gan's lab found that cutting out the Cathepsin B gene increased the plaque deposition in mice with Alzheimers disease symptoms. The mice showed the human form of amyloid amyloid precursor protein, APP. These researchers also discovered that Cathepsin B build up within the amyloid plaques and that it acted to decrease levels in neurons. The researchers also found that introducing a pathological form APP called APP1-42 into the neurons drastically increased cathepsin B in young and middle aged mice with human APP, but not old mice. From this observation, the researchers concluded that the upregulation of Cathepsin B could represent a protective mechanism that fails with aging and a failure like this could mean that it plays a role in late-onset sporadic Alzheimer’s disease.
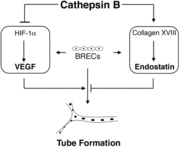
Another mechanism of action that Cathepsin B takes on is its function to regulate angiogenic threshold of endothelial cells. Cathepsin B has the ability to suppress the intrinsic angiogenic switch. When bovine retinal endothelial cells (BREC) are cultured between two layers of collagen, the BRECS can produce both proangiogenic factors (cascular endothelial growth factor) and antioangiogenic factors (endostatin). Cathepsin B can suppress the production of VEGF and increase the levels of endostatin. Under these specific conditions the tube formation is low, but it can be induced by adding VEGF. Blocking Cathepsin B activity allows for the release of endogenous control mechanism and VEGF levels increase and the endostatin levels decrease. A diagram representation of how Cathepsin B allows for this mechanism to occur is shown.
Medical Implications
Cathepsin B is very important in the field of medicine. The regulatory secretory pathway of neurons is the major source of toxic beta-amyloid peptides that accumulate in Alzheimer’s disease. Also, Cathepsin B has been shown to play a role in numerous cardiovascular diseases.
References
1. http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/Genes/CTSBID40202ch8p23.html
2. http://www.genenames.org/data/hgnc_data.php?hgnc_id=2527
3. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/1508
4. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20833970
5. http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?pdbId=1HUC
6. http://www.rxpgnews.com/research/aging/dementia/alzheimers/printer_4986.shtml
7. Im, Eunok, Annapurna Venkatakrishnan, and Andrius Kazlauskas. "Cathepsin B Regulates the Intrinsic Angiogenic Threshold of Endothelial Cells." The American Society for Cell Biology 16.8 (2005): 3488-3500. Web. http://www.molbiolcell.org/content/16/8/3488.full
8. Jia, Zongchao, Sadiq Hasnain, Tomoko Hirama, Xavier Lee, John S. Mort, Rebecca To, and Carol P. Huber. "Crystal Structures of Recombinant Rat Cathepsin B and a Cathepsin B-Inhibitor Complex IMPLICATIONS FOR STRUCTURE-BASED INHIBITOR DESIGN (*)." The Journal of Biological Chemistry (1995): N. pag. Web. <http://www.jbc.org/content/270/10/5527.full#ref-list-1>.
9. Musil D, Zucic D, Turk D, Engh RA, Mayr I, et al. (1991) The refined 2.15 A X-ray crystal structure of human liver cathepsin B: the structural basis for its specificity. Embo J 10: 2321–2330.