The Crystal Structure of the C-terminal region of Death Associated Protein 5 (DAP5-CTD, 3d3m)
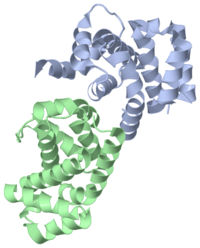
of a C-terminal domain of human DAP5/p97 (DAP5-CTD) between residues L730 and A897. FoldIndex predicted unstructured character of the end of the C-terminus (amino acids 899–907) and it is not seen in the structure. The asymmetric unit of DAP5-CTD (3d3m) consists of two independent monomers. Each monomer comprises a globular α-helical HEAT-Repeat (HR) domain consisting of eight helices (rainbow representation), which folds into four HRs: α1α2, α3α4, α5α6, and α7α8. A pair of interacting antiparallel helices linked by a flexible interunit loop forms an HR unit. This fold is widespread in protein–protein interactions (e.g. eIF4GI; ATR, ATM, and TOR families). The boundary of the segment with missing electron density (residues 789–795), which includes the caspase cleavage site between α3 and α4, is marked.
Aromatic and acidic boxes (AA-boxes) consist of an aromatic/aliphatic motif, divided by a stretch of acidic residues. These acidic residues form an electron-negative patch on DAP5-CTD. The in AA-boxes (E859, E862, E863, E864, E871, D872, and E895) together with exposed residues of α4-α5 interunit loop (D822 and E825), are shown as sticks in orange. (same view) shows the electronegative patch (red) constructed by these residues. AA-boxes mediate specific binding to positively charged motifs of proteins. In the cases of DAP5/p97 and eIF4GI, AA-box is involved in binding with a stretch of 8 basic amino acids (RK box) of Mnk1 protein kinase.
During apoptosis, activation of caspase causes the cleavage of DAP5/p97 at position D792 located at the C-terminus. This cleavage activates DAP5/p97 function in cells. Similar cleavage site was not found in homologous proteins (eIF4GI, eIF2Bε, and eIF5). The structure of DAP5-CTD does not show electron density between residues 789 and 795, which contain this cleavage site. Protease cleavage sites (especially caspase cleavage sites) are frequently situated in flexible, unstructured regions of proteins. In eIF4GI, eIF2Bε, and eIF5, where the caspase cleavage site is absent, is structured and characterized by an α3-α4 interunit loop. The superposition of α3 (orange) and α4 (lime) of DAP5-CTD to those of eIF4GI (1ug3, blue) is shown on the right.
There are only 3 pairs of between α3 and α4 of DAP5-CTD. In contrast, there are more interactions at the stabilizing the interaction between α3 and α4 in eIF4GI.
The DAP5-CTD consists of two : A (residues 730–788, shown in space-filling representation) and B (residues 796–897, shown as green ribbon) that are weakly held together. of segment B from DAP5-CTD exposes a hydrophobic surface, which interacts with helix α4. This hydrophobic surface could participate in forming protein–protein interactions. The loss of its (red) can cause inability of DAP5-CTD to bind positively charged motifs of Mnk1 and eIF2β.