This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
1diz
From Proteopedia
|
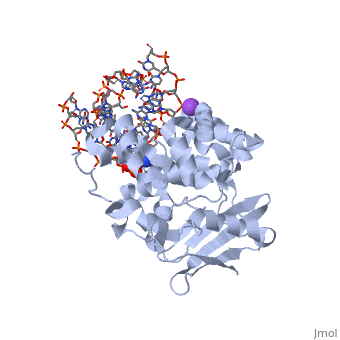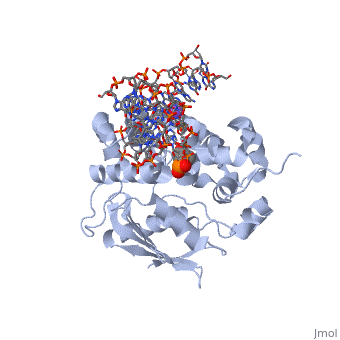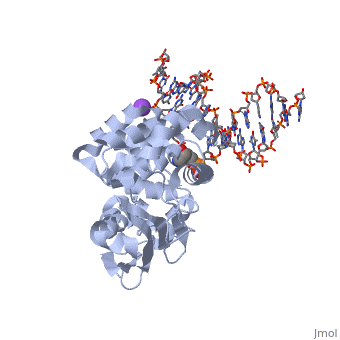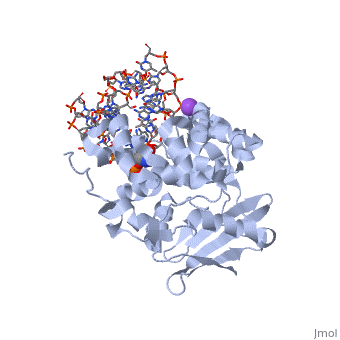
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF E. COLI 3-METHYLADENINE DNA GLYCOSYLASE (ALKA) COMPLEXED WITH DNA
Overview
The Escherichia coli AlkA protein is a base excision repair glycosylase, that removes a variety of alkylated bases from DNA. The 2.5 A crystal, structure of AlkA complexed to DNA shows a large distortion in the bound, DNA. The enzyme flips a 1-azaribose abasic nucleotide out of DNA and, induces a 66 degrees bend in the DNA with a marked widening of the minor, groove. The position of the 1-azaribose in the enzyme active site suggests, an S(N)1-type mechanism for the glycosylase reaction, in which the, essential catalytic Asp238 provides direct assistance for base removal., Catalytic selectivity might result from the enhanced stacking of, positively charged, alkylated bases against the aromatic side chain of, Trp272 in conjunction with the relative ease of cleaving the weakened, glycosylic bond of these modified nucleotides. The structure of the, AlkA-DNA complex offers the first glimpse of a helix-hairpin-helix (HhH), glycosylase complexed to DNA. Modeling studies suggest that other HhH, glycosylases can bind to DNA in a similar manner.
About this Structure
1DIZ is a Single protein structure of sequence from Escherichia coli with NA as ligand. Active as DNA-3-methyladenine glycosylase II, with EC number 3.2.2.21 Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
DNA bending and a flip-out mechanism for base excision by the helix-hairpin-helix DNA glycosylase, Escherichia coli AlkA., Hollis T, Ichikawa Y, Ellenberger T, EMBO J. 2000 Feb 15;19(4):758-66. PMID:10675345
Page seeded by OCA on Tue Nov 20 13:19:01 2007