1dkf
From Proteopedia
|
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A HETERODIMERIC COMPLEX OF RAR AND RXR LIGAND-BINDING DOMAINS
Contents |
Overview
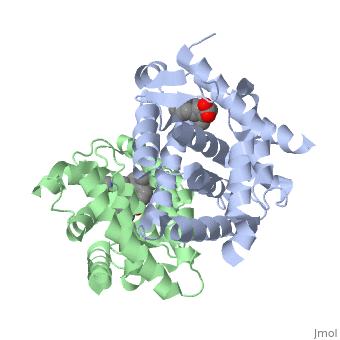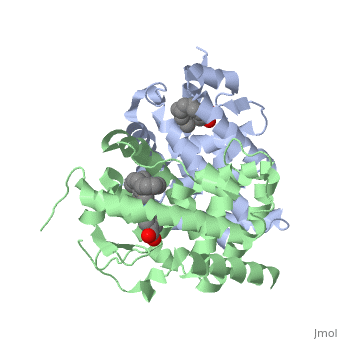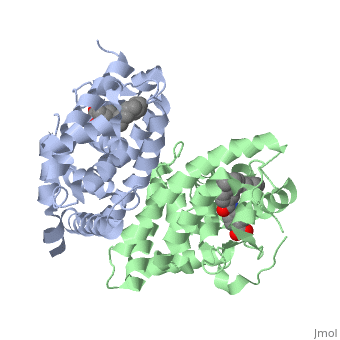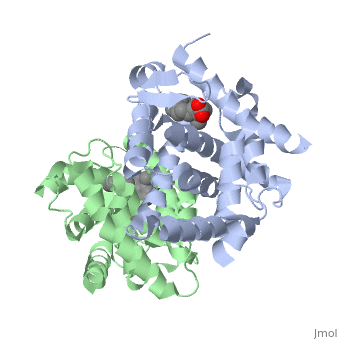
The crystal structure of a heterodimer between the ligand-binding domains, (LBDs) of the human RARalpha bound to a selective antagonist and the, constitutively active mouse RXRalphaF318A mutant shows that, pushed by a, bulky extension of the ligand, RARalpha helix H12 adopts an antagonist, position. The unexpected presence of a fatty acid in the ligand-binding, pocket of RXRalpha(F318A is likely to account for its apparent, "constitutivity." Specific conformational changes suggest the structural, basis of pure and partial antagonism. The RAR-RXR heterodimer interface is, similar to that observed in most nuclear receptor (NR) homodimers. A, correlative analysis of 3D structures and sequences provides a novel view, on dimerization among members of the nuclear receptor superfamily.
Disease
Known disease associated with this structure: Leukemia, acute promyelocytic OMIM:[180240]
About this Structure
1DKF is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Homo sapiens and Mus musculus with BMS and OLA as ligands. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Crystal structure of a heterodimeric complex of RAR and RXR ligand-binding domains., Bourguet W, Vivat V, Wurtz JM, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H, Moras D, Mol Cell. 2000 Feb;5(2):289-98. PMID:10882070
Page seeded by OCA on Mon Nov 12 16:33:23 2007
Categories: Homo sapiens | Mus musculus | Protein complex | Bourguet, W. | Chambon, P. | Gronemeyer, H. | Moras, D. | SPINE, Structural.Proteomics.in.Europe. | Vivat, V. | Wurtz, J.M. | BMS | OLA | Helical sandwich | Heterodimer | Hormone/growth factor receptor | Protein-ligand complex | Spine | Structural genomics | Structural proteomics in europe