2f4m
From Proteopedia
|
The Mouse PNGase-HR23 Complex Reveals a Complete Remodulation of the Protein-Protein Interface Compared to its Yeast Orthologs
Overview
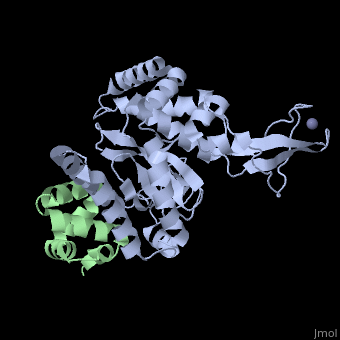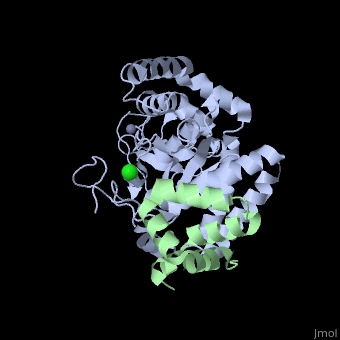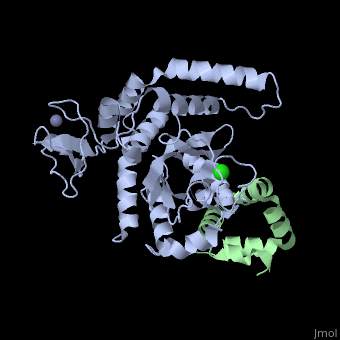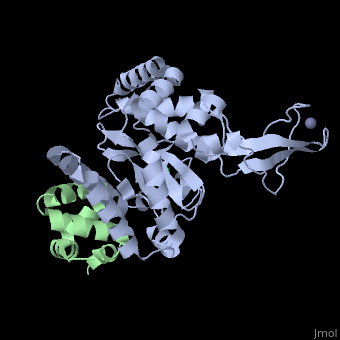
Peptide N-glycanase removes N-linked oligosaccharides from misfolded, glycoproteins as part of the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation, pathway. This process involves the formation of a tight complex of peptide, N-glycanase with Rad23 in yeast and the orthologous HR23 proteins in, mammals. In addition to its function in endoplasmic reticulum-associated, degradation, HR23 is also involved in DNA repair, where it plays an, important role in damage recognition in complex with the xeroderma, pigmentosum group C protein. To characterize the dual role of HR23, we, have determined the high resolution crystal structure of the mouse peptide, N-glycanase catalytic core in complex with the xeroderma pigmentosum group, C binding domain from HR23B. Peptide N-glycanase features a large cleft, between its catalytic cysteine protease core and zinc binding domain., Opposite the zinc binding domain is the HR23B-interacting region, and, surprisingly, the complex interface is fundamentally different from the, orthologous yeast peptide N-glycanase-Rad23 complex. Different regions on, both proteins are involved in complex formation, revealing an amazing, degree of divergence in the interaction between two highly homologous, proteins. Furthermore, the mouse peptide N-glycanase-HR23B complex mimics, the interaction between xeroderma pigmentosum group C and HR23B, thereby, providing a first structural model of how the two proteins interact within, the nucleotide excision repair cascade in higher eukaryotes. The different, interaction interfaces of the xeroderma pigmentosum group C binding, domains in yeast and mammals suggest a co-evolution of the endoplasmic, reticulum-associated degradation and DNA repair pathways.
About this Structure
2F4M is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Mus musculus with ZN and CL as ligands. Active as Peptide-N(4)-(N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminyl)asparagine amidase, with EC number 3.5.1.52 Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Structure of the mouse peptide N-glycanase-HR23 complex suggests co-evolution of the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation and DNA repair pathways., Zhao G, Zhou X, Wang L, Li G, Kisker C, Lennarz WJ, Schindelin H, J Biol Chem. 2006 May 12;281(19):13751-61. Epub 2006 Feb 24. PMID:16500903
Page seeded by OCA on Wed Nov 21 10:21:47 2007
Categories: Mus musculus | Peptide-N(4)-(N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminyl)asparagine amidase | Protein complex | Kisker, C. | Lennarz, W.J. | Schindelin, H. | Wang, L. | Zhao, G. | Zhou, X. | CL | ZN | Glycoproteins | Nucleotide excision repair | Peptide:n-glycanase | Transglutaminase | Ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation