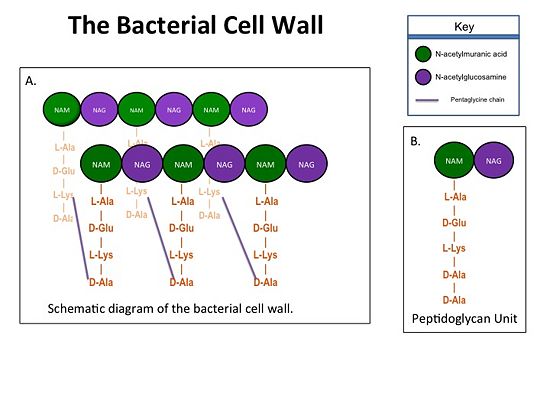
Structure of a Resistant Transpeptidase
Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is resistant to all β-lactams because it acquires an alternative PBP, PBP2a, that is not bound or inhibited by any β-lactams. PBP2a is composed of two domains: a non-penicillin binding domain and a domain . The NBP domain of PBP2a is anchored in the cell membrane, while the TP domain “sits” in the periplasm with its active site facing the inner surface of the cell wall. The active site contains which catalyzes the cross-linking of the peptidoglycan rows with pentaglycine cross-links.
Catalytic Mechanism of PBP2a
(a) The D-Ala-D-Ala side-chain substrate of the peptidoglycan accesses the active site of
the PBP2a.
(b) Ser403 nucleophilically attacks the peptide bond of the terminal D-Ala residues of the
substrate. The terminal D-Ala residue then exits the active site.
(c) The now terminal D-Ala residue forms a covalent bond to Ser403, while a crosslinking
pentaglycine chain enters the active site.
(d) A covalent bond forms between the pentaglycine chain and the terminal D-Ala
residue, regenerating the active site serine residue.
The entire process takes 4 milliseconds.
How do antibiotics work?
The β-lactam antibiotics inhibit bacterial growth by inhibiting PBPs and ultimately cell wall
synthesis. Specifically, β-lactams are molecular mimics of D-Ala-D-Ala, which is the normal
substrate of PBPs. Nucleophillic attack of the β-lactam results in the PBP being irreversibly
inhibited by the β-lactam. As a result, the synthesis of the cell wall is inhibited which leads
to cell lysis.
Figure 2. Mechanism of action of β-lactams. (a) Structure of a β-lactam (penicillin)
showing the amide, carboxyl, and β-lactam ring groups. (b) Structure of the D-Ala-
D-Ala substrate. (c) Overlay of the D-Ala-D-Ala substrate in red with penicillin
demonstrating molecular mimicry.
PBP2a and Ceftobiprole
MRSA becomes resistant to β-lactams by acquiring an alternative PBP, PBP2a, that is
neither bound nor inhibited by β-lactams. Recently, two cephalosporins – and
ceftaroline – that have anti-MRSA activity have been developed. Ceftobiprole is able to
inhibit PBP2a because additional chemical groups at the R2 position of the cephalosporin
backbone are able to interact with additional amino acid residues in PBP2a; specifically
. As a result of its tighter binding to PBP2a, ceftobiprole is able to more
efficiently react with the serine active site residue and therefore inhibit the activity of
PBP2a.
Figure 5. Mechanism of action of ceftobiprole. (a) Structure of ceftobriprole.3
(b) The R2 group of ceftobiprole is bound by PBP2a, Tyr446, and Met641. This
increased binding allows the serine residue active site (Ser403) to hydrolyze the β-
lactam ring and become irreversibly inhibited. (c) Schematic of β-lactam covalently
bonded to active site blocking entrance to the substrate.