Production
Originally, paclitaxel was produced through the extraction of the drug from the bark of Taxus trees. This process was unsustainable because nearly 40,000 mature trees were required to meet the demands for the drug each year. A semi-synthetic route was developed and utilized for paclitaxel production using Taxol precursors, which can be extracted from the needles of Taxus trees. This process is more sustainable because the Taxus needles can be harvested depending on their seasonal availability without the destruction of the tree, but the process uses harsh, expensive solvents and has a low product yield. In 2004, the production of paclitaxel through plant cell culture was approved by the FDA. This was the first plant cell culture production route approved for the production of a pharmaceutical. Currently, Bristol-Myers Squibb is producing paclitaxel for pharmaceutical use solely through the sustainable plant cell culture process.
Plants in their natural environment cannot flee from non-ideal conditions, so they rely on an intricate defense system (i.e., stress response) characterized by the synthesis of secondary products that enhance survivability. During this defense response, energy flux shifts from metabolism conserved across species (i.e., growth) to specialized metabolic pathways that include compounds such as paclitaxel (Taxus spp.) [1] It is produced through an intricate metabolic pathway in response to a 'stress' on the tree. In culture, this stress response can be induced using the compound methyl jasmonate [2]. Methyl jasmonate is a largely conserved activator of specialized metabolic pathways across many plant systems [3] [4] [5]. It has been shown that methyl jasmonate participates in a positive feedback biosynthetic pathway, implying that adding the compound to culture will result in the production of more methyl jasmonate and therefore an increased downstream stress response [6].
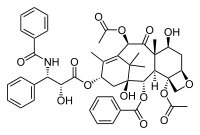
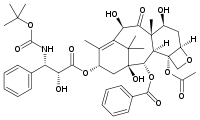
Docetaxel
Docetaxel (Taxotere, sanofi-aventis) is a semi-synthetic analog of Taxol that was discovered during the search for a more easily produced taxane anti-cancer agent. The hydroxyl group modification on docetaxel leads to an increase in the lipid solubility of the drug. It was first approved by the FDA in 1996 and is currently used in the treatment of breast, stomach and prostate cancer. Currently, Taxotere is produced from paclitaxel precursors which are extracted from Taxus brevifolia, the readily available Wester Yew.
Mechanism of action
Both Taxol and Taxotere bind to cell microtubules, promoting their assembly into bundles and preventing cell mitosis. This eventually leads to the death of the cells. Although the mechanism of action for both drugs is the same, Taxotere has been found to be twice as potent as Taxol.
Molecular Playground Banner: "Docetaxel (Taxotere), an analaog of the plant derived anti-cancer agent paclitaxel"
References
- ↑ Wilson SA, Cummings EM, Roberts SC. Multi-scale engineering of plant cell cultures for promotion of specialized metabolism. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2014 Oct;29:163-70. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2014.07.001. Epub, 2014 Jul 24. PMID:25063984 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.07.001
- ↑ Wilson SA, Roberts SC. Recent advances towards development and commercialization of plant cell culture processes for the synthesis of biomolecules. Plant Biotechnol J. 2012 Apr;10(3):249-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00664.x., Epub 2011 Nov 8. PMID:22059985 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00664.x
- ↑ Carvacho HB, Perez C, Zuniga G, Mahn A. Effect of methyl jasmonate, sodium selenate and chitosan as exogenous elicitors on the phenolic compounds profile of broccoli sprouts. J Sci Food Agric. 2014 Sep;94(12):2555-61. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6596. Epub 2014 Mar , 18. PMID:24497113 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6596
- ↑ Gu XC, Chen JF, Xiao Y, Di P, Xuan HJ, Zhou X, Zhang L, Chen WS. Overexpression of allene oxide cyclase promoted tanshinone/phenolic acid production in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Plant Cell Rep. 2012 Dec;31(12):2247-59. doi: 10.1007/s00299-012-1334-9. Epub, 2012 Aug 29. PMID:22926031 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1334-9
- ↑ Sabater-Jara AB, Onrubia M, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Palazon J, Pedreno MA, Cusido RM. Synergistic effect of cyclodextrins and methyl jasmonate on taxane production in Taxus x media cell cultures. Plant Biotechnol J. 2014 Oct;12(8):1075-84. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12214. Epub 2014 Jun, 9. PMID:24909837 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12214
- ↑ Sasaki Y, Asamizu E, Shibata D, Nakamura Y, Kaneko T, Awai K, Amagai M, Kuwata C, Tsugane T, Masuda T, Shimada H, Takamiya K, Ohta H, Tabata S. Monitoring of methyl jasmonate-responsive genes in Arabidopsis by cDNA macroarray: self-activation of jasmonic acid biosynthesis and crosstalk with other phytohormone signaling pathways. DNA Res. 2001 Aug 31;8(4):153-61. PMID:11572481