The human genome has 56 bromodomains across 42 proteins. Bromodomains are found in mammals. Bromodomain testis specific(BRDT) and expressed in testis, spermatocytes, spermatids, and spermatozoa. BRDT is also known as known as CT9 and RING3-like protein and belongs to the bromodomain extra terminal (BET) family. BRDT is expressed in pachytene and diplotene spermatocytes and round spermatids. BRDTis not in testis subjects with sertoli cell only syndrome.
Function
Bromodomain testis specific is a monomer that is only fully functional as a dimer. BRDT is a transcriptional regulator,located in the nucleus, for gene expression during spermatogenesis. BRDT is important to healthy progeny, without it sperm is unable to correctly compact genome. BRDT gives rise to the shape of sperm cells, without it the sperm cells are misshapen.
BRDT and fertility
Loss of one of the bromodomains or even single point mutations leads to decrease spermatogenesis and defective sperm. If both bromodomains are knocked out it leads to loss of fertility.
Relevance
Male contraception has been eluding scientists for years and is a desired area to prevent unplanned pregnancies. In studies of an anti-cancer drug triazolotheinodiaepine known as JQ1 that inhibits BRD4 in cancer pathogenesis. In experiments in mice it is seen, due to structural similarities, JQ1 blocks the production of sperm in testes. The binding of JQ1 in the acetyl-lysine pocket prevents recognition of acetylated histone H4KAC4. JQ1 in studies is not seen to affect hormone levels(leutinizing hormone. follicle stimulating hormone, testosterone), mating behaviors or harmful effects to eventual offspring. Also JQ1 is not seen to cause sterility in mice. The effects of JQ1 on fertility are reversible and dose and time dependent effects on fertility. In mice it reduces size of testis, seminiferous tubes, and number of spermatozoa as well as the mobility of spermatozoa.

Analysis of Structure
The functional unit for BRDT is two bromodomain motifs, each monomer is composed of 4 anti-parallel alpha helixes. The 2 monomers are not unique to one another. At the end of the helix bundles is the acetylated-lysine binding site binding site. BRDT belongs to the histone acetyltransferase superfamily. BRDT is tissue restricted to the testis. BRDT activates the histones by hyper acetylation at the promoter of genes leading to condensed acetylated chromatin of a haploid spermatid. Running an alignment gives 200 sequence similarities which shows that this sequence is highly conserved among organism in the phylogenic tree. This was also seen when running multiple alignments and the sequence was similar among several different organisms.
Analysis of related Sequences
Bromodomain testis specific in humans shares 97% sequence identity with bromodomain testis specific in Sumatran Orangutans. It also shows 99% sequence similarity. These genes are close orthologs with such similar sequence identity and they both serve a function in fertility. The most distant sequence alignment is a black flying fox with and identity of 89% and still is an ortholog to BRDT in humans.
Evolution of BRDT
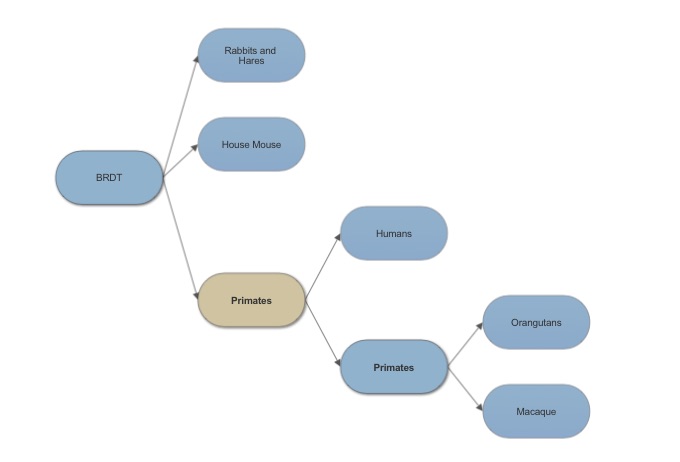 Looking at the evolution of BRDT it is easy to see why mice are a choice of animal model for assessing fertility affects due to BRDT.
Looking at the evolution of BRDT it is easy to see why mice are a choice of animal model for assessing fertility affects due to BRDT.


