Lysophosphatodic Acid
Function
LPA, a signaling phospholipid, can attach to three specific G-protein-coupled receptors. LPA can activate multiple pathways in particular, Ras and Pho which belong to the family of GTPases. Another use of LPA is it can help in stimulation of cell migration [1].
Structure
Comparison of S1P and LPA
Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptors (LPA) are part of a larger family known as lysophospholipid receptor family (EDG family). Within this family there is a structure called S1P1. Since only the structures for LPA1 and S1P1 are known in the EDG family, comparisons are made between the two structures [2].
There is a difference in binding paths between these two receptors. The binding path in the LPA
1 is located in the extracellular milieu. While in the S1P
1 the ligands are able to have access to the membrane so that the binding can occur.
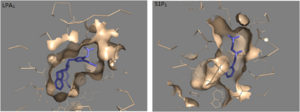
Figure 2: Comparison of the binding pockets of LPA
1 and S1P
1 receptors
There is a difference in the shape of the electron density from the binding pocket. In S1P
1 the binding pocket has more of an oval shape. For the LPA
1 receptor the binding pocket has a spherical shape. Since the binding pocket is more spherical it gives LPA
1 the ability to be able to recognize a larger group of chemical species. In particular the ability to bind with acyl chains of varying lengths
[2].
Function
Relevance
Clinical Testing
LPA is still in the clinical stage of testing. So far the LPA receptors have had physiological effects on every organism that it has been tested with. There have been studies done looking at what happens with infertility, fibrosis, pain, and cancer when they come into contact with LPA receptors. LPA receptors are commonly found in serum and saliva. [1].
Pain
Since LPA receptors are present in the nervous system, they are able to help manage neuropathic pain [3].
Cancer
To look at the effects of LPA on cancer, there was a study done with mice [4]. It was seen that when in the presence of LPA1 receptors the mice would not contract fibrosis. Mice who had fibrosis were given LPA1 regulated LPA-induced fibroblast. Over time the mice who had fibrosis began to have their lungs repaired. The amount of fluid in their lungs decreased.